Presentation (through 13 June 2013)
advertisement

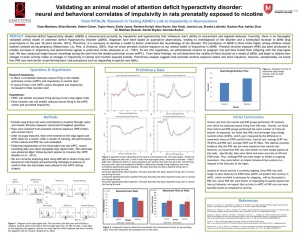
Impact of prenatal nicotine exposure on impulsivity and neural activity in medial prefrontal cortex Team RITALIN: Research in Testing ADHD's Link to Impulsivity in Neuroscience 13 June 2013 Introduction Prenatal Nicotine Exposure (PNE) PNE is linked to many psychiatric disorders Women who smoke during pregnancy are three times as likely to have children diagnosed with ADHD 1 in 5 women still smoke during pregnancy Nicotine causes changes in the development that alters dopaminergic & noradrenergic pathways in the brain Several studies show behavioral, neuroanatomical, & neurochemical disturbances after PNE Benefits of methylphenidate, a common ADHD drug, point to PNE as a valuable animal model of impulsivity Introduction Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Symptoms: impulsivity, hyperactivity, & inattention Affects 5-10% of all school age children Twentyfold increase in prescription of ADHD drugs in the past 30 years Diagnoses based on qualitative observations Limited research on the neurobiology of the disorder ADHD drugs are addictive stimulants Fetal nicotine rats and humans with ADHD have similar deficits on behavioral tasks for hyperactivity & impulsivity Introduction Modeling Impulsivity Animal model validity Face validity Conduct validity Predictive validity What areas or circuits are involved? How can we uncover more about the neurobiology? Introduction Medial Prefrontal Cortex (mPFC) Introduction Stop Signal Task (SST) Introduction Research Questions I. Is there a correlation between neural firing in the mPFC cortex and impulsivity in control rats? II. Is neural firing in the mPFC cortex disrupted and impulsivity increased in fetal nicotine rats? III. Is there a correlation between this disrupted firing and increased impulsivity? Methodology Phase 1: Rat Breeding & Selection Acclimate dams to nicotine in water Breed rats Compare populations Select pups Significant differences in water consumption & mother weights No significant differences in pregnancy duration, pups per litter, pup birth weight, or locomotion* Randomly selected 8 males each from 37 PNE pups (from 3 dams) and 39 control pups (from 3 dams) Methodology Phase 2: SST Training & Surgery Task training Between group differences observed Implant electrodes Compare movement times and percent correct on stop and go trials Results Percent Correct during Training Sessions 84 79 Percent Correct 74 69 Control 64 59 Nicotine 54 49 44 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Day 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Results Percent Correct during Training Sessions with Stop Trials 90 Control Go Trials Percent Correct 80 70 Nicotine Go Trials 60 Control Stop Trials 50 Nicotine Stop Trials 40 30 1 2 3 4 Day 5 6 Results Movement Times during Training Sessions 0.31 0.3 0.29 Time (s) 0.28 0.27 Control 0.26 Nicotine 0.25 0.24 0.23 0.22 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Day 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Results Movement Time during Training Sessions with Stop Trials 0.36 Control Go Movement Times 0.34 Nicotine Go Movement Times Time (s) 0.32 0.3 Control Stop Movement Times 0.28 0.26 Nicotine Stop Movement Times 0.24 0.22 1 2 3 4 Day 5 6 Results Post-Surgery Behavior Percent Correct Trials p ˂ 0.05 80 Percent Correct 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Control Go trials Stop trials Stop Change Reaction Time Movement Time on Trials 120 800 700 100 600 80 Time (ms) Movement Time (ms) p ˂ 0.05 900 Nicotine Group 500 400 300 60 40 200 20 100 0 Control Go trials Group Stop trials Nicotine 0 Control Group Nicotine Methodology Phase 3: Neural Recording & Analysis Neural Recording Histology Data Analysis 12 rats from the control and PNE groups performed 157 sessions, over which we collected neural firing from 346 cells Methodology Histograms for Above/Below Baseline Firing Results Histograms for Preferred/Nonpreferred Stop/Go Trials Results Distributions for Preferred/Nonpreferred for Go Direction Results Histograms for Contra/Ipsi Stop/Go Trials Results * legend: go ipsi - blue go contra - green stop ipsi - red stop contra - yellow Subtraction Plots for Preferred/Nonpreferred Stop/Go Trials Results Discussion Preliminary Conclusions Behavior PNE rats were more impulsive (as measured by SCRT) However, they were better at basic task procedures (eg responding to spatial cue lights) Neural recordings Signals from neurons which encode stopping an already initiated movement were attenuated in PNE rats as compared to controls Signals from neurons which encode direction towards the correct behavioral response were also attenuated as compared to controls This points to a neurophysiological pathway disruption in inhibiting impulsivity caused by PNE Discussion Future Directions For my team: Finish collecting data for additional controls Complete data analysis Present data at Society for Neuroscience Conference Write & present our thesis at the Senior Thesis Conference For someone else: Try a different task (or SST with different parameters) Give nicotine postnatally Administer ADHD drugs to PNE rats and controls My Team Questions? Questions?