Chapter 11
Managing Change and Innovation
Why Change?
• IBM
– (1960 – 2000) From hardware, software company
– (2000 – present) To a service company (mainly,
consulting)
• If organizations don’t successfully change and
innovate, they die
Copyright ©2012 by South-Western, a division of Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
2
Innovation & Changing Workplace
• The adoption of a new idea or behavior by an
organization
• Change and innovation can come from outside
forces
• Managers want to initiate change from the inside
• Disruptive innovation is a goal for global
competition
• Trickle-up / reverse innovation: Jeep at China
3
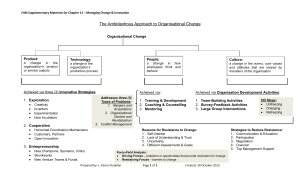
Organizational Change
• Change is not easy;
• organizations must take an ambidextrous approach
– Incorporating structures and processes that are
appropriate for:
– Creative impulse and for the systematic implementation
• Managers encourage flexibility and freedom to
innovate
4
Changing Things: New Products
and Technologies
• Product Change – a change in the
organization’s product or service outputs
• Technology Change – a change in the
organization’s production process
• Three innovation strategies:
1. exploration,
2. cooperation, and
3. entrepreneurship
5
Three Innovation Strategies
Exploration
• Creativity – novel ideas that meet perceived needs
or offer opportunities
• Idea incubator – a safe harbor where employees
can develop ideas and experiment without
interference from company bureaucracy or politics
– Yahoo Brickhouse Top management support
Copyright ©2012 by South-Western, a division of Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
7
Characteristics of Creative People and Organizations
The World’s Most Innovative Companies
9
Cooperation – (1) Internal Coordination
• Horizontal Linkage Model:
– Simultaneously contribute to innovation
– Horizontal coordination mechanisms:
• Marketing = Research = Manufacturing
– Key to Success:
• MANAGEMENT – Planning, organizing, leadership, control
• Team Building
• Project Manager
10
Cooperation – (2) External Coordination
• Includes customers, partners, suppliers
• Open innovation – commercialization of ideas
beyond the organization
– P&G – Patent
– LEGO + Hollywood studios
• Crowdsoucing
– Threadless – web 2.0 (open, share, participate)
11
Coordination Model for Innovation
Innovation Roles
• Managers should support entrepreneurship activities and
foster idea champions
– Energy and effort is required to promote a new idea
• Sponsors approve and protect ideas when critics
challenge the concept
• New-venture teams give free rein to creativity
• Skunkworks are informal, autonomous, secretive groups
that focus on breakthrough ideas
• New-venture funds provide resources for new ideas
13
Four Roles in Organizational Change
Changing People and Culture
• Changes in how employees think; Changes in
mind-set
People change = Training and Development (T&D)
Culture change = Organizational Development (OD)
• Large culture change is not easy
15
Training and Development
• Training – Frequently used approach to
changing people’s mind-sets
• Training and development is emphasized for
managers
– Behavior and attitudes will influence people and
lead to culture change
16
Organizational Development
• Planned, systematic process of change using
behavioral science (psychology)
• Addresses three types of problems:
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A)
Organizational decline and revitalization
Conflict management
17
OD Activities
• Team-building activities: Enhancing cohesiveness and
success of organizational groups and teams
• Survey-feedback activities: an employee questionnaire
asking “values, climate, participation, leadership, and
group cohesion”
• Large-group interventions: participants from all parts
of the organization to discuss problems or opportunities
and plan for change
OD Steps
• Unfreezing:
– Participants must be made aware of problems and be willing to
change; Diagnosis Identifies work-related problems
• Changing:
– when employees learn new skills to be used in the workplace;
Intervention; Implements a plan for training managers and
employees; Include team building, survey feedback, intergroup
coaching, process-consultation, or symbolic leadership.
• Refreezing.
– When individuals acquire new attitudes or values; Rewarded;
Institutionalized in the organizational culture
11.6 OD Approaches to Culture Change
Implementing Change
• Outline the Need for Change
– Show the performance gap (disparity) b/w existing &
desired performance levels
– Get employees involved in the change as early as
possible; in the planning stage; Empower them!
• Understand the Resistance to Change
– Self-Interest
– Lack of Understanding and Trust
– Uncertainty
– Different Assessments and Goals
– Job security
21
11.7 Force-Field Analysis
• Change is a result of the competition
between driving and restraining forces
– Driving forces – problems or opportunities
that provide motivation for change
– Restraining forces – barriers to change
22
Force-Field Analysis: A Case
23
Tactics for Overcoming Resistance to Change
24
Discussion Questions
• Define organizational change and explain the forces driving innovation and
change in today’s organizations.
• Identify the three innovation strategies managers implement for changing
products and technologies.
• Explain the value of creativity, idea incubators, horizontal linkages, open
innovation, idea champions, and new-venture teams for innovation.
• Discuss why changes in people and culture are critical to any change process.
• Define organization development (OD) and large-group interventions.
• Explain the OD stages of unfreezing, changing, and refreezing.
• Identify sources of resistance to change.
• Explain force-field analysis and other implementation tactics that can be used
to overcome resistance.
25
Discussion Questions (continued)
•
•
Describe how IBM has changed during last two decades.
Explain the major motive of Chrysler to produce Jeep at China in early 2000s, in terms of
change management.
•
Explain ambidextrous approach in change management.
•
Describe Yahoo’s Brickhouse, from the innovation strategy perspectives.
•
Explain briefly key to success of horizontal linkage.
•
Describe P&G’s purchase of patents, in terms of innovation strategy.
•
Explain how LEGO survived in early 2000s, by innovation strategy.
•
Explain briefly crowdsourcing.
•
List three features of Web 2.0, in contrast to Web 1.0.
•
Describe innovation strategies of Treadless.
•
Explain briefly a skunkworks.
26