Dev SWPPP PowerPoint Presentation
advertisement

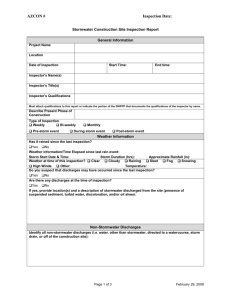
Developing a Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) Introduction Information needed for developing a SWPPP Step-by-step process for ensuring that pollutants are not making their way into the stormwater discharges from your site Stormwater Locator http://www.cicacenter.org/swrlnew.cfm Getting Started Must We Develop a SWPPP? Clean Water Act requires operators of “discharges associated with industrial activity” obtain a NPDES Most industrial stormwater discharges are covered under general permits. In order to submit a SWPPP, the following must occur in this order… Read general permit and determine eligibility for permit coverage Develop a SWPPP Submit Notice of Intent (NOI) What is Stormwater? Water from rain or snowmelt Does not immediately infiltrate into the ground Flows over or through natural or man-made storage or conveyance systems Results in increased surface runoff Picks up industrial pollutants Discharges into nearby waterbodies or stormwater sewer systems Major Sources for Pollutants in Stormwater Loading and Unloading Operations Exposed Storage (outdoors or open to runoff) Exposed Process Activities Dust or Particulate Generating Processes Illicit Connections and Non-Stormwater Discharges Waste Management How to Implement a Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) Elements of a SWPPP A typical SWPPP includes the following elements: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Stormwater Pollution Prevention Team Site Assessment and Planning Selecting Control Measures Procedures for Inspections and Monitoring Completing your SWPPP Keeping Records of Your Implementation Activities Element 1 Your Stormwater Pollution Prevention (P2)Team Your team should… Include those people most familiar with the facility and its operations Define goals for the facility’s stormwater management program Be responsible for implementing general permit requirements and P2 requirements Pollution Prevention Team Element 2 The Site Assessment and Planning Purpose The purpose of the site assessment is to look at your facility and determine what materials and activities are a source of contamination to the stormwater running off the site The Site Assessment Conduct an assessment of activities: Detailed walk through to create a site map Identify locations where industrial materials or material handling activities take place Inventory of materials and pollutants Locate areas with spill or leak potential Identify non-stormwater discharges Evaluation of the sampling data for the site Site evaluation summary The Site Description - Maps Include a general location map and also a site map that indicates the following: Flow directions of runoff Storm drains / inlets and outfalls (i.e., locations where stormwater exits the property, including pipes, ditches, swales and other conveyance structures) Site Map - Locations of Other Features Footprint of significant structures and impervious surfaces Nearby receiving waters (indicate their impairment status) Stormwater conveyances, BMPs & monitoring points Exposed materials, significant spills & other potential pollutant sources Industrial activities (fueling stations, loading and unloading areas, vehicle maintenance areas, waste handling areas, processing & storage areas) Sources of run-on from adjacent properties containing significant quantities of pollutants Pre-BMP Site Map Site Assessment – Material Inventory Identify and inventory industrial materials and activities exposed to stormwater, and their associated potential pollutants: raw materials intermediate products, by-products, final products & waste products material handling equipment or activities industrial machinery industrial production and processes pollutants such as crankcase oil, cleaning solvents, etc. Provide description of materials management practices: treatment practices and structural / nonstructural control measures Material Inventory (cont’d) The Site Assessment – Spills and Leaks Document where potential spills and leaks could occur and the corresponding outfalls Document all leaks/ spills containing a hazardous substance or oil in a reportable quantity for the past 3 years An Reportable Quantity (RQ) for oil is the amount of oil that violates applicable water quality standards or causes a film / sheen / discoloration of the water surface or shoreline, or causes a sludge / emulsion beneath the water surface or on adjoining shorelines For other substances RQ levels are expressed as pounds released over any 24 hour period and are listed at 40 CFR 117.3 and 40 CFR 302.4 Significant Spills and Leaks The Site Assessment Non-Stormwater Discharges Identify all potential sources of non-stormwater discharges Examples of allowable non-stormwater discharges: Discharges from fire-fighting activities Potable water, including water line flushings Routine external building washdown that does not use detergents Examples of unauthorized non-stormwater discharges: Surfactant-laden washwater Sewage cross connection Demonstrate & certify unauthorized discharges have been eliminated Describe the evaluation method used and test results Indicate the location of the evaluation Provide the date of the test or evaluation Non-Stormwater Discharge Assessment Site Assessment - Evaluate Sampling Data Evaluate any stormwater data