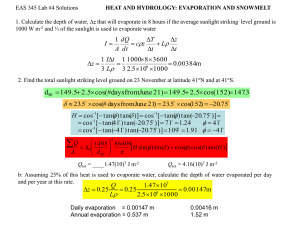
ppt, 6.6mb - Wet Rocks
advertisement

Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Teacher Earth Science Education Programme PARTNERS PRINCIPAL PLATINUM GOLD Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Teacher Earth Science Education Programme PARTNERS SILVER BRONZE • The Australian National University • Department of Primary Industries, Vic • Earth Science Western Australia • Pitney Bowes Business Insight • PowerWorks • Queensland Resources Council • Rob Kirk Consultants • The University of Sydney • The University of Tasmania Anglo Coal Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation CS Energy Department of Sustainability and Environment, Vic Essential Petroleum Flinders University Gordon Wakelin King Great Artesian Basin Coordinating Committee Hot Dry Rocks Macquarie University Sandy Menpes Monash Energy Museum Victoria Our Water Our Future, Vic Petroleum Geo-Services Primary Industries and Resources SA Stanwell Corporation Velseis ZeroGen Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Wet Rocks – Learning about Groundwater The Botany Bay Sands Aquifer Teacher Earth Science Education Programme The Botany Sands Aquifer • This presentation provides: – Information on the Botany Sands aquifer as a source of water for early settlers – The contamination of the aquifer by industry and the subsequent management response – Potential opportunities for use of the aquifer through managed aquifer recharge Teacher Earth Science Education Programme The Botany Sands Aquifer Area Total Water Allocated Total Water Used Average Salinity Sustainable Yield Depth to top of aquifer 141km2 5,859 ML/yr no data 500 mg/L 22,500 ML/yr 3m Source: http://www.centennialparklands.com.au/environment/managing_the_parklands_environment/understanding_the_ botany_aquifer Teacher Earth Science Education Programme The Botany Sands Aquifer and the environment • Ponds that are in part supported by groundwater: Eastlakes, Lachlan, Golf Courses, Race Course, Mill Pond Source: managed-aquifer-recharge-botany-aquifer-Apendix-B-PUB-1006.pdf Teacher Earth Science Education Programme As a water supply …. Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Aquifer contamination What is DNAPL? Dense, non-aqueous phase liquid. That is a liquid that is heavier than water and does not readily dissolve into water Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Aquifer contamination Contaminants in groundwater form “plumes”. Some of the contamination stays in the same form (phase) as when it leaked into the ground. Some of it will dissolve into groundwater, forming a plume of different concentrations outward from the main source. Teacher Earth Science Education Programme The main contaminants What are Chlorinated Hydrocarbons? Chlorinated hydrocarbon (CHC) is a generic term given to chemical compounds containing chlorine, carbon and hydrogen. The term can be used to describe pesticides such as lindane and DDT, industrial chemicals such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB), chlorine waste products such as dioxins and furans, and drycleaning products such as PCE. How did CHCs contaminate the Botany Groundwater? It is suspected that they came from: The former Solvent Plant The former EDC storage tanks The former TCE Plant The former CTC/PCE storage tanks The former Open Heavy Ends Drums Storage Area The former Effluent Treatment Plant Overflow Area The former re-drumming areas adjacent to the Heavy Ends Drums Storage Area. http://www.oricabotanytransformation.com/ Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Aquifer contamination Contaminants impact groundwater well away from the site of the spill. Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Groundwater Embargo Area Approach to Contamination Management Management Zones Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Opportunities for the future – Managed Aquifer Recharge Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Opportunities for the future – Managed Aquifer Recharge Capture stormwater or use treated wastewater, and get it into the aquifer through bores or infiltration basins Pump the water out either at the point of injection or further down the system when needed Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Opportunities for the future – Managed Aquifer Recharge Centennial Lakes – what happens now, and the opportunity for enhancing this system Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Opportunities for the future – Managed Aquifer Recharge Opportunity to increase the amount of water in the storage to increase use, or provide increased security of use in dry periods. Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Summary • The Botany Sands aquifer was a significant source of water for Sydney in the 1800’s • Contamination of the aquifer has had a significant impact on the useability of the aquifer • Management of the contamination recognises that it can’t all be cleaned up, and that restrictions on use into the future are a part of the overall management framework • There is an opportunity, where the aquifer is not affected by contamination, to use Managed Aquifer Recharge to provide additional water storage for use. Teacher Earth Science Education Programme Links to other topics • Permeability and porosity • Recharge • Contamination – contaminant movement and behaviour, remediation