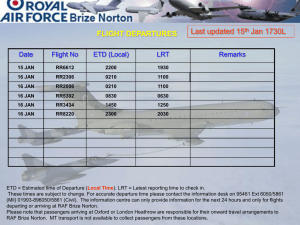
Third Edition
ANTHONY GIDDENS ● MITCHELL DUNEIER ● RICHARD APPELBAUM ● DEBORA CARR
Slides created by Shannon Anderson, Roanoke College
Chapter 14: The Sociology of the Body
Health, Illness, and Sexuality
1
Important topics
•
•
•
•
•
•
Social forces and the body
Theoretical approaches to health and illness
Alternative medicine
Health inequalities
Global health and infectious diseases
Sexuality and society
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
2
Sociology of the body
• Explores the relationship between society and
the body
• Examines the ways that cultural and social
factors affect health and other conditions of the
body
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
3
Bodies
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
4
Society and eating
• A dual example of a sociological approach to
understanding the body: our relationship with
food.
– Eating disorders
– Obesity
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
5
Anorexia and bulimia
• 90% of those with eating disorders are women
• 20% of anorexics will die from anorexia
• Our diet culture:
– 25% of men and 45% of women are dieting
– 60% of girls age 13 diet
– Over 80% of girls age 18 diet
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
6
BMI
BMI = 703 x ____weight ___
height x height
_____________________________________
Note: Weight in pounds, and height in inches.
Category
BMI Range
Underweight
< 18.5
Normal weight
18.5–24.9
Overweight
25.0–29.9
Obese I
30.0–34.9
Obese II
35.0–39.9
Obese III (Morbidly Obesity)
40.0 +
__________________________________________________
Source: National Heart, Lung, Blood Institute 1998.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
7
Obesity epidemic in the U.S.
•
•
•
•
•
1990: 0 states > 15% obese
2008: 32 states > 25% obese
We live in an “obesogenic” social environment
Poverty also contributes to obesity
Despite the fact that over 60 percent of adults
are overweight, there remains a powerful
stigma attached to obesity.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
8
Socialization of nature
• Processes that were once natural, or biological,
are now influenced by social forces and social
decisions.
• Norms and culture can lead to unhealthy
behaviors.
• Society, then, is affecting the body.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
9
Being ill
• A phenomenological or symbolic interactionist
approach to illness: what is the experience of
being sick?
• How are daily patterns, relationships, and
activities disrupted?
• How do we react? How do we cope?
• How do we deal with stigma?
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
10
The sick role
• A functionalist approach looks at how the sick
person tries to minimize any damage her
illness might create.
• The sick role has three basic expectations; they
are:
– Not responsible for the poor health
– Entitled to release from normal duties
– Expected to work to get well
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
11
Alternative medicine
•
The norm in Western societies is a
biomedical model of health.
Increasingly alternative forms of medicine
are now available.
•
–
–
–
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM)
Traditional Chinese medicine
Osteopathy
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
12
Health inequalities
•
Improvements in health and healthcare are
not equally distributed among societies.
• There are inequalities both within and
between countries dealing with:
– Class
– Race
– Gender
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
13
The spread of diseases
• Infectious diseases are often spread through travel
and high population density.
• Colonialism was a major engine for the spread of
disease.
– New diseases were introduced to populations.
– New farming techniques led to problems.
• Infectious diseases are still a much bigger
problem in the developing world today.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
14
HIV/AIDS
• Despite significant advances in treatment,
HIV/AIDS remains a global epidemic.
• Major inequalities persist in terms of access to
treatment and diagnosis of new cases.
• The majority of new cases are heterosexuals.
• Almost half are women.
• Over half are in sub-Saharan Africa.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
15
Map 14.1 The Number of HIV- Positive People
around the World
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Looking AIDS in the Face
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Barriers to success
•
•
•
•
•
Money
Stigma
Lack of nutrition
Lack of medical literacy
Ongoing motherchild transmission
•
Economic impact keeps deepening the spiral
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
18
Sex and sexuality
• Sex norms vary considerably across cultures.
• There are many possible sexualities (not just
heterosexual, homosexual, and bisexual).
• There are great variations in norms of sex
practice as well as sexual attractiveness.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
19
Sex in Western culture
•
•
•
•
Increasingly permissive
Increasingly egalitarian according to gender
1960s era was the shifting point
Men are happy with the increasingly open
sexuality of women, but also a bit undone or
confused by it.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
20
Sex in America
Social Influences on Sexual Behavior
Number of Sex Partners Since Age 18
0
partners
GENDER
1
partner
2–4
partners
5–10
partners
11–20
partners
21+
partners
Median number
of sex partners
since age 18
Total average
Men
Women
% of the population
AGE
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
18 – 24
25 – 29
30 – 39
40 – 49
50 – 59
% of the population
MARITAL STATUS
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Never married
Never married
Married
Divorced *
Divorced *
% of the population
* Divorced, widowed, or separated
Living alone
Living with someone
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
SOURCE: Laumann et al. 1994.
21
Sex in America
Social Influences on Sexual Behavior
Number of Sex Partners Since Age 18
0
partners
EDUCATION
1
partner
2–4
partners
5–10
partners
11–20
partners
21+
partners
Median number
of sex partners
since age 18
Some high school
High school
graduate
Some college
College graduate
% of the
population
Advanced
degree
RELIGION
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
No religion
Mainline Protestant
Conservative Protestant
Catholic
Jewish
Other religion
% of the population
RACE &
ETHNICITY
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
White
Black
Hispanic
Asian
Native American
% of the population
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
SOURCE: Laumann et al. 1994.
22
Sexual orientation
• Homosexuality was once seen as mental illness.
• The bigger question today: is it social or
biological?