sampling available from the past 5 years Identify or pinpoint any pollutants of concern, hotspots, or control measures that are not functioning correctly. Useful for selecting BMPs The Site Assessment - Site Evaluation Summary Becomes the foundation for the SWPPP. Identify & locate on-site industrial materials and activities. Determine whether the materials and activities may contaminate stormwater discharges. Use the information to develop a plan to reduce or eliminate discharge impacts to protect receiving water quality. Summary of Pollutant Sources Element 3 Selecting Control Measures aka Best Management Practices (BMPs) BMP Selection & Plan Design Provide a narrative description of the BMPs that you have selected for the site BMP Selection & Plan Design Minimize Exposure Good Housekeeping Maintenance Spill Prevention and Response Procedures Erosion and Sediment Controls Management of Runoff Salt Storage Piles or Piles Containing Salt Sector-Specific Requirements Employee Training Non-Stormwater Discharges Waste, Garbage, and Floatable Debris Dust Generation and Vehicle Tracking of Industrial Materials Numeric Effluent Limitations Based on Effluent Limit Guidelines Additional Controls to Address Impaired Waters BMP #1 – Minimize Exposure Minimize exposure of manufacturing, processing, material storage areas, unloading areas, dumpsters and other disposal areas. Move industrial materials and activities inside or protect them with storm resistant coverings. Try to minimize the creation of new impervious surfaces BMP #2 - Good Housekeeping Involves maintaining a clean and orderly work site so that pollutants don’t have a chance to enter stormwater, such as... Improving operations and maintenance of industrial machinery and processes Implementing careful material storage practices Scheduling routine cleanup operations Maintaining up-to-date inventory control BMP #3 - Preventive Maintenance Develop a program that ensures BMPs and industrial equipment are kept in good condition to prevent /minimize releases of pollutants: Regularly inspect and maintain equipment; include schedules Recommend keeping a maintenance log Make equipment/BMP repairs before next rain event Equipment (tanks, drums, hoses) should be checked for signs of deterioration BMP #4 - Spill Prevention & Response Procedures Minimize the potential for leaks/spills that may be exposed to stormwater Label containers (e.g., “Used Oil”) that could be susceptible to spillage Implement barriers between material storage and traffic areas, secondary containment provisions, and procedures for material storage and handling Have procedures for expeditiously stopping, containing, and cleaning up leaks/spills Train employees BMP #5 - Erosion and Sediment Controls The SWPPP plan should identify activities that present a potential for significant soil erosion Grading Seeding Mulching Sodding Sediment traps Silt fences Sediment ponds Stabilized entrances BMP #6 - Management of Runoff Management of runoff reduces pollutants that are discharged from the site Employ structures, practices intended to divert, infiltrate, reuse, or otherwise reduce stormwater runoff Must be site-specific Vegetative swales Berms Collection and reuse of stormwater Inlet controls Snow management Inflitration devices Wet retention measures BMP #7 - Salt Storage Piles or Piles Containing Salt Cover and isolate to ensure pile does not come into contact with stormwater runoff BMP #8 – Sector-Specific Requirements EPA’s 2008 MSGP regulates discharges from 29 industrial sectors Review your general permit to determine if there are sector specific discharge requirements BMP #9 - Employee Training Training program should include topics such as spill prevention, good housekeeping, recordkeeping, material management practices, etc… BMP #10 – Non-Stormwater Discharges Unauthorized nonstormwater discharges cannot be discharged from your facility Specifically authorized by a separate, individual NPDES permit BMP #11 - Waste, Garbage, and Floatable Debris Stormwater must not carry waste, garbage and debris to receiving waters. Identify and implement control measures to keep exposed areas free of such waste. BMP #12 - Dust Generation and Vehicle Tracking of Industrial Materials Minimize generation of dust and off-site tracking or raw, final or waste materials Sprinklers/irrigation Vegetative cover Mulch, tillage, stone Wind breaks Spray on chemical soil treatments BMP #13 - Numeric Effluent Limitations Based on Effluent Limit Guidelines Federal effluent limits are maximum concentrations of a specific pollutant allowed in a discharge Exceedance is a permit violation BMP #13 (cont’d) Applies to runoff from: Spray down / intentional wetting of logs at wet deck storage areas Phosphate fertilizer manufacturing Asphalt emulsion facilities Cement manufacturing facilities Mine dewatering discharges at crushed stone, construction sand and gravel, or industrial sand mining facilities Hazardous waste and non-hazardous waste landfills Coal storage piles at steam electric generating facilities to runoff from phosphate fertilizer, asphalt emulsion, material storage piles, mine dewatering discharges, waste landfills, and coal storage piles Element 4 Procedures for Inspections and Monitoring Visual Inspections Regular visual inspections are a means to ensure that all elements of the plan are in place and working properly Designate