Pathological cycling in addiction (Koob, Neuron
advertisement
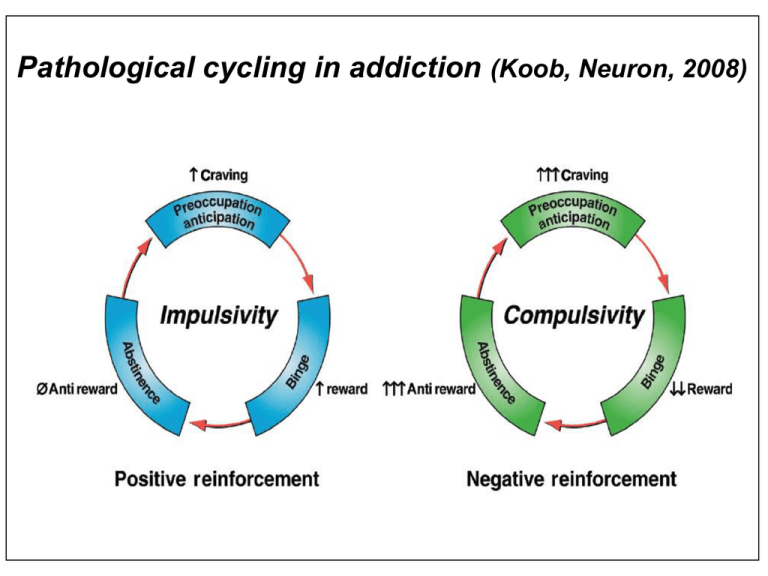
Pathological cycling in addiction (Koob, Neuron, 2008) Drugs of abuse increase synaptic DA in the Nucleus Accumbens (Di Chiara and Imperato, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 1988) ethanol nicotine Limbic motor subcircuit Dorsal-striatal motor subcircuit (motor habits) Glutamate release associated with addiction (You et al., J. Neurosci., 2007; LaLumiere and Kalivas, J. Neurosci. 2008) Cocaine self-administration Nac core heroin Glutamate Receptor Families AMPA Kainate NMDA Metabotropic Go Gi, Gq GluR1 GluR2 GluR3 GluR4 GluR5 GluR6 GluR7 KA1 KA2 NMDAR1 NMDAR2A NMDAR2B NMDAR2C NMDAR2D NMDAR3 mGluR1 mGluR5 mGluR2 mGluR3 mGluR4 mGluR6 mGluR7 mGluR8 LTP and LTD of excitatory synaptic transmission as a substrate for associative learning Control LTP Drugs of abuse induce LTP at excitatory synapses on DAergic neurons in the VTA (Kauer and Malenka, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 844, 2007) Bidirectional loss of synaptic plasticity at the PFC/NAc core synapses following chronic cocaine (Mussawi et al., Nat. Neurosci., 2009) NAc LTP LTD Transiction to addiction is associated with a persistent impairment in NMDA-dependent LTD in the NAcc core Kasanetz F., Deroche-Gemonet V., Berson N., Balado E., Lafourcade M., Manzoni O., Piazza P.V. Science 328, 1709, 2010 The “perfect” drug: 1. inhibits the reinforcing properties of drugs and associated cues 2. reinstates the mechanisms of control by the PFC over the VTA-NAc 3. interferes with maladaptive mechanisms leading to hedonic allostasis 4. relieves physical and motivational withdrawal symptoms 5. prevents relapse in response to drug priming, context, and stress 6. has an impact on the negative reinforcement generated by the stress neural circuit (extended amygdala) mGlu2 mGlu3 mGlu1 mGlu5 mGlu4 mGlu6 mGlu7 mGlu8 mGlu5 receptors: potential targets for The treatment of addiction GS MAPK, PI-3-K Negative allosteric modulators of mGlu5 receptors: Fragile X, GERD, migraine, nicotine addiction, Parkinson’s disease/L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias Fenobam AFQ056 ADX10059 ADX48621 STX107 AZD2516 Reinforcing effects of cocaine are absent in mGlu5 knockout mice (Chiamulera et al., Nature, 2001) Activation of mGlu5 receptors is required for incentive motivation for the reinforcer (Markou, Biol. Psych. 2007) 1. Amplification of PF/VTA excitatory synapses by mGlu5 receptors Extinction training after cocaine self-administration lowers surface mGlu5 receptors in the Nacc core to inhibit drug seeking mGlu5 Knackstedt et al., J. Neurosci. 30, 2010 mGlu5 receptor blockade reduces methamphetamine reinforcement and reimstatement (Gass et al., Neuropsychopharm. 34, 2008) mGlu5 receptor blockade is protective against Methamphetamine (“Shabu”) toxicity Lewy bodies in the substantia nigra of a Parkinsonian patient Intracytoplasmic inclusions after methamphetamine injection Forno et al., 1996 Fornai et al., 2003 Ubiquitin a-Synuclein Saline Parkin Methamphetamine Fornai et al., 2003