• Most sociologists believe it is a combination.
• While attitudes have clearly shifted, homophobia
and overt discrimination and violence remain.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
23
Gay and lesbian rights
• Is this a civil rights issue?
• What is being sought?
– Anti-discrimination laws
– Marriage rights
– Adoption rights
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
24
This concludes the Lecture
PowerPoint Presentation for
Chapter 14: The Sociology of the Body
For more learning resources, please visit our online StudySpace at:
http://www.wwnorton.com/college/soc/essentials-of-sociology14/
W. W. Norton & Company
Independent and Employee-Owned
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
25
Clicker Questions
1. Which of the following best describes the field known as “sociology
of the body”?
a. It investigates how and why our bodies are affected by our social
experiences and the norms and values of the groups to which we
belong.
b. It investigates any kind of regular intervention we make into the
functioning of our bodies in order to alter them in specific ways.
c. It investigates anything we use to adorn our bodies, such as glasses,
watches, and jewelry.
d. It investigates the increasing use of such devices as cell phones,
pagers, and hand-held computing devices that make it possible for
people to communicate over large distances.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
26
Clicker Questions
2. What is the “socialization of nature”?
a. Phenomena that used to be “natural,” or given by nature (such
as the circumstances under which a woman can get pregnant),
have now become “social”—they depend on our own social
decisions (such as coming off the birth control pill or not using
condoms).
b. It is the use of agricultural land for house building and of
nature reserves for tourism.
c. It is the public ownership of natural resources.
d. It is the provision of birth control and abortion by public
hospitals.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
27
Clicker Questions
3. According to Talcott Parsons, which of the following is one of
the three pillars of the sick role?
a. The sick person is personally responsible for being sick.
b. The sick person is not entitled to withdrawal from normal
responsibilities.
c. The sick person should work to regain health by exercising and
dieting.
d. The sick person should consult a medical expert.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
28
Clicker Questions
4. Anorexia and obesity are both conditions of the body, yet the
causes reflect
a. social factors more than physical or biological factors.
b. the changing expectations about men’s and women’s roles.
c. the spread of fast food restaurants over the past forty years.
d. increased globalization and contact among societies with
different standards.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
29
Clicker Questions
5. Most sociologists currently believe that sexual orientation
a. results from biological factors.
b. results from social factors.
c. results from both biological and social factors.
d. results primarily from biological factors and secondarily from
social factors.
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
30
Clicker Questions
6. Which of the following is a part of what Kelly Brownell calls
the “obesogenic environment”?
a. sedentary jobs, which have replaced physical jobs such as
farming
b. restaurants that no longer offer “kids meals,” which provided
smaller portions
c. large grocery stores that are popping up in poor neighborhoods
and selling low-cost produce
d. lack of sidewalks in rural and suburban areas, which make
exercising outdoors potentially harmful
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
31
Art Presentation Slides
Chapter 14
The Sociology of the Body:
Health, Illness, and Sexuality
Anthony Giddens
Mitchell Duneier
Richard P. Appelbaum
Deborah Carr
Chapter Opener
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
The first woman is painfully thin as a result of famine
and malnutrition, sadly common problems in areas of
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
the world plagued by frequent drought and crop failure.Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
The second has become painfully thin by her own doing; people
suffering from anorexia feel compelled by a variety of personal
and social pressures to lose weight, and will often continue to
view themselves as overweight even when they have reached
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
a state of emaciation.
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
The third woman is severely overweight and is preparing
for a dangerous gastric bypass surgery.
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Why do many parents turn to fast food to feed their
families? What are the consequences?
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Ayurvedic treatment: Ayurvedic physician Kumar Das
uses a hot iron rod and fabric soaked in herbs to heal
an arthritic hip.
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Dr. Regina Benjamin, a family physician dedicated to serving
the working- class families in a small shrimping community
on the Gulf Coast, visits one of her patients at home.
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Globalization and Everyday Life
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Globalization and Everyday Life
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Looking AIDS in the Face
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Map 14.1 The Number of HIV- Positive People
around the World
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
Sex in America
Social Influences on Sexual Behavior
Number of Sex Partners Since Age 18
0
partners
GENDER
1
partner
2–4
partners
5–10
partners
11–20
partners
21+
partners
Median number
of sex partners
since age 18
Total average
Men
Women
% of the population
AGE
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
18 – 24
25 – 29
30 – 39
40 – 49
50 – 59
% of the population
MARITAL STATUS
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Never married
Never married
Married
Divorced *
Divorced *
% of the population
* Divorced, widowed, or separated
Living alone
Living with someone
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
SOURCE: Laumann et al. 1994.
Sex in America
Social Influences on Sexual Behavior
Number of Sex Partners Since Age 18
0
partners
EDUCATION
1
partner
2–4
partners
5–10
partners
11–20
partners
21+
partners
Median number
of sex partners
since age 18
Some high school
High school
graduate
Some college
College graduate
% of the
population
Advanced
degree
RELIGION
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
No religion
Mainline Protestant
Conservative Protestant
Catholic
Jewish
Other religion
% of the population
RACE &
ETHNICITY
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
White
Black
Hispanic
Asian
Native American
% of the population
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
© 2011 W. W. Norton Co., Inc.
SOURCE: Laumann et al. 1994.
The Stonewall Inn nightclub raid in 1969 is regarded as the
first shot fired in the battle for gay rights in the United States.
Essentials Of Sociology, 3rd Edition
Copyright © 2011 W.W. Norton & Company
W. W. Norton & Company
Independent and Employee-Owned
This concludes the Art Presentation Slides
Slide Set for Chapter 14
Essentials Of Sociology
THIRD EDITION
by
Anthony Giddens
Mitchell Duneier
Richard P. Appelbaum
Deborah Carr