Evidence-based practice - Creative Teaching Framework
advertisement

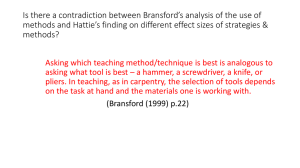
Evidence-based practice - what does this mean to you? Evidence-based Practice “It is hard to conceive of a less scientific enterprise among human endeavours. Virtually anything that could be thought up for treatment was tried out at one time or another, and, once tried, lasted decades or even centuries before being given up. It was, in retrospect, the most frivolous and irresponsible kind of experimentation, based on nothing but trial and error, and usually resulting in precisely that sequence” (p.159) The medical profession before the drive for evidence-based practice (Thomas, 1979, p.159) “The key question is whether teaching can shift from an immature to a mature profession, from opinions to evidence, from subjective judgements and personal contact to critique of judgements “ (Hattie, 2009, p.259) Is Evidence-based practice possible for Teaching? “…over the past 3 decades, we have amassed enough research and theory about learning to derive a truly research based-model of Instruction” (Marzano, 1992, p.2) “There are systematic and principled aspects of effective teaching, and there is a base of verifiable evidence of knowledge that supports that work in the sense that it is like engineering or medicine” (Darling-Hammond & Bransford, 2006, p.12) “We have a rich educational research base, but rarely is it used by teachers, and rarely does it lead to policy changes that affect the nature of teaching” (Hattie, 2009, p.2) The Challenge for Evidence-based teaching: Moving Teaching from Mystery to Heuristics “Heuristics represent an incomplete yet distinctly advanced understanding of what was previously a mystery. But that understanding is unequally distributed. Some people remain stuck in the world of mystery, while others master its heuristics. The beauty of heuristics is that they guide us toward a solution by way of organized exploration of possibilities.” (Martin, R, 2009, The Design of Business, p.12) Another sneaky question for you – Where are you now? Some Pioneers in the Field • Bransford, J. et al., (1999), Brain, Mind, Experience & School. National Academy Press: Washington, DC. • Marzano, R. (2007), The Art and Science of Teaching: A Comprehensive Framework for Effective Instruction. ASCD. • Mayer, R.E. & Alexander, P. A., (2010), Handbook of Research on Learning and Instruction. Routledge: London. • Petty, G., (2009), Evidence-Based Teaching: A Practical Approach. Nelson Thornes: Cheltenham. • Hattie, J., (2009), Visible Learning. Routledge: New York. • Hattie, J., (2012), Visible Learning For Teachers: Maximizing Impact On Learning. Routledge: London. • Hattie, J. & Yates, G. C. R., (2014), Visible learning and the Science of How we Learn. Routledge: New York. A Revolution in Teaching “Teaching is about to embark on a revolution, and like medicine, abandon both custom and practice, and fashions and fads, to become evidence-based” Half a million experiments in real classrooms have uncovered the teaching methods that work best. These can improve students’ attainment by two grades compared to conventional practice. The fifty or more methods – some old, some new: • can each raise pass rates by 20% to 30% • are creative, challenging, and greatly enjoyed by students • require the learner to do more in class …. and the teacher less! • equip students for progression, by “teaching intelligence”. (Geoff Petty, Evidence-based Teaching) Big Method effects on Student Attainment from Hattie’s metaanalysis (1) No. Influence Mean effect size 2 Feedback Students getting feedback on their work from the teacher or from themselves (self-assessment or from peers or some other sources. Note: some feedback has more effect than others. For example, peer assessment is 0.63 and self-assessment is 0.54 0.81 3 Whole-class interactive teaching (direct instruction) A specific approach to active learning in class, which is highly teacher led, but very active for students. This involves summaries reviews and a range of active learning methods, including questioning 0.81 4 Strategy training Explicit teaching of subject-specific and general study and thinking skills, integrated into the curriculum 0.80 11 Cooperative learning 0.59 Specific teaching methods such as jigsaw that give students responsibility for learning and teaching each other 12 Challenging goals for students Giving students a summary in advance and a purpose for the learning 0.59 Big Method effects on Student Attainment from Hattie’s metaanalysis (2) No. Influence Mean effect size 14 Mastery learning Students must work (tested and re-tested) until they achieve the pass mark 0.55 16 Creativity Programmes Teaching creative thinking 0.52 20 Study Skills Teaching students useful study skills without integrating it into the curriculum 0.49 27 Advance Organizers Giving students a summary in advance and a purpose for the learning 0.46 28 Concept Mapping 0.45 67 Problem-based learning Giving students a