for PHASE II of
advertisement

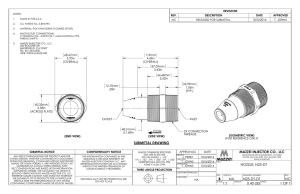
Water Cluster Technology Seminar Intro REUSE WATER CASE HISTORY Larry Burbach Mazzei Injector Company, LLC June 17, 2010 Water Reuse • Water needs Scarcity - out Surface Supplies & Water pacing Aquifer Storage supplies worldwide • Governments – Municipalities – reuse/recycle no longer a choice • New concerns – removal of chemical contaminants, endocrine disrupters (EDC), pesticides, petroleum additives Storm water recovery – high DS1600-LF GDT™ rain seasons, the need was to Degas capture runoffSeparators in the water shed and resupply (restore) for PHASE II of the aquifer City of Wichita’s Aquifer Storage and Recovery Project (ASR-II) June 2010 Potable standards required – Aquifer Storage need to remove all regulated and Recovery organic and inorganic • Removal of atrazine contaminants – farm land • Design & Test Corporate ‘Partners’ runoff tested high in o Mazzei pestesides o Lakos and herbacides o Rain-for-Rent o Fresno State University – WET Lab City of Wichita used MIC for Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) Project ozone injection at the Cheney Facility – injectors, flash reactors and degas equipment with great success $400 million project Ensures stable and reliable water supply through 2050 Takes excess water flow out of Little Arkansas River, treats it to meet water-quality standards, and pumps it underground into the Equus Beds acuifer for later use Phase I was completed in 2006 with the capacity to pump up to 10 million galls of water a day into the aquifer. When Phase II is completed in 2012, that number will jump to 40 million gallons a day. ASR-II AOP selected for the removal PHASE II: During thisof phase, the water treatment plant will use atrazine membranes to treat the water and advanced oxidation to remove the atrazine and provide disinfection so that all of the water recharged meets the safety standards established by the Kansas Department of Health and Environment. Both of these are proven cutting edge technologies – but the success of phase II of this project would only be achieved if a degassing system could be designed to work at system operating parameters. Mazzei was selected for their proven ability to adapt their products to specific operating conditions. Certification Testing Was Performed at the Dublin San Ramon Services District on Micro- and Media Filtered Water Demonstration project completed in CA – toSand validate Filtration A the AOP process with either membrane/micro or sand filtration Microfiltration Program Design • Air Products Halia – AOP SMALL FOOTPRINT – vs o Very effective at organic destruction large storage tank o Large pressure drop across system • Mazzei Degas System o Remove 95% (min) of all undissolved ozone and oxygen gases o Mazzei System must perform at 1.5 psi influent pressure Examples of Full-Scale HiPOx Reactors Hypox reactors require interior static mixing and nozzles causing a significant pressure drop across the system Halia Advanced Oxidation Pilot System Solution – Step 1 • Modify Mazzei standard product (DS1600) – to DS1600LF • Mazzei and Lakos engineers redesigned degas separator for reduced flow at 1.5 psi inlet pressure • Lakos manufacturing division built prototype to be tested Cheney installation required engineering changes to the MIC Mazzei Ozone Injectors & GDT Degas Separators Wichita, degas system toKansas accommodate high supply pressures – 175psi TM The Mazzei GDT™ Degas Separator is designed to remove entrained gas bubbles from pressurized water streams. Mazzei was asked to create a custom degas separator to meet the performance criteria of the ASR-II Advanced Oxidation Process (AOP). The challenge of designing the custom degas separator was removing gases at extremely low operating pressures. Prepared for oxygen service – full penetration welds required Contract Requirements Burns and McDonald, CAS System validationwitness at specifiedof PM• and Wichita parameters by Engineering test validation Company and City prior to contract award • Delivery date NLT September 2010 • Validation must be witnessed at full flow conditions (3472 GPM) Solution – Step 2 • Prototype delivered to WET Lab on time for validation phase • Rain-for-Rent contracted to complete custom installation of the largest system ever tested at WET – pipes cut to fit on site • WET Lab testing began prototype validation – testing design critical at full flow – inlet and discharge head ‘visual’ measurements as well as air flow into the water stream and out of the degas separator vent valve. Figure V. Degas separator process testing set-up The WET Lab’s capabilities were key to our success – precise monitoring of flow and pressures were required by B&C and CAS PM – all controlled by Joe on a PDA – data logged stored through telemetry DS1600LF Arriving at ICWT Gantry allowed for safely offloading and positioning the separator which weighed nearly 6000 lbs. DS1600LF Unloaded Largest system ever tested at the WET Lab – height • Rain-for-Rent restrictions requiredinstallation the use of • WET Facilities the water flume channel to– Joe Oliphant reduce the overall height of • Height restrictions the system insideresolution the test facility Sight glass to set and monitor influent pressure – air supply line located on riser measured and set at .1 : 1 gas to liquid ratio Success!! The initial test run of the degas separator was successful. - The final test run witnessed by Burns and McDonnell verified degas separator performance resulting in final approval of Mazzei’s submittal to supply ASR-II with six custom DS1600-LF GDT™ Degas Separators. DS-1600 LF-A Test Data Separator Water. Flow (GPM) Separator Inlet (PSIG) Gas Removal (%) Target 3,472.0 1.5 97.0% Total Average 3,489.6 1.5 97.4% Acknowledgments The successful development of the custom degas separator was due to the teamwork and the design skills of the engineers at Mazzei and Claude-Laval Corporation, our partner in the development GDT™ Degas Separator Separator performance testing was conducted at the Fresno State University Water & Energy Technology (W.E.T.) Laboratory – custom installation performed by Rain-for-Rent. Thank You