File - KSS Science
advertisement
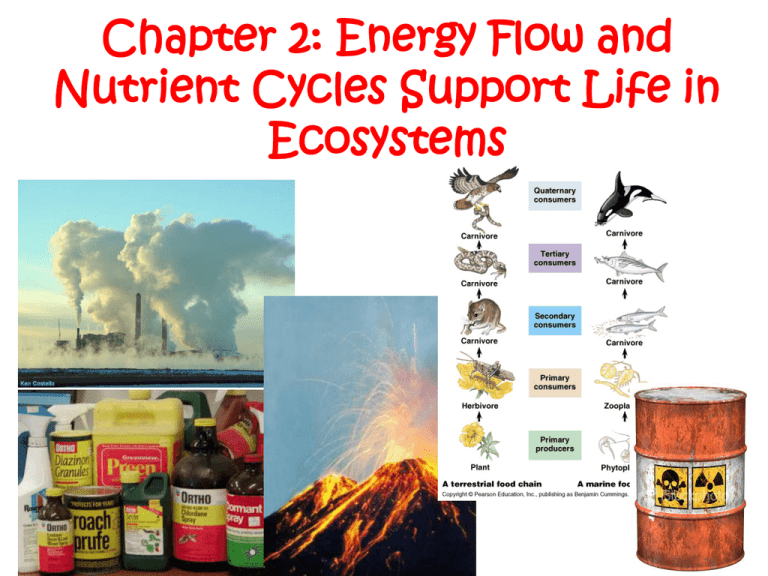
Chapter 2: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles Support Life in Ecosystems Today Virtual lab http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/BL_03 /BL_03.html Diagram page 76 textbook Nutrient cycling (CARBON) Stores 6 main processes C is cycled Anthropogenic effects Workbook pages A 54-year old sealed terrarium (planted in 1960) no fresh air or water 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Human activities can upset the natural balance of nutrient cycles: - land clearing - agriculture - industry - motorized transportation Nutrient Cycling • Nutrients: chemicals that are needed for plant and animal growth and other life processes. • Are accumulated in atmosphere, oceans, and land masses • Stores: location of nutrient accumulation Nutrient Cycling • Nutrient Cycling: movement in and out of stores • Caused by biotic and abiotic processes • Cycles are near balance (input = output) You need to know about C, N, & P cycles But O and H are also needed for life Carbon Cycle Carbon Stores • All living things contain carbon in their cells How carbon is stored: 1. Short term stores - vegetation on land, in oceans - animals and decaying OM in soil - atmosphere as CO2 - top layers of ocean Carbon Stores 2. Long-term stores: - intermediate and deep oceans - coal deposits - marine deposits and sedimentary rock Carbon Stores Store Marine sediments and sedimentary rock Oceans (intermediate/deep) Coal Deposits Soil and organic matter Atmosphere Terrestrial Vegetation Oil and Gas Deposits Amount of C /Gigatonnes 68 000 000 to 100 000 000 Where is most carbon stored? 38 000 to 40 000 3 000 1 500 to 1 600 750 540 to 610 300 Carbon Stores • Sedimentation: – Traps many long-term carbon stores – Layers of soil/decomposing OM get buried – turn into rock/coal/oil/gas by SLOW geological processes Carbon Stores • Limestone (CaCO3 ) forms from shell deposits on ocean floor • Long-term carbon stores are aka carbon sinks Carbon Cycle Carbon is cycled through ecosystems by: 1. Photosynthesis 2. Cellular respiration 3. Decomposition #1) Photosynthesis chemical reaction in plants and cyanobacteria where sunlight (solar energy) is used to make glucose (chemical energy) Sun + 6H20 + 6CO2 → C6H12O6 + 6O2 (sun + water + carbon dioxide → sugar + oxygen) #1) Photosynthesis • recycles carbon and oxygen through ecosystems By eating plants, consumers obtain energy and take carbon into their cells. #2) Cellular Respiration • Opposite of photosynthesis • chemical reaction in mitochondria of cells where oxygen is used to liberate energy from glucose. 6O2 + C6H12O6 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy #3) Decomposition • the breaking down of dead organic matter • Decomposers (bacteria + fungi) convert organic molecules (carbohydrates) back into carbon dioxide. Today Nutrient cycling (CARBON) Review 6 main processes C is cycled What are YOU doing? PHosphorUs and Nitrogen (Phun with a P-H!) You’re the next contestant! • http://www.bcscience10.com/docs/puzzles/section02_1_puzzle/index.html • One lucky volunteer gets to click the link and be the host while I check WB 24-26 • You have 10 minutes… Other ways carbon is cycled #4) Ocean processes (CO32-) sediments, marine organisms remember CaCO3! We made some in a lab. #5) Volcanic eruptions release CO2 #6) CO2 is rapidly released during forest fires (slowly for decomposing trees) Human activities and the carbon cycle • Industry, motorized transportation, land clearing • Industrial revolution (160 yrs ago) CO2 levels increased by 30% from increase of fossil fuel burning • Increase in CO2 in the previous 160 000 ya was 1-3% • We release C from long-term stores FAST (coal, oil, gas) Anthropogenic effects • Burning fossil fuel reintroduces C to the cycle that was removed in a long term store • CO2, a greenhouse gas, is the most common form of carbon absorbs heat in atm. • Contributes to global climate change Anthropogenic effects? • Clearing land reduces amount of carbon taken from atmosphere by plants during photosynthesis • Farm plants remove CO2, but less than natural vegetation Agriculture: cows are carbon culprits • Our obsession with cows is causing almost 10% of global warming emissions http://qz.com/128662/ourobsession-with-cows-is-causing-almost-10-of-globalwarming-emissions/#/h/15425,1/ • Cows release methane from digestion (23x stronger than CO2) • Feed is not environmentally friendly • Breaking down the carbon cycle http://www.bcscience10.com/media/EP_carbon_cycle.swf Carbon cycle • http://www.bcscience10.com/protect/flash_u1_carbon_cycle.html Today Nutrient cycling (CARBON) Review 6 main processes C is cycled What are YOU doing? PHosphorUs and Nitrogen (Phun with a P-H!) BONUS CHALLENGE… tell me what you learned about nutrient cycling from THE link that was NOT covered in class (5 marks maximum, handed in at beginning of next class) www.kssscience.weebly.com