problem to solve that requires them to teach themselves 0.06 What does an Effect Size look like in terms of student attainment? • As a baseline an effect size of 1.0 standard deviation is massive and is typically associated with: – Advancing the learner’s achievement by one year – Improving the rate of learning by 50% – A two grade leap in GCSE grades • Effect size is a way to measuring the effectiveness of a particular intervention to ascertain a measure of both the improvement (gain) in learner achievement for a group of learners AND the variation of student performances expressed on a standardised scale. By taking into account both improvement and variation it provides information about which interventions are worth having • NOTE: For students moving from one year to the next, the average effect size across all students is 0.40. Hence, effect sizes above 4.0 are of particular interest. Some important considerations about Effect Sizes As Hattie notes: “…some effect sizes are ‘Russian dolls’ containing more than one strategy. For example, ‘Feedback’ requires that the student has been given a goal, and completed an activity for which the feedback is to be given; ‘whole-class interactive teaching’ is a strategy that includes ‘advance organisers’ and feedback and reviews” (p.62) It is also important to balance effect size with level of difficulty of interventions. For example, providing ‘advance organizers’, which are summaries in advance of the teaching, has an effect size of 0.46, which is pretty average. However, they only take 3 minutes at the beginning of the lesson, and potentially offer almost a grade improvement in terms of student’s achievement. Furthermore, the effect size depends on how effectively you implement the strategy, as you would expect Hattie and Beyond: Essential Questions • How do effective methods produce positive impacts on the learning process? • What are the key factors and core principles of learning that impact learner attainment (Model of Learning)? • How might teaching professionals use this knowledge thoughtfully in their practice (e.g., designing effective instructional strategies) to enhance student learning and attainment? • What are the implications for the professional development of teachers? Activity: Select one of Hattie’s high effect size methods and explain how it works in terms of how humans learns Effective Teaching – and Learning - requires Good Attention “It’s biologically impossible to learn anything that you’re not paying attention to; the attentional mechanism drives the whole learning and memory process” (Sylwester, 1998, p.6) “The shape and content of life depends on how attention has been used…. Attention is the most important tool in the task of improving the quality of experience” (Csikszentmihalyi, 1990, p.33) Ask Michelle Pfeiffer Interest and perceived value initiate and drive the learning process “There can be no mental development without interest. Interest is the sine qua non for attention and apprehension. You may endeavour to excite interest by means of birch rods, or you may coax it by the incitement of pleasurable activity. But without interest there will be no progress” (Whitehead, 1967, p.37) Importance of challenge • “Succeeding at something that you thought was difficult is the surest way in which to enhance self-efficacy and self-concept as a learner” (Hattie, 2012, p.58) • “Educating students to have high, challenging, appropriate expectations is among the most powerful influence in enhancing student achievement” (Hattie, 2012, p.60) Beliefs can positively (or negatively) influence the learning process I belief, through effort, a top grade is possible I’m not smart and its all blur, lah, and I’ll fail “If you think you can or think you can’t, you’re right” (Henry Ford) “We forget that beliefs are no more than perceptions, usually with a limited sell by date, yet we act as though they were concrete realities” (Adler, 1996, p.145) Attribution Theory: Mindsets Carol Dweck) Fixed Mindset (Intelligence is static ) Growth Mindset (Intelligence can be developed) Leads to a desire to look smart and therefore a tendency to: Leads to a desire to learn and therefore a tendency to: • Avoid challenges • Embrace challenges • Get defensive and give up when faced with • Persist in the face of setbacks obstacles • See effort as the path to mastery • See effort as something less able people need, and not for the smart • Learn from criticism • Ignore useful negative feedback • Find Lessons and inspiration in the • Feel threatened by the success of others success of others As a result, they may plateau early As a result, they reach ever-higher and achieve less than their full potential levels of achievement “There are differences in attainment gains relating to whether teachers believe that achievement is difficult to change because it is fixed and innate, compared to teachers who believe that attainment is changeable (the latter leading to higher gains)” (Hattie, 2012, p.92) Impact of Motivation & Beliefs on learning Marzano (1988) categorized teaching strategies and other ‘interventions’ depending on whether they activated in the student: • • • The self-system – A set of beliefs the student holds about his or her capabilities, the meaning and value of what they have been asked to do, along with the likelihood of success The meta-cognitive system – Students setting themselves goals, monitoring their progress towards these goals and adapting t difficulties The cognitive system – This is the system that reasons, and thinks in other ways with the information at its disposal, to achieve the desired goals. He found that activating the self-system had greatest effect, the metacognitive system the next most effect, and the cognitive system least, though it is still substantial. Interestingly, he argued it is the self-system that activates the metacognitive system, which actives the cognitive system, which creates learning. (Marzano – A Theory-Based Meta-Analysis of Research on Instruction) Implications of Marzano’s research Highlights the importance of the teachers role in motivating students by encouraging them to see the value of what they are about to learn, and to believe in their own capacity to learn it. “..if something can be learned, it can be learned in a motivating manner” (p.23) “..every instructional plan also needs to be a motivational plan” (p.24) (Wlodkowski, R. J., 1999, Enhancing Adult Motivation to Learn) Core Principle 1: Motivational strategies are incorporated into the design of learning experiences Effect size: 0.48. However, this is a Russian Doll (Meta-principle) as it runs across a range of method uses Instructional strategies must facilitate: • Meeting fundamental universal needs (e.g., Mastery, Autonomy, Relatedness, Purpose) • Making learning interesting for the particular learner group (e.g., meaningful, sufficiently challenging, differentiated) • Reframing limiting beliefs (e.g., promote a Growth Mindset) where necessary "People often say that motivation doesn't last. Well, neither does bathing - that's why we recommend it daily“ (Zig Zagler) Effective Learning needs Structure • students must be aware of the purpose, key points and principles in what they are learning • “It is indisputable that, from the students’ perspective, clear standards and goals are a vitally important element of an effective educational experience. Lack of clarity on these points is almost always associated with negative evaluations, learning difficulties and poor performance” (Ramsden (1992, p.127) “Teachers are successful to the degree that they can move students from single to multiple ideas then relate and extend these ideas such that learners construct and reconstruct knowledge and ideas. It is not the knowledge or ideas, but the learner’s construction of the knowledge and ideas that is critical. Increases in student learning follows a reconceptualization as well as an acquisition of information” (Hattie, 2009, p.37) Importance of Clear Outcomes The Chim (Cheem) version ‘Would you tell me, please, which way I ought to go from here, said Alice?’ ‘That depends a good deal on where you want to get to, said the cat’ ‘I don’t much care where…’ said Alice ‘Then it doesn’t matter which way you go,’ said the cat. (Adapted from Alice in Wonderland, Lewis Carroll) “The ability to know what you want is the single most important skill in managing your life” (McDermott, 1998) Core Principle 2: Learning goals, objectives and proficiency expectations are clearly visible to learners Effect Sizes: Challenging Goals 0.56 (Hattie); Specifying Goals, 0.97 (Marzano) Learning design must incorporate: • Clearly communicating goals, objectives and performance standards through real world examples • Ensuring goals are challenging for the learner group (e.g., achievable with effort) • Explicit teaching of learning intentions and success criteria to ensure learners understanding of what they look like, sound like and feel like Core Principle 3: Learners prior knowledge is activated and connected to new learning • Effect sizes: Improving student engagement through opportunities to respond, 0.60; Self-verbalization/self-questioning, 0.64; Remediation Feedback, 0.65 • Prior knowledge is the lens through which students will perceive and react to new information provided in a learning event. • “All new knowledge gains its form and meaning through its connection with pre-existing knowledge and its influence on the organization and reorganization of prior knowledge” (Shulman 1991, p.10) • Ausubel (1978) went as far as arguing that: “If I had to reduce all of educational psychology to just one principle, I would say this: the most important single factor influencing learning is what the learner already knows. Ascertain this and teach him (sic) accordingly”(p.163) Core principle 4: Learning is enhanced through multiple methods and presentation modes that engage the range of senses Another Russian Doll principle as it runs across a range of method uses “…it is desirable to