perception-cognition-emotion
advertisement

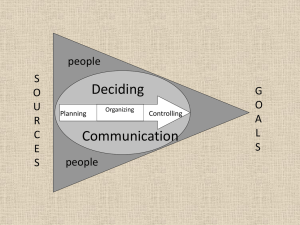
Perception, Cognition & Emotion What are the perceptual Biases Frames Cognitive Biases Emotions • What is perception • Whatever happens between occurrence of a stimulus and our behavioral reaction to it • Many processes in between…. Stimulus Attention Recognition Perception Translation Behavior • Perceptual Biases • Stereotypes • Generalize from one individual many individuals of a group – Due to time pressure, cognitive stress, mood • Halo • Generalize from one attribute many attributes – Due to lack of experience with person, celebrity status, moral qualities of attributes • Perceptual Biases (cont’d) • Selective perception (aka confirmation bias) • Reliance on evidence that is consistent with beliefs than over that is inconsistent – Perpetuates stereotypes, halos etc • Projection (aka false consensus effect) • Assume other is similar to you in interpreting & responding to situation • Framing – Individual interpretations of negotiation situation • E.g., objective of negotiation, expectations for outcomes, information used to argue case, procedures, criteria for evaluating outcome – Some types of frames are similar to concepts of strategy, goals, interests, rights, power…..! • E.g., substantive, outcome, aspiration, process… • Types of frames (similar to other concepts) – Substantive vs. Process • to have a particular way of thinking of what the conflict is about vs. how to resolve the conflict – Outcome vs Aspiration • Achieve a certain outcome vs. satisfy needs or interests – Rights • Correct, legitimate, fair – Power • coercion, economic pressure, legitimate authority, expertise – Give an example… • Types of frames (cont’d) – Identity • Definition of oneself – E.g., group membership, place of birth etc. – Characterization • Definition of the other party – Prior experience w/other party, reputation, image projected early in negotiation – Loss-gain • Risk vs. reward – E.g., Loss of $$ vs. gain in value of item • How frames work… (note similarity to how interests operate) – More than one frame @ one time – Mismatches of frame conflict – frames differences in negotiation – Type of Issues Frames – Frames agreements – Differences in values, personalities, background etc differences in frames • How frames operate within the course of a negotiation • What gets discussed: stock issues • Build a strong case for own position, refute other party’s argument • Diagnosis/Formula/Detail • Discuss multiple secondary items transform negotiation (develop issues) • Reframing: attack arguments, making case, management of multiple issues • Cognitive Biases • • • • • • Escalation of commitment Fixed-pie beliefs Anchoring & Adjustment Loss vs. Gain frame Availability (vividness) Winner’s curse (counterfactuals) • Cognitive Biases • Overconfidence • Law of Small numbers (extrapolating from experience) • E.g., “Hot hand” • Self-serving Biases: • fae, a-o, false consensus (b23) • Endowment Effect • Ignoring other party’s cognitions • Reactive devaluation • minimize concessions made by disliked other • Managing misperceptions & cognitive biases • Awareness is not sufficient, • E.g., discussing how to set offers etc. does not reduce anchoring and adjustment effects – Reframe when frames are mismatched • Define & evaluate problem, discuss in structured way • Arunachalam & Dilla 1995 • Emotions in Negotiation • Negotiation processes & outcomes Positive & Negative Emotions • Positive Emotions Positive Outcomes – Integrative processes – Positive attitude toward other side – Promote persistence • Negotiation processes Positive Emotions – Fair procedures – Favorable social comparisons • Negative Emotions Negative Outcomes – Definition of situation as competitive/distributive – Escalation of conflict – Retaliation • Negotiation processes & outcomes Positive & Negative Emotions (cont’d) • Negative Emotions Negative Outcomes – Definition of situation as competitive/distributive – Escalation of conflict – Retaliation • Negotiation Processes Negotiation Emotions – Competitive mind-set – From Impasse – Beginning of a negotiation • Positive emotions negative outcomes • Scrutiny of counter arguments is less • Susceptibility to deceptive tactics • Positive emotions positive expectations. If those are are not met via integrative agreements, other party is treated more harshly • Negative emotions positive outcomes • Information value – motivation to resolve situation or leave it • Words used to trigger negative emotion to convey seriousness of purpose – .g., anger is a double edged sword…. • Using emotion as a negotiation tactic – Positive emotional tone • agreements incorporating future business relationship • Induce compliance w/ ultimatum offers – Adjust strategy based on emotion of other party • Angerlower demands • Smaller concessions when anger threatens outcomes of negotiation • Worry/disappointment lower demands • Guilt/regret higher demands • EI Emotional tuning of messages to other party’s emotions