Thalamus & Hypothalamus

Hypothalamus
NEU 257
3/3/2011
The diencephalon
• “between brain”
• Posterior part of embryonic forebrain
• Lies between brainstem and cerebral hemispheres
• Includes: thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, epithalamus
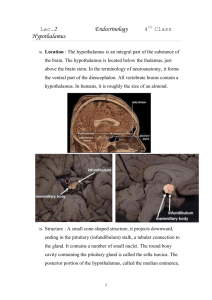
Hypothalamus: General description
• Below rostral thalamus (hypo =“under”/”beneath)
• Vital regulatory functions include: temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, blood osmolarity, goal seeking behavior, emotional behavior, visceral nervous system, sexual activity, food & water intake, aggression
• Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle
• Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function
• Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections
Involvement with 3 major systems
• Endocrine system (HPA: hypothalamopituitary-adrenal axis)
• Autonomic nervous system
• Motivation system
….Also adaptive emotional behavior
Gross anatomy of the Hypothalamus science.tjc.edu/ images/brain/Index.htm
Main Inputs to Hypothalamus
• receives info on external and internal conditions:
– specific sensory info (e.g., direct retinal projection)
- input from visceral senses (NTS: nucleus of the solitary tract: taste )
– contains many neurons that are sensitive to local temperature, osmolarity, glucose, sodium
– circulating hormones influence it via the circumventricular organs
Retinohypothalamic tract
III
SCN SCN
Circumventricular organs
•Brain regions near ventricles that lack a blood-brain barrier, e.g., subfornical organ, OVLT, median eminence, area postrema
•Highly vascularized
•Influenced by circulating hormones, osmotic changes, substances in CSF, afferent fibers from other parts of the nervous system
Peptidergic neuroendocrine cells:
Magnocellular neurons
• “Large” neurons
• Located in paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei
• Secrete oxytocin and vasopressin into general circulation via posterior pituitary
• Oxytocin uterine contraction & milk secretion
• Vasopressin vasoconstriction, water resorption by the kidney
Brainmaps.org
Magnocellular Secretory System clem.mscd.edu/~raoa/ bio2320/endo1/sld003.htm
Peptidergic neuroendocrine cells:
Parvocellular neurons
• “small” neurons
• Located in medial basal region, arcuate and tuberal nuclei, periventricular region, preoptic and paraventricular nuclei
• Secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones into portal vasculature via anterior pituitary
• Nobel prize awarded to Guillemin (Salk),
Schally and Yalow in 1977 for their
(independent) work in proving the hypothesis that the hypothalamus releases hormones that regulate the pituitary
Brainmaps.org
Hypothalamic Portal System clem.mscd.edu/~raoa/ bio2320/endo1/sld003.htm
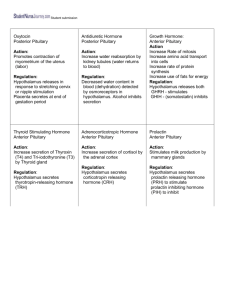
Hypothalamic inhibitors
Hypothalamic hormone
Prolactin release-inhibiting hormone
(PIH), dopamine
Growth hormone release-inhibiting hormone (GIH; somatostatin)
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone release inhibiting factor (MIF)
Anterior pituitary hormone
Prolactin
GH, thyrotropin
MSH
Hypothalamic releasers
Hypothalamic hormone
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
(TRH)
Corticotropin-releasing hormone
(CRH) gonadotropin-releasing hormone
(GnRH)
Growth-hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
Prolactin-releasing factor (PRF)
Melanocyte-stimulating hormonereleasing factor (MRF)
Anterior pituitary hormone
Thyrotropin, prolactin
Adrenocorticotropin,
LH, FSH
GH
Prolactin
MSH, b
-endorphin b
-lipotropin
Peripheral Influence of Hypothalamus clem.mscd.edu/~raoa/ bio2320/endo1/sld003.htm
Hypocretin
•Also known as “orexin”
•Peptide involved in arousal and feeding behavior
•Project to thalamus, cortex and brainstem regions associated with arousal, cardiovascular control, and autonomic functions
•Few thousand neurons
•Loss of hypocretin neurons implicated in human narcolepsy
From Thannickal et al., Neuron 27: 469, 2000