HEALTH ISSUES FACING
AUSTRALIA’S YOUTH
Year 11 H&HD
Unit 1/ AOS 3
KEY KNOWLEDGE
–
–
–
–
–
Health issues facing Australia’s youth
The key features of one health issue for Australia’s
youth, including:
Its impact on all dimensions of health and
development
The incidence, prevalence and changes over time
(trends) of the selected issue
Determinants of health that act as risk and/or
protective factors
Government, community and personal strategies or
program designed to promote health and development
of youth
Rights and responsibilities of youth in accessing and
using relevant services.
ASSESSMENT
Your SAC for this Area of Study will be in the
form of an oral presentation.
You will focus on 1 health issue of particular
interest to you and present to the class.
So.. You will need to learn all content as usual,
but pay specific attention in research to the topic
you like most! 3 periods of research
DIABETES MELLITUS
a chronic condition in which the sufferer is
unable to utilize the blood glucose correctly.
Different types include: Type 1, Type 2 and
Gestational diabetes.
What do you think the difference is between Type
1 and Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 1- insulin dependent
Type 2- Non-insulin dependent (often referred to
as ‘Lifestyle’ type).
If you choose Diabetes to focus on- it will be easier
to link the determinants of health to Type 2
diabetes!
Go to page 128 and write a summary of diabetes
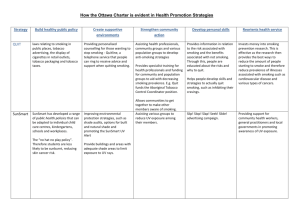
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
Diabetes Australia
http://www.diabetesaustralia.com.au/About-DiabetesAustralia/What-Diabetes-Australia-Does/RaisingAwareness/
International Diabetes Federation
http://www.idf.org/
http://www.diabetesatlas.org/
Complete Q1&2 Case study review, p129.
Q1 and 6, p130.
ASTHMA
A chronic condition characterised by the
narrowing of the air passages, leads to a
difficulty in breathing.
Contributes highly to the burden of disease in
Australia, through the years lived with a
disability (YLD).
Australia has the highest asthma rate in the
world.
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
Asthma cycle of care program
http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/c
ontent/asthma-cycle
Asthma friendly schools program
http://asthmafriendlyschools.org.au/home/index.php
The sensitive choice program.
http://www.sensitivechoice.com.au/
Asthma Australia
http://www.asthmaaustralia.org.au/partners/australian
_government.php
ASTHMA POSTCARD ACTIVITY
Design a postcard that could be given to students
at LSC that addresses one of the issues caused by
Asthma and the impact of this on health and
development.
Include a slogan and make sure your asthma
health promotion postcard is relevant to the
target market your message is for.
WEIGHT ISSUES
Being overweight is not the only health concern
regarding body weight that can affect youth.
People can be underweight or overweight and
often obese.
OBESITY
Having a BMI of 30+ or a waist measurement of
more than 89 cms for women and 102 cms in
men.
UNDERWEIGHT
Eating disorders are most commonly experienced by
adolescent females. However males also account for
eating disorder figures.
Anorexia Nervosa
http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Anorexianervosa/Pages/Lynsey-and-Helen-stories.aspx
http://www.cbsnews.com/video/watch/?id=5285479n
http://www.5min.com/Video/How-Cori-Lives-withAnorexia-Nervosa-287355456
Bulimia Nervosa
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hBvPQ9WKCe0
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
Go for your life
Measure up
www.health.gov.au/internet/healthyactive/publis
hing.nsf/content/publications
www.makeanoise.ysp.org.au
www.eatingdisorders.org.au
www.butterflyfoundation.org.au
TOBACCO SMOKING
Single most preventable cause of ill health and
death in Australia.
If an individual is to start smoking, they are most
likely to do so during youth, despite being illegal
until the age of 18 years of age.
Increases the chance of premature death and
cancer, CVD and respiratory illness.
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
www.quit.org.au
ALCOHOL USE
Binge drinking is common in youth and can lead
to severe health issues.
Read the DHA recommendations- p131
Youth who consume excessive alcohol place
themselves at more risk of injury (falls, assault,
road crashes and violence) and unprotected sex.
BINGE DRINKING
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BYwuMPPwrU
'Everybody hurts when you speed' - Three minute
montage - TAC campaign - The Ripple Effect
http://www.youtube.com/user/TACVictoria?v=Al25
O1MW8dM&feature=pyv&ad=5479360161&kw=
tac%20commercial&gclid=CKCzvKDg3qgCFQH1
bwodTWP6yg
Smashed clip
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pJM1MKD8glo
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
www.alcohol.gov.au
Case study review Q1-3, p134.
Q4 &5, p135.
ILLICIT DRUG USE
Tied to a range of health issues including social
isolation, mental illness and family breakdown.
The most commonly reported illicit drugs used by
young people are: marijuana, ecstacy, painkillers,
hallucinogens, tranquillisers, inhalants, and
cocaine.
AGE ARTICLE
http://www.criticaltimes.com.au/features/this-druglives-up-to-our-worst-nightmare/
1.
2.
3.
4.
Read the article an complete the following Q’s:
Explain the short term side effects of using ice.
Explain how the long term use of ice (or other
drugs) can impact on the health and development of
youth.
Explain why so many Australians are using this
drug.
Identify steps that you feel parents and the
community can take to address the number of youth
using Ice.
