Mythological Criticism: Archetypes & Literary Analysis
advertisement

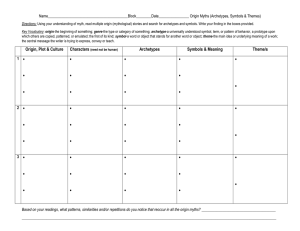
MYTHOLOGICAL CRITICISM Sierra Cappel, Lunia Oriol, and Kae Moulton KEY INFORMATION • A mythological critic uses hopes, fears, and expectations set by certain cultures to uncover universal ideas or themes in certain literature. • Carl Jung, a psychologist in the 1930’s, to explain that we all share a general subconscious and archetypes are universal • Sir James Frazer studied myth from different cultures and found that stories differ from detail to detail but in substance are the same. • Northrop Frye founded the principal that all literature share a similar pattern. • It has strong connections with social anthropology and psychoanalysis KEY WORDS Fears Religion (Water, Rising on the third day, the devil, lambs) Myth (The Odyssey, Gods, Herculean Quest) Explanation Human flaws Colors THE PROS AND CONS STRENGTHS • Humans respond instinctively to archetypal elements because we, according to psychologist Carl Jung, are born with a “collective unconscious”, a level below the subconscious where the brain collects and stores archetypes. • The large variety of archetypes all relate to human flaws and experiences WEAKNESSES • Ignores historical, philosophical, and aesthetic parts of a work • Reduces the work to basic plot and character types CITATIONS http://www.grossmont.edu/karl.sherlock/English160/Resources/GlossaryDr amaLitTerms.htm#MythologicalCriticism http://www.intech.mnsu.edu/bunkers/archetypal_theory.htm http://www.lebanon.k12.mo.us/lhs/faculty/croden/archetypes%20and %20archetypal%20criticism.html http://public.wsu.edu/~delahoyd/archetypal.crit.html http://prezi.com/upx9b5f-y-y5/archetypal-criticism/