have multiple ways of teaching and there is no need to classify students into different ‘intelligences” (Hattie, 2012, p.91) “Learning is not a spectator sport. Students do not learn much just by sitting in class listening to teachers, memorizing pre-packaged assignments, and spitting out answers. They must talk about what they are learning, write about it, relate it to past experiences, apply it to their daily lives. They must make what they learn part of themselves” (Chickering & Gamson, 1987, p.3) Another bit of Educational Jurassic Park – finally put to bed • “One of the more fruitless pursuits is labelling students with ‘learning styles’. This modern fad for learning styles, not to be confused with the more worthwhile notion of multiple learning strategies, assumes that different students have differing preferences for particular ways of learning (Pashler, McDaniel, Rohrer, & Bjork, 2009; Riener & Willingham, 2010). • Often, the claim is that when teaching is aligned with the preferred or dominant learning style (for example, auditory, visual, tactile, or kinesthetic) then achievement is enhanced. While there can be many advantages by teaching content using many different methods (visual, spoken, movement), this must not be confused with thinking that students have differential strengths in thinking in these styles” (p89) Core Principal 5: Content is organized around key concepts and principles that are fundamental to understanding the structure of a subject Effect sizes: Direct instruction, 0.59; Concept mapping, 0.60; Advanced organizers, 0.46 Knowledge is increasing exponentially and we may be living in a rapidly changing volatile world – but our brains are the same as 10,000 years ago. Managing cognitive load is now becoming a so-called 21ist century skill. • Understanding involves making personal meaning – seeing relations between constructs and building new learning on old; moving from concrete to abstract – reliant on both acquiring knowledge bases and organizing them through good thinking Core Principle 6: Good thinking promotes the building of understanding Effect size: Metacognitive strategies; 0.69; Creativity programmes, 0.65: Questioning, 4.1; Teaching learning strategies, 0.62; Teaching learning strategies,0.63 “The best thing we can do, from the point of view of the brain and learning, is to teach our learners how to think” (Jenson, 1996, p.163) “Thought is the key to knowledge. Knowledge is discovered by thinking, analyzed by thinking, organized by thinking, transformed by thinking, assessed by thinking, and, most importantly, acquired by thinking” (Paul, 1993 vii) Thinking is the cognitive process that builds Understanding Metacognitive Strategies enhance learning capability • Metacognition refers to the awareness of, and ability to monitor and control, one’s cognitive and affective processing in order to enhance learning • Metacognition plays a central role in learning by helping to guide the learner’s cognitive processing of the to-be-learned material • Good metacognitive capability is the basis of becoming a self-regulated learner, which is a major goal of education • Explicitly teaching students to be more metacognitive in their problemsolving enhances their performance and success rates (e.g., Bransford, Hattie) Note: Learning strategies can involve physical tools such as mind-mapping, etc., but it’s the internal cognitive processes inside our heads – covert strategies – that really makes the difference in terms of quality of learning Core Principle 7: Learning Design utilizes the working of memory systems E N V Sensory Memory I Sight R Hearing O Touch N Smell M Taste E N T Working Memory Executive Organizing Function Limited Capacity 5-9 bits of information Forgetting Integrating – Conscious, Subconscious & Unconscious Long –Term Memory Infinite Capacity Another Russian Doll principle: Our Memory Systems are fundamental to all learning – how these are managed affects the rate and quality of learning Working Memory • While human brains have potentially unlimited storage capacity by means of long term memory, all new learning has to firstly pass through working memory, which has a limited capacity of around 7 ± 2 bits of information. This poses problems of Cognitive Load for learning , but as Clark & Lyons (2004) point out: “…it is in working memory that active mental work, including learning, takes place. Working memory is the site of conscious thought and processing” (p.48) Long Term Memory • Long term memory, once viewed as an inert dumping ground, is crucial for learning and the development of expertise. For example, Kircher et al (2006) point out: “...long term memory is now viewed as the central dominant structure of human cognition. Everything we see, hear and think about is critically dependent on and influenced by our long-term memory” (pp.3-4) • Research clearly shows that a major factor that differentiates experts from novices is that expert problem-solvers are able to draw on the vast knowledge bases in their long-term memory and quickly select the best approach and procedures for solving a given problem As Kircher et al allude: “We are skillful in an area because our long-term memory contains huge amounts of information concerning that area. That information permits us to quickly recognize the characteristics of a situation and indicates to us, often unconsciously, what to do and how to do it” (p.4) Minimize Forgetting through Review: Utilizing the working of WM & LTM Probability of recall 100% Recall without reviews Recall with reviews at intervals 10 minutes next day next day next week with continuous periodic reviews Some Pedagogic Implications of the working of memory Systems Lessons should: • be chunked into segments to avoid/reduce cognitive overload • Include activities to create cognitive engagement (Good Thinking) • build in review time on the Content (e.g., Key Concepts, Principles) - to ensure effective transfer from Working Memory to Long-term memory (Memory Systems). Seems like a Russian Doll Tasks involving thinking help to build better constructs (understanding of concepts) as students get more familiar with the material and start to chunk bits of it together themselves. However, encouraging to them to notice the constituent parts and their relations – Making Thinking Visible – is useful Memory is strengthened by repetition rather than total time, hence recall is crucial Chunked material, especially, when well established in LTM, takes less space in WM, enabling more space to concentrate on the thinking process rather than memorization Graphic Organisers and other visual representations (effect size 1.2 to 1.3) How Visual representations work: • Diagrams cannot contain all the details – so the learner is forced to isolate the key points and their relations – which imposes a structure on the information. This helps to see ‘the wood from the trees’ • Recall is almost always visually triggered; hence visual representation acts as a cue triggering the full memory • Only structured information can go in Long term memory, so this helps the transmission from WM to LTM and subsequent recall • Facilitates the Whole –Part –Whole strategy in helping to make connections (e.g., relating information) • Related information is quite high up in the SOLO taxonomy – hence fostering and building a deep understanding of the topic WPW Learning Model The basic WPW Learning Model can be depicted as follows: Whole Part Learning Segments Segment # 1 Segment # 2 Segment # 3 Segment # 4 Segment # 5 The ‘first whole’ creates an organizational framework for new content The supporting component elements - ‘parts’ - are then systematically developed The ‘second whole’ links these parts together to foster understanding SOLO Taxonomy: some Key Points SOLO models how learning develops and the qualitative aspects of this development. When we learn a new topic we start near the bottom of the taxonomy (however bright we are), and as our learning improves we climb the taxonomy, adding detail but also relations. SOLO can be used to specify acceptable or unacceptable levels of performance in suitable tasks and subject areas. Experts structure their understanding around principles rather than around topics “Expertise is not just knowing more. Experts structure or organise their knowledge around Deep subject principles, and understand the conditions when these principles apply. Their memory is indexed so that relevant knowledge can be retrieved. When solving a problem they look to see what conditions apply, and so retrieve all the information that is relevant to that task. They don’t need to search the whole of their permanent memory. That is, they can transfer their knowledge, which makes it fully ‘functional’” (Bransford, 2000, p.24) Hence the importance of teaching core principles that underpin the structure of a topic – this enables the learner to transfer their learning to entirely new contexts. SOLO: Structure of the Observed Learning Outcome Developmental Base with minimal age SOLO Description 1 Capacity 2 Relating Operation 3 Consistency & Closure Formal Operations (16+ years) Extended Abstract Maximal: cue + relevant data + Interrelations + hypotheses Deduction and induction. Can generalize to situations not experienced Inconsistencies resolved. No felt need to give closed decisions – conclusions held open, or qualified to allow Logically possible alternatives. Concrete Generalization (13-15 years) Relational High: cue + Relevant data + interrelations Induction. Can generalize within given or experienced context using related aspects No inconsistency within the given system, but since closure is unique so inconsistencies may occur when he goes outside the system Middle Concrete (10-12 years) Multistructural Medium: cue + Isolated relevant data Can “generalize” only in terms of a few limited and independent aspects. Often inconsistent and variable conclusions made Core Principle 8: The development of expertise requires deliberate practice Effect sizes: Spaced and mass practice, 0.71; Challenging goals, 0.52; Remediation feedback, 0.65; Mastery learning, 0.50 Deliberate Practice is characterized by several elements: • • – Activity specifically designed to improve performance, often with a teacher’s help – It can be repeated a lot (needs to be) – Feedback on results is continually available – Highly demanding mentally (whether a physical or mental task) – It isn’t much fun (in the main, but may be for some) Typically requires a teachers help – one who can see more objectively what needs to be improved and how Built around the principle of stretching the individual beyond existing performance level – relates to challenging but achievable goals (must be as clearly defined as possible) “If the activities that lead to greatness were easy and fun, then everybody would do them, and they would not distinguish the best from the rest” (Colvin, 2008, p.72) How Deliberate Practice Works • Great performers possess large, highly developed, intricate mental models of the domain, enabling them to: – – – Make sense of new knowledge more effectively and efficiently as they have vast stores of organized knowledge in LTM, Distinguish relevant information from irrelevant information Predict what will happen next in a domain specific situation • “The best performers observe themselves closely… monitor what is happening in their own minds, and ask how its going. Researchers call this metacognition …top performers do this more systematically than others do; it’s an established part of their routine” (p.118) • It enable great performers to perceive more, to know more and to remember more than most people. The effects go beyond that: – Many years of intensive deliberate practice changes the body and the brain – concept of neuroplasticity The impact of assessment in student learning • It is now clearly recognized that assessment is not simply a means to measure learning that has already occurred, but is a major facilitator in the learning process itself. As Boud (1988) illustrated: “There have been a number of notable studies over the years which have demonstrated that assessment methods and requirements probably have a greater influence on how and what students learn than any other single factor. This influence may well be of greater significance than the impact of teaching or learning materials” (p.35) Feedback is so important in the learning process • There is much of merit in the learning stakes for clear, concise and timely feedback: clarifying what good performance is (e.g. goals, criteria, standards) identifying gaps in performance and specific learning needs closing the gap between current and desired performance positive beliefs and self-esteem the development of self-assessment in learning appropriate modification of instructional strategies “…all students should be educated in ways that develop their capability to assess their own learning” (Hattie, 2012, p.141) Core Principle 9: Assessment is integrated into the learning design to provide quality feedback Effect sizes: Feedback between teachers and students, 0.75; Peer assessment, 0.63; Self-assessment, 0.54; Providing formative evaluation to teachers, 0.90 Assessment is not separate from the instructional process but an integral part of it. As Perkins (1992) suggests, once considered thoughtfully: “Teaching, learning, and assessment merge into one seamless enterprise” (p.176) Core principle 10: A Psychological Climate is created which is success orientated and fun • • Effect sizes: Teacher-student relationships, 0.72; Class environment, 0.56. Also, this is a Russian Doll, as it fosters the building of Rapport. “Rapport is the ultimate tool for getting results with other people” (Robbins, 2001, p.231) The importance of fostering the psychological climate has been fully documented by Jensen (1996): “Learners in positive, joyful environments are likely to experience better learning, memory and feelings of self-esteem” (p.98) Far from limiting the learning experience, humour is now seen to have many positive impacts, such as: • • • • • • Refreshing the brain Creating mental images that retain learning Reinforcing desired behaviour and makes classroom management easier Developing positive attitudes Promoting creativity Contributing to the enjoyment of teaching How to Build Good Rapport with students • Frederickson (1980) suggested that Positive Emotions, in addition to making people feel good and improving their subjective life experiences, have the potential to broaden people’s way of thinking and help them build physical, intellectual and social resources. There are many specific ways to promote this: – looking directly at students, showing empathic listening, good observation of what’s going on (sensory acuity), using smile when appropriate, supporting encouraging language and calibrated body language, etc. – Asking students questions about their interests, concerns with learning and acting on the information received over time – Having a sense of humour and encouraging it