qualified, trained plant personnel to perform inspections Track results, make changes and maintain records of results Records must reflect when, who and what was found Visual Inspections (cont’d) Perform visual inspections (observation and recording of results) quarterly Must have an inspection schedule in SWPPP Annually, must perform visual inspection when a stormwater discharge is occurring Must make necessary changes to facility control measures as a result of inspection Visual Inspections (cont’d) Inspection date/time Names and signatures of facility personnel performing inspection Weather conditions Any previously unidentified discharges Any control measures needing maintenance or replacement Visual Inspections (cont’d) Any incidence of non-compliance observed Any additional control measures needed to comply with permit 1st 30 minutes of a storm event that involves a discharge (or as soon as practicable) visually inspect stormwater sample in clear container at each discharge point and look for: color, odor, clarity, floating solids, settled solids, suspended solids, foam, oil sheen, other obvious pollution Area/Activity Inspected? Controls Adequate (appropria te, effective, and operating) ? Corrective Action Needed and Notes 1 Material loading/unloading and storage areas Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 2 Equipment operations and maintenance areas Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 3 Fueling areas Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 4 Outdoor vehicle and equipment washing areas Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 5 Waste handling and disposal areas Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 6 Erodible areas/construction Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 7 Non-stormwater/ illicit connections Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 8 Salt storage piles or pile containing salt Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 9 Dust generation and vehicle tracking Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 10 (Other) Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 11 (Other) Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions 12 (Other) Yes No N/A Yes No Describe Corrective Actions Monitoring Data Controlled Samples sent to a certified laboratory Monthly Quarterly Annually Submit reporting data to EPA within 30 days of laboratory results Annual report to EPA Reporting Additional reporting to EPA includes: spills, leaks, releases of hazardous substances/oil oral report within 24 hours of noncompliance that endangers health/environment 5 day follow-up report to the 24 hour oral report any planned changes to your facility anticipated non-compliance Transfer of ownership The need to correct information on the Notice of Intent Required Monitoring Quarterly benchmark – parameters depends on SIC code Annual effluent limitations – parameters depends on regulated activity State or Tribal requirements – depends on facility location Annual impaired waterbody – depends on impairment (s) Additional monitoring required by EPA – if notified by EPA Reporting All monitoring date must be submitted to EPA within 30 days of lab results Additional reporting includes: Spills, leaks, releases of hazardous substances Oral report of non-compliance within 24-hours 5-day follow-up written report Annual report on SW must be submitted (standard form may be used) Element 5 Completing your SWPPP Completing your SWPPP Implement the selected BMPs Train all employees to carry out the goals of the plan Plan Evaluation Annual site compliance evaluation must include the following: Inspect stormwater drainage areas Evaluate the effectiveness of BMPs Ensure proper operation of structural measures (traps, ponds, etc.) Revise the plan, if needed, within 2 weeks Prepare a report summarizing inspection results Sign the report and keep it with the plan Plan Evaluation (cont’d) Recordkeeping and internal reporting Must maintain records of spills, leaks, inspections and maintenance activities Plan revisions Major changes in a facility’s design and/or operation will necessitate changes in SWPP plan Endangered Species/Historic Places You must include documentation that supports endangered species and historic place requirements as identified in the MSGP Certification and Submission of SWPPP Date and sign SWPPP Include a copy of the Multi Sector General Permit (MSGP) attached to your SWPPP The confirmation letter you receive from the Notice of Intent (NOI) processing center is not sufficient Modification of SWPPP Modify SWPPP whenever necessary to address any changing or additional conditions SWPPP on the Internet For first time MSGP applications (i.e., new dischargers, new sources, other eligible dischargers), you must post your SWPPP on the internet By posting on internet the discharge authorization date granted from EPA could be 30 days instead of 60 days Element 6 Keeping Records of Your Implementation Activities Keeping Records Document compliance Conduct inspections Within requirements of your permit Keep records of activities Keep records of corrective actions Ensure reliable reports kept on-site with your SWPPP Accessible, complete, up-to-date Additional Documentation Permit records Spill records Employee training records Maintenance records Inspection records Monitoring records Corrective action records Questions?