Who is eligible for services? - CAHF
advertisement

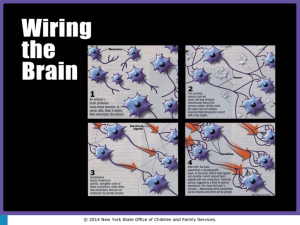
Developmental Disabilities The Regional Center History The Lanterman Act 1969 Developed by parents and requires localized community service systems for persons having a developmental disability in California. • Non-profit private corporations • 5 year performance contracts with the State • State and Federally funded & regulated • 21 Regional Centers statewide • Over 225,000 active cases statewide INLAND REGIONAL CENTER serves both San Bernardino and Riverside counties. It is the largest of all 21 regional centers in California and currently serves over 23,000 persons of all ages. IRC has over 550 Consumer Service Coordinators (CSCs) with each having caseloads of 62+ persons. Consumers are seen Quarterly at a minimum at their home, day program, and/or school. Each has an Annual Review and Individual Program Plan (IPP) developed annually with goals and objectives that are determined by the consumer with the Planning Team. Information about Programs & Services The California State Department of Developmental Services is responsible for coordinating services for California residents with developmental disabilities. Local Regional Centers ensure local community access to services and supports. A “Person-Centered Planning” approach is used in making decisions regarding where a person with developmental disabilities will live and the kinds of supports that may be needed. Everyone has a Planning Team that includes the person utilizing the services, family members, regional center staff, and anyone else who is asked to be there by the individual. The team works together to make sure that the services that people are getting support their choices in where they want to live, how and with whom they choose to spend the day, and hopes and dreams for the future. Services Provided by Regional Centers Regional Centers provide diagnosis and assessment of eligibility. They help plan, access, coordinate and monitor the services and supports that are needed because of a developmental disability. There is no charge for the diagnosis and eligibility assessment. Once eligibility is determined, a service coordinator is assigned to help develop a plan for services, tell you where services are available, and help you get the services. Most services and supports are free regardless of age or income. Parents are required to “share the cost” of 24-hour out-of-home placements for children under age 18. This share depends on the parents' ability to pay. Open cases can be inactivated and re-activated by consumers or their families as needs change throughout the life span. Regional Center services are voluntary. Some of the Supports provided by the Regional Centers include: •Information and referral •Assessment and diagnosis •Lifelong individualized planning and service coordination •Purchase of necessary services included in the Individual Program Plan •Resource development •Outreach •Assistance in finding and using community and other resources •Advocacy for the protection of legal, civil, and service rights •Early Intervention services for at-risk infants and their families •Genetic counseling •Family support •Planning, placement, and monitoring for 24-hour out-of-home care •Training and educational opportunities for individuals and families •Community education about developmental disabilities Supportive services and living arrangements available for persons with developmental disabilities include: •Day Program Services •Education Services •Work Services Programs •Supported Employment •Work Activity Programs •Supported Living Services •Affordable Housing •Family Home Agency •Foster Family Agency •Independent Living •In-Home Supportive Services •Respite Services •Transportation Services •Community Care Facilities (CCFs) •Intermediate Care Facilities (ICFs) Who is eligible for services? To be eligible for services, a person must have a disability that begins before the person's 18th birthday, be expected to continue indefinitely and present a substantial disability (Section 4512 Calif. W & I Code.) Infants and toddlers (age 0 to 36 months) who are at-risk of having developmental disabilities or who have a developmental delay may also qualify for services. (Section 95014 of the Calif. Gov.Code.) In addition, individuals at-risk of having a child with a developmental disability may be eligible for genetic diagnosis, counseling and other prevention services. Eligibility is established through diagnosis and assessment performed by Regional Centers. Persons must reside in California. The 5 Categories of Eligibility Mental Retardation is characterized by significant limitations both in intellectual functioning (i.e., an IQ of approximately 70 or below) and in adaptive behavior as expressed in conceptual, social, and practical adaptive skills. Levels of retardation are reported as mild, moderate, severe, profound, no MR (i.e., mental retardation is not present), or unknown. Epilepsy is defined as recurrent, unprovoked seizures. Seizures can cause loss of muscle control, tremors, loss of consciousness, and other symptoms. These include petit mal (absence seizures) and grand mal seizures of various types. If a person is seizure free for several years with or without medication, eligibility for Regional Center services may be reviewed. Cerebral Palsy includes two types of motor dysfunction: (1) Non-progressive lesion or disorder in the brain occurring during intrauterine life or the perinatal period; and is characterized by paralysis, spasticity, or abnormal control of movement or posture which is manifest prior to two or three years of age, (2) other significant motor dysfunction appearing prior to age 18. Cerebral Palsy refers to a group of disorders that affect a person's ability to move and to maintain balance and posture. It is due to a non-progressive brain abnormality, which means that it does not get worse over time, though the exact symptoms can change over a person's lifetime. People with cerebral palsy have damage to the part of the brain that controls muscle tone. Muscle tone is the amount of resistance to movement in a muscle. It is what lets you keep your body in a certain posture or position. Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder with multiple causes. Autism is defined as a syndrome causing gross and sustained impairment in social interaction and communication with restricted and stereotyped patterns of behavior, interests, and activities that appear prior to the age of three. The number of people reported with Autism include both the diagnosis of Autism-Full Syndrome and the diagnosis of AutismResidual State or Spectrum Disorder. Autism is one of the most investigated yet puzzling diagnosis. Fifth category for eligibility: Other developmental disabilities similar to mental retardation that require treatment (care and management) similar to that required by individuals with mental retardation. These must occur before age 18 years, be a substantial handicap, be expected to continue indefinitely, and involve brain damage or dysfunction. These do not include conditions that are solely psychiatric or physical in nature. (Examples - Schizophrenia, Alzheimers, Spina Bifida, Prader Willi Syndrome, etc.) Trends of 4 major categories of Developmental Disabilities diagnosed in California Exceptions to birth or Early Start diagnosis for eligibility for services: Traumatic Brain Injuries (auto, bicycle, motorcycle accidents, falls, injuries), near drowning, and other incidents/illnesses can cause a child or adult with normal development to contract cerebral palsy, seizures, mental retardation, or a similar condition. Some conditions benefit from rehabilitation efforts – some do not. If this occurs before age 18, they would be eligible for RC services. Combinations of Eligible Disabilities Demographics of Regional Center clients in California AGES Definitions of Residence Types Own Home-Family: Home of a family member or guardian. Community Care: Settings such as a Community Care Facilities (CCF) Foster Homes for Children, and Family Homes for Adults (FHA) ILS/SLS: Independent Living Setting (ILS) or Supported Living Setting (SLS) SNF/ICF: Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) or Intermediate Care Facility (ICF). ICF includes ICF/Developmentally Disabled (ICF/DD), ICF/Developmentally Disabled-Habilitation (ICF/DD-H), and ICF/Developmentally Disabled-Nursing (ICF/DD-N) Developmental Center: State Developmental Center (SDC) operated by DDS Other: Settings such as hospitals, community treatment facilities, rehabilitation centers, psychiatric treatment centers, correctional institutions, and other settings in the community. TYPE OF RESIDENCE What do the Regional Centers spend funds on? “QUESTIONS?” Meet some IRC consumers… Inland Regional Center 1365 South Waterman San Bernardino, CA 92408 (909) 890-3000