from students – seeing the ‘funny side’ in situations of adversity on occasions, but keeping them moving to productive outcomes – Praising effort and a ‘can do’ attitude, being up-beat about what’s going on in the classroom It is our behaviour that directly connects to results, even though our thinking may be responsible for generating the behaviour” (Molden, 2001, p.59) Core Principles – How they work While each principle focuses attention on a key area relating to effective pedagogy, they are mutually supporting, interdependent and potentially highly synergetic. As Stigler & Hiebert (1999) highlight: ‘‘Teaching is a system. It is not a loose mixture of individual features thrown together by the teacher. It works more like a machine, with the parts operating together and reinforcing one another, driving the vehicle forward’’ (p.75) Hatties (2009) summary of highly effective teachers fully captures this synergy in practice: “..it is teachers using particular teaching methods, teachers with high expectations for all students, and teachers who have created positive student-teacher relationships that are more likely to have the above average effects on student achievement” (p.126) Good pedagogy is always situated As Darling-Hammond & Bransford (2005) point out: “…teachers not only need to understand basic principles of learning but must also know how to use them judiciously to meet diverse learning goals in contexts where students differ in their needs” (p.78) Bruner (2006) captures this most fully, when he asserts that: “The challenge is always to situate our knowledge in the living context that poses the “presenting problem” …And that living context, where education is concerned, is the schoolroom – the schoolroom situated in the broader culture” (p.160) Which is why Bransford (1999) is so right when he points out: “Asking which teaching method/technique is best is analogous to asking what tool is best – a hammer, a screwdriver, a knife, or pliers. In teaching, as in carpentry, the selection of tools depends on the task at hand and the materials one is working with” (p.22) Using Core Principles Thoughtfully - The Fly Fishing Analogy Key situated factors involve: The specific learning outcomes (e.g., recall of facts, conceptual understanding, competence) Learner characteristics (e.g., maturation, motivational level, prior competence) Learning context and resource availability (e.g., learning environment, facilities, resources) A frame on Teaching Expertise Note: this is a Conceptual Model, not hierarchical in that one stage must be achieved before the next. It is essentially Iterative However, Competent and Creative teachers employ a strong pedagogic literacy - whether Explicit or Tacit) Creative Teaching (Adaptive Expertise) Ability to situationally create highly effective pedagogy Competent Teaching Ability to design and facilitate learning experiences based on a sound pedagogic literacy Pedagogic Literacy Understanding key knowledge bases relating to how humans learn Professional Development in developing Teacher quality “We know a good deal about the characteristics of successful professional development: it focuses on concrete classroom applications of general ideas; it exposes teachers to actual practice rather than descriptions of practice; it offers opportunity for observation, critique and reflection; it provides opportunity for group support and collaboration; and it involves deliberate evaluation and feedback by skilled practitioners with expertise about good thinking” (Elmore and Burney, 1999, p.263) Professional development – A complimentary frame Darling-Hammond & Bransford (2005) who summarize that: “Emerging evidence suggests that teachers benefit from participating in the culture of teaching – by working with the materials and tools of teaching practice; examining teaching plans and student learning while immersed in theory about learning, development and subject matter. They also benefit from participating in practice as they observe teaching, work closely with experienced teachers, and work with students to use what they are learning” (Darling-Hammond & Bransford , 2005, p.404) Supported Experiments • Identify tough topics or concepts that student find hard or boring to learn • Develop an instructional strategy that employs the methods that work best and customize them to the situated context ( e.g., learning outcomes, student characteristics, resource availability), based on your professional judgement (collaboration with colleagues helps) • Conduct the lessons and get feedback on the influence of learning (e.g., students feedback, performance on assessment tasks, peer observation) • Review the evidence and make modifications • Practice the methods in a relatively short period of time, making improvements and refining practice (has similarity with Lesson Study) • Embed the success in Active Schemes of Work that are shared and subsequently used for professional development and continual improvement (From the work of Geoff Petty)