Depressants (D.4)
advertisement

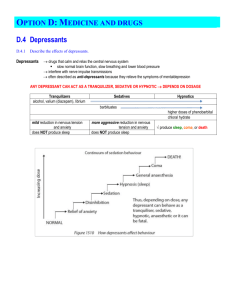
D.4.1 Describe the effects of depressants. Depressants? • Drugs which depress the CNS. • Interfere with transmission of nerve impulses in the neurones. • Slow down bodily functions including mental activity. • Most commonly taken depressant is alcohol • (H3C-CH2-OH) • Sometimes called anti-depressants. • Relieve symptoms of mental depression. D.4.1 Describe the effects of depressants. Effects? 0 Low Doses: 0 Little, or no effect. 0 Moderate Doses: 0 Feeling of calm, relieve anxiety. 0 Large Doses: 0 Induce sleep. 0 Extremely high Doses: 0 Death. D.4.2 Discuss the Social and Physiological effects of the use and abuse of ethanol. Alcohol? 0 In Medicine: 0 Alcohol used as antiseptic before injections and to harden skin. 0 Drinking: 0 Psychological and physical dependence; alcoholism. 0 Huge social costs due to: 0 Road accidents, violent behaviour , family breakdowns. D.4.2 Discuss the Social and Physiological effects of the use and abuse of ethanol. Short Term Effects. 0 Moderate quantities: 0 Feeling of relaxation, confidence, increased sociability. 0 Dilates small blood vessels. 0 Flushing and feeling of warmth. 0 Judgement, concentration, progressively impaired. 0 Violent behaviour. 0 Slurred speech, loss of balance. 0 High quantities: 0 Loss of consciousness. 0 Risk of death from inhalation of vomit or stoppage of breathing. D.4.2 Discuss the Social and Physiological effects of the use and abuse of ethanol. Long Term Effects. 0 Heavy Drinking: 0 Severe liver disease. 0 Cirrhosis, liver cancer. 0 Linked with coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, strokes, increasing risk of dementia. 0 Can cause miscarriage and foetal abnormalities during pregnancy. 0 Sudden discontinuation by heavy users can cause delirium tremens (the ‘DTs’). 0 Severe shaking, can last up to four days. D.4.3 Describe and explain the techniques used for the detection of ethanol in the breath, the blood and urine. Breathalyzer & Chromatography 0 Breathalyzer: 0 Acidified potassium or sodium dichromate(VI) crystals turn green as they are reduced by alcohol to Cr3+. 0 Chromatography: 0 Blood or urine sample using gas liquid chromatography D.4.3 Describe and explain the techniques used for the detection of ethanol in the breath, the blood and urine. 0 Absorption of infrared radiation: 0 C-H bonds in ethanol absorbs infrared radiation of a particular wavelength D.4.4 Describe the synergistic effects of ethanol with other drugs. 0 Alcohol enhances the effect of other drugs because it depresses the CNS (Synergistic effect) 0 Fatal. 0 Alcohol taken with Aspirin increases the risk of stomach bleeding D.4.5 Identify other commonly used depressants and describe their structures. Other Depressants 0 Commonly prescribed to: 0 Reduce anxiety, relieve stress, help insomnia. 0 These include the benzodiazepines and Prozac. 0 Usually only prescribed for limited period while counselling or psychotherapy are used, as these an induce dependence. 0 Also used as a premedication in hospitals before general surgery. D.4.5 Identify other commonly used depressants and describe their structures. Structures. Diazepam (Valium) Nitrazapam (Mogadon) Fluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac)