Details (Ao1) and Evaluation (Ao2) of treatments for abnormality
advertisement

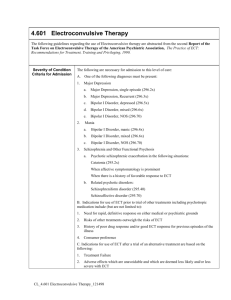
MONSTER treatments session! Treatments from the 4 approaches to abnormality… Behaviourist Treatments • NAME and EXPLAIN the treatment… • NAME: Systematic Desensitization (its on the spec!) If maladaptive behaviours have been learnt by classical or operant conditioning it should be possible to change them. ‘SD’ takes a practical problem-solving approach based upon classical conditioning. It uses reverse conditioning to replace a maladaptive response to a stimulus with an adaptive response. AO1: The Procedure of Systematic Desensitization (MUST) •Taught to use muscle relaxing techniques. •Client imagines a Sgraded series of anxiety provoking produces situations, from those causing After therapist theintervention least anxiety upto S the highest. Original situation •Relaxation & anxiety cannot exist together. •Treatment ends when client is desensitized. •Can be applied through imagination (in Vitro) and moved towards real life (in Vivo). R1 R2 Relaxation Hierarchy of anxiety provoking situations Reciprocal inhibition Complete treatment In vivo & In vitro AO1: You ‘could’ then apply the treatment to a case study… You could apply the procedure to real life disorders. Find a case study of an abnormality e.g. anxiety disorder. Be prepared to explain how this treatment could be applied. AO2: Evaluating Systematic Desensitization ✔ Positive: It is effective. There is research support for a range of anxiety disorders. McGrath et al (1990) suggest that 75% of people with phobias respond to this treatment ✘Criticism: There are quicker alternatives, such as ‘Flooding’ ✘Criticism: There are problems with using ‘InVitro’ as not everyone can imagine a situation. ‘In-Vivo’ is more effective and long-lasting. Biological Treatments • NAME and EXPLAIN the treatment… • NAME: Drug treatments and ECT (they are on the spec!) Drug Treatments: Anti-anxiety; Antidepressant; Anti-Psychotic ECT: Electro-convulsive therapy – procedure and it’s use (mainly used to treat severe depression) AO1: Drug Treatments (explain) • Anti-anxiety: Tranquilizers called Benzodiazepines (BZ’s) such as “Valium” calm the nervous system and muscles, and increases GABA which calms the brain activity • Anti-depressant: SSRIs improve mood by increasing levels of serotonin. • Anti-Psychotic: Major tranquilizers like ‘phenothiazines’ sedate symptoms of hallucinations and delusions for people with psychotic disorders like schizophrenia. They block the dopamine receptor AO1: The Procedure of ECT (MUST) • Patient lies on the bed in loose clothing and receives an anaesthetic and muscle relaxant drug • Electrodes are fixed to their head on the temples, usually just one electrode on the nondominant hemisphere (usually the right hand side) • An electric current of 70-130 volts is passed through the brain for 30 seconds • This induces a convulsion (a seizure similar to an epileptic fit) that lasts for about a minute • Once the patient comes around from the anaesthetic, they usually remember nothing about the procedure AO2: Evaluating Drug Treatment ✘Drugs may have side-effects ✘Drug treatments are not effective for all people ✘There are ethical problems with the use of drugs ✘Only focuses on treatment of symptoms Effective in short-term AO2: Evaluating ECT It is a quick form of treatment compared to drugs or psychological treatments ✘It is unclear how it actually works ✘There are still some side-effects of ECT ✘Ethical issues as it has historically been used more as punishment or control in mental hospitals of the past Cognitive Treatments • NAME and EXPLAIN the treatment… • NAME: CBT: it’s aims, procedures and examples Each session has a ‘cognitive’ element AND a ‘behavioural’ element Examples include REBT and Beck’s Cognitive Therapy AO1: The Procedure of CBT • Cognitive element: direct questioning and diagrams used with client to find out their beliefs about their anxiety or depression etc • Behavioural element: Client and therapist decide together how the beliefs can be tested through role-play and homework assignments, so that the client can recognise their faulty-thoughts and beliefs. Client is set new goals in graded stages of difficulty so that they can build on their own success AO2: Evaluating CBT Diverse applications: CBT is very popular in the NHS as it is economic and short-term. Can be used for stress management as well as family, marital and educational problems It is appealing to people who don’t like the idea of other treatments… It is ethical, as the client and the therapist work together on the problem, making joint decisions about treatment ✘ BUT, clients can become dependant on their therapist ✘ It is less effective than drugs at treating depression Psychoanalysis Treatment • NAME and EXPLAIN the treatment… • NAME: Psychoanalysis and it’s different methods It aims to bring repressed impulses and traumatic experiences into conscious awareness to be dealt with, and cure neurotic symptoms like phobia and anxiety, while gaining an insight into conflicts and anxieties that underlie abnormal behaviour Methods: Dream Analysis; Free Association; Transference AO2: Evaluating Psychoanalysis ✘It can be expensive and time-consuming compared to other treatments. ✘Difficult to measure effectiveness Most appropriate for treating neurotic disorders like anxiety, and actually treats the cause, not just the symptoms