Chemicals and autism
advertisement

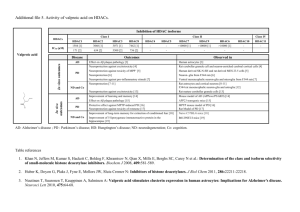
Can chemicals cause autism? Michael Li Anne Lor Richard Li Brian Tang 1001201772 998970920 1001980421 998951282 What is Autism Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder that results in: ● Deficit in social skills from infancy ● lack of communicative ability ● Repetitive interests Autism is a biological genetic disorder: ● Monozygotic twins share 90% concordance ● Dizygotic twins share 10% concordance Autism Neuropathology The brains of autistic individuals develop abnormally. ● Overdevelopment of regions of the brain responsible for social behavior o Frontal Cortex o Temporal Cortex o Amygdala ● Abnormalities in the white matter of an autistic brain o Increased amounts of short-range connections Savants o Decreased amounts of long-range connections Causes of Autism ● No concrete evidence linking a chemical agent to autism. ● Some possible environmental chemical causative agents include: o Lead o Mercury o Valproic Acid o Paracetamol Valproic Acid ● anticonvulsant ● treat seizures, prevent migraine headaches, and the treatment of epilepsy Studies of Valproic Acid and ASD ● Fetal Valproate Syndrome ● Linked to increased risk of ASD ● 11 year study on cognitive development of children born to mothers with epilepsy Rodent Model ● Mice were injected with valproic acid ● In utero exposure of VPA resulted in physical malformations ○ also showed signs of ASD Epigenetics in ASD? ● VPA can inhibit histone deacetylases ● genetic material: ○ negatively-charged DNA ○ positively-charged histones ● access to genes decreases with increasing strength of DNA/histone interactions ● acetylation removes positive charge from histones ○ DNA/histone interactions broken, leading to increased gene expression ● deacetylation reintroduces positive charge ○ DNA/histone interactions restored, leading to decreased gene expression A Possible Mechanism ● VPA prevents deacetylation → increased gene expression ● ASD caused by brain tissue overgrowth in areas controlling social/emotional functioning(?) ● increased gene expression leads to increased growth of neural tissue(?) Other Possible Chemical Agents Paracetamol (acetaminophen) ● Study found that children who had pre-natal exposure to paracetamol for more than 28 days had neurodevelopmental outcomes ● Suggested correlation between prenatal paracetamol use and autism prevalence ● However, no definitive evidence to suggest correlation = causation Other Possible Chemical Agents Lead ● Autistic children tend to have significantly higher lead blood levels in comparison to children who do not have autism ● Suggests that lead is a possible causative agent for autism, but no definitive evidence yet ● Again, no evidence to suggest correlation = causation Summary Slide ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ASD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that impairs communicative ability Individuals with autism show abnormal brain development characterized by the overdevelopment of the frontal cortex, temporal cortex and amygdala. Studies conducted of children exposed to valproic acid prenatally showed a higher risk of neurodevelopmental disorders Rodent model is used to further investigate the link between prenatal valproic acid exposure and ASD Valproic acid inhibits histone deacetylation, thus leading to increased gene expression and tissue overgrowth in areas of the brain involved in emotional and social functioning Correlation between pre-natal paracetamol use and prevalence of autism exists. However, there is a lack of evidence to suggest that paracetamol causes autism. Autistic children tend to have higher lead blood levels than healthy children. Although a correlation exists, no mechanism is established on how lead may cause autism. References American Psychiatric Association (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association V. Bambini-Junior, L. Rodrigues, G.A. Behr, J.C. Moreira, R. Riesgo, C. Gottfried Animal model of autism induced by prenatal exposure to valproate: Brain Res., 1408 (2011), pp. 8–16 behavioral changes and liver parameters Takuma, K., Ago, Y., Matsuda, T., Hashimoto, H., Hayata-Takano, A., Takano, E., et al. (2014). Chronic treatment with valproic acid or sodium butyrate attenuates novel object recognition deficits and hippocampal dendritic spine loss in a mouse model of autism. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 126C, 1-43. Chomiak T, Turner N, Hu B. 2013. What we have learned about autism spectrum disorder from valproic acid. Pathology Research International, 2013: 712758. Brandlistuen, RE., Ystrom, E., Nulman, I., Koren, G., and Nordeng, H. 2013. Prenatal paracetamol exposure and child neurodevelopment: a sibling-controlled cohort study. Int J Epidemiol. 42(6):1702. El-Ansary AK., Bacha, AB., and Ayahdi, LY. 2011. Relationship between chronic lead toxicity and plasma neurotransmitters in autistic patients from Saudi Arabia. Clin Biochem. 44(13): 1116-1120.