Embedded Systems Framework
advertisement
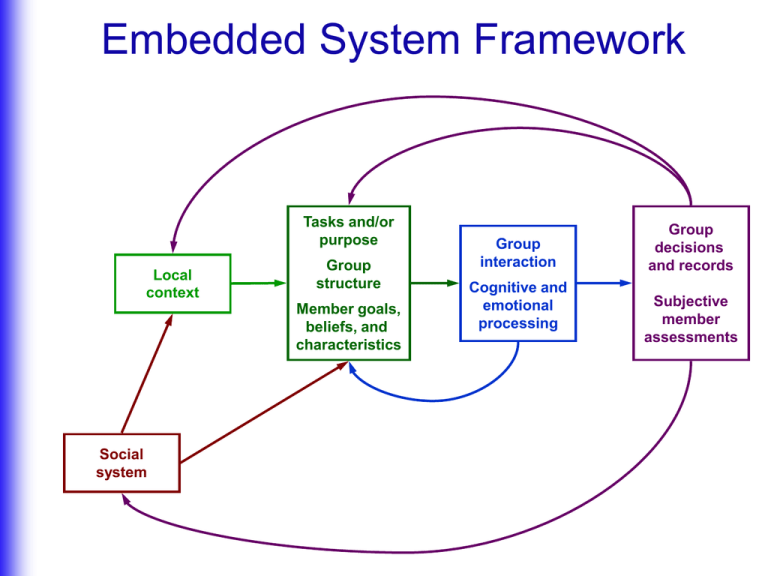
Embedded System Framework Tasks and/or purpose Local context Group structure Member goals, beliefs, and characteristics Social system Group interaction Cognitive and emotional processing Group decisions and records Subjective member assessments Embedded System Framework Ch. 3 - Juries Trial evidence, jury instruction Courthouse and presiding judge Jury size and decision rule Juror beliefs, values, and experiences Constitution Social norms Media system Civic attitudes/ behaviors Narrative processing Jury verdict or finding Majoritarianism, argument distribution, momentum Subjective Assessments of jury service Embedded System Framework Ch. 3 - Group decision making Nature of issue or problem Group size Time available Attitude type and distribution Argument systems Discussion functions and sequencing Valence and content of arguments used Content and quality of decision(s) and/or report Embedded System Framework Ch. 4 - Group procedures Task complexity and importance Formal codes and bylaws Procedural expertise and traditions Resources available for training/support Designated group longevity and mission Procedural legal requirements Norms for arranging physical space and comm. networks Strong reciprocity Political culture (democratic norms, power relationships) Group structure: comm. network, arrangement, discussion procedures, and decision rule Faithfulness of procedural appropriation Discussion functions and sequencing Group development Degree and intensity of conflict Procedural knowledge, expectations, and preferences Consideration of others’ views Quality and representativeness of group decision Duration of discussion Confidence in (and commitment to) decision and group Embedded System Framework: Ch. 5 - Group size, diversity, creativity, information sharing, and related factors Emphasis on innovation and diversity Strength of link between status and expertise Resources devoted to training Economic pressure to innovate Changing workforce demographics Social stratification Anti-discrimination laws Cultural orientations (individualist/collectivist, hierarchical/egalitarian) Equality and dynamism of group structure Maturity and cohesion of group Group size and resources Distribution of expertise and external ties Members’ status consciousness and openness to diversity, change, and new ideas Integration of physical resources Idea generation Information seeking and exchange Attention to group structure and process Originality and quality of decisions and/or recommendations Effectiveness of coordinated action Satisfaction with process and outcomes Embedded System Framework Ch. 6 - Teamwork Leadership (facilitation, role clarification, coordination) Commitment to team model Task complexity and task type (coordination vs. cooperative) Training and support Leader role established Mutual performance monitoring Authority structure Structural flexibility Backup behavior Stress/pressure applied to learn Shared mental models Environmental monitoring and adaptation Team orientation and mutual trust Athletic archetype of teamwork Collectivist cultural norms Clear communication Team effectiveness Embedded System Framework Ch. 6 - Role and status distribution Institutionalized role system Status allocation Level of social stratification Conventional role norms and distributions Diffuse status characteristic stereotypes Role structure (behavioral requirements/ restrictions) Distribution of speaking opportunities/ interruptions Status system Distribution of attention, influence, and respect Behavioral expectations Productivity Distribution of rewards/ resources Satisfaction, comfort, and resentment Embedded System Framework Ch. 7 - Group cohesion formation Nature of the task and/or task-related conflict Distribution of felt and wanted relational needs and conflict orientations Individualist/ collectivist norms Culturally salient relational tensions Relational communication and conflict Group cohesion Embedded System Framework: Ch. 8 - Normative, symbolic, and identity conflict and convergence Task requires intraand/or inter-group cooperation vs. competition Inter-group conflicts with other local groups Organizational socialization practices Institutional support for inter-group contact Equality of member status relationships Nature and strength of group norms Salience of different social identities (and primary group identity) Confidence in one’s independent judgment Participants’ diverse identities and allegiances Pool of social identities, (including to other groups) group archetypes, and salient symbols or dramatic narratives Individualist/collectivist cultural orientations Socialization to conform with/adapt prototypical norms Distribution and management of deviance (rejection, norm adjustment) Symbolic conflict and convergence Dialogue and storytelling Group cohesion Subjective assessment of group’s qualities Increase/reduction in inter-group stereotypes and prejudices Exclusion/departure from the group Embedded System Framework Ch. 9 - Group-based personal growth and learning Cooperative vs. competitive group task Support for group leadership training Collaborative, competitive, or individualistic work/reward system Degree of ambiguity in group structure (roles, procedural norms) General recognition of non-conscious processes Group/social skill Knowledge/ understanding of topics (health, etc.) Group cohesion/ mutual trust Self-disclosure and emotional processing Participants’ willingness to express emotion and engage in conflict Dramatic role playing and self-expression Awareness of own and group’s non-conscious behavior Direct confrontation of emotional conflict Self-esteem/ confidence Participants’ personal emotional/psychological histories and health Cultural emphasis on personal development Non-directive/ interpretive group leadership Embedded Systems Theory summary Nature of group task (esp. coop./competitive) Institutional support/ training for groups Decision rule and discussion procedures Rigor of discussion Role/power relationships Completeness of information exchange Leadership style/ability Competitiveness and equity of power/status relations and rewards Group maturity/flexibility Positive/negative social relations Group cohesion, trust, and commitment Procedural monitoring/talk Policies toward diversity/innovation Distribution of member beliefs, attitudes, information Symbolic expression/ Narrative processing Socio-economic divisions/stratification Cultural orientations (individualist/collectivist, hierarchical/egalitarian) Pool of group archetypes, roles, social identities, and cultural myths Legal/constitutional procedural requirements Member social identities and ties to other groups Member mental health (self-confidence, anxiety) Treatment of deviance Quality of group decisions/ performance Assessment of fairness/quality of group process Attitudes toward different social groups