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
www.druginfo.adf.org.au
www.cyds.adf.org.au
www.quit.org.au
SUN PROTECTION
Australia has one of the highest rates of skin
cancer.
Youth are the most informed group on dangers of
skin cancer, BUT also the least likely to protect
themselves!!
CLARE OLIVER
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_KmHEJXYZr
Q
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
www.cancervic.org.au
www.skincancer.gov.au
www.sunsmart.com.au- slip, slop, slap, seek
slide!
New regulations for Solariums.
Case Study: True Price of a sun tan pg. 137 Q1-8
SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
Sexual Health: the capacity to enjoy and manage
sexual and reproductive behaviour in accordance with
a social and personal ethic.
Reproductive Health: state of complete physical,
mental and social wellbeing and not merely the
absence of disease or infirmity, in all matters relating
to the reproductive system and to its functions and
processes.
Individuals have the right to be informed and have
access to safe,effective,affordable and acceptable
methods of healthcare and family planning.
Teenage pregnancy
STIs
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JkaBKJcN_Hg
.
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
www.fpv.org.au National STI Strategy 20052008
www.sexlife.net.au
Case study-Youth chlamydia rate on the rise
review Q’s 1&2, p140.
MENTAL HEALTH
Capacity of an
individual to
experience regular
mental functioning, in
terms of being able to
cope with change and
adversity as well as
establishing and
maintaining
meaningful
relationships.
MENTAL ILLNESS
Mental
Health Problem V’s Mental Illness
When the difficulties experienced by a person are
mild, temporary and able to be treated within a short
period of time.
Difficulties experienced by a person are more serious,
persistent and require a long-term treatment plan.
“A psychological dysfunction experienced by an
individual and usually involving distress, impairment
in the ability to cope with everyday life, and thoughts,
feelings and/or behaviour that are not typical of the
person or appropriate within society or specific
culture” (Grivas etal, 2005, p289).
MENTAL ILLNESS
Anxiety
Eating Disorders
Attention-Deficit Disorders
Learning Disorders
Schizophrenia
Depression
Often involve substance abuse.
Most illnesses generally lead to or are a part of
depression in some form- hence the risk of suicide
to youth!
ANXIETY DISORDERS
“chronic feelings of tension, distress, nervousness
and apprehension or fear about the future, with a
negative effect”.
MOST common mental disorders!
Interferes with the individual’s ability to function
in everyday life.
Generalized anxiety disorder, Panic Disorder,
Phobias, OCD and Post-traumatic stress
disorder.
P142-143
Read through the above as a class.
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
www.beyondblue.org.au
www.butterflyfoundation.org.au
www.headroom.net.au
www2.youthbeyondblue.com
SANE http://www.sane.org/information/videoshowroom
If you select mental health, the textbook has a
large section of information available to add to
your research.
FOOD ALLERGIES
An abnormal immune response to a specific part
of a food.
Can be fatal.
A sudden or severe allergic reaction is know as
anaphylaxis and requires urgent medical
attention. Sufferers carry an epipen incase of an
attack.
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
http://www.allergyfacts.org.au Anaphylaxis
management in schools
Q6, p144.
Case study review Q1-3, p146.
HOMELESSNESS
There are many factors that may lead to youth
becoming homeless.
List 3 reasons that you can think of.
Homeless youth are more likely to experience
poor mental health, barriers to education,
reduced employment opportunities,
discrimination and social exclusion.
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
www.reachout.com.au
www.youthoffthestreets.com.au
CYBER-SAFETY
Cyber-bullying has been reported as one of the
most serious concerns for youth in schools today.
People who are bullied often suffer low self
esteem and high school absenteeism and much
worse.
CYBER BULLYING - FOR MY YEAR 9
ENGLISH ENGLISH CLASS
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2RwhmTaAI6o
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
www.netalert.gov.au
www.cybersmartkids.com.au
INJURIES
Traffic accidents
Suicide
Poisonings
The injury that you are best to focus on if you
select is based on Traffic Accidents.
GOVERNMENT, COMMUNITY AND
PERSONAL PROGRAMS OR STRATEGIES.
www.arrivealive.com.au
www.youthsafe.org.au
www.kidshelpline.com.au
Key skills Exam Practice Question, p154.
PERSONAL STRATEGIES
There are a number of strategies that a young
person can undertake to help promote their
health and development including:
Understanding health issues affecting youth
enabling informed decision making and health
empowerment
Gaining knowledge on health, health issues and
how to maintain good health
Taking responsibility for one’s own actions and
health behaviours.
Reducing risk factors and not participating in
risk-taking behaviours, such as being pressured
to participate in risk-taking behaviours, for
example binge-drinking.
Having the resilience to say no when subjected to
peer group pressure situations
Choosing friends who have the same attitudes
and values as you.
Becoming involved in activities that have a
positive influence on health, such as sporting
teams, dancing groups or Scouts
Knowing your rights and responsibilities
RIGHTS AND RESPONSIBILITIES FOR ACCESSING
AND USING RELEVANT HEALTH SERVICES.
RIGHTS:
Safety
Dignity
Privacy
The satisfaction of basic
needs
Choice
To be heard
To be informed
Refuse treatment
Access
Health care
High quality healthcare
confidentiality
RESPONSIBILITIES
Provide accurate as well as
complete information.
Ask questions and discuss
concerns.