Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems PPT
advertisement

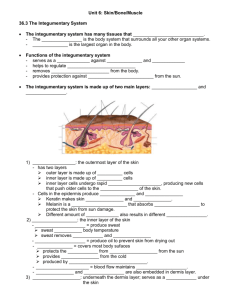
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Ch. 36 Skeletal System -The skeletal system has 206 living bones in the average human body. Function: -supports the body -protects internal organs -provides for movement -stores mineral reserves -blood cell production -Bones are made up of the elements phosphorus and calcium. Two Divisions of the Skeletal System: 1. Axial- skull, vertebral column, and rib cage 2. Appendicular- bones of the arms, legs, pelvis, and shoulder Bone Structure Periosteum- outer layer Compact Bone- thick solid layer Haversian Canals- tubes that contain blood vessels and nerves. Spongy Bone- found at the tips of long bones; porous; contains red bone marrow. Bone Marrow- center core of bones; contains yellow bone marrow. Growth Plate- area of dividing bone cells in kids and young adults. Cartilage- connective tissue found at the tips of bones; layer of protection. Bone Development -Human embryos are made of cartilage. -Cartilage hardens to bone as the ‘birth’ date gets closer. Process is ossification. -Some areas of cartilage stay intact throughout the life of a human. Types of Bone Cells: Osteocytes- mature bone cells. Osteoclasts- break down old bone cells. Osteoblasts- produce new bone cells. *Your body continually breaks down old bone cells and replaces them with new bone cells. Types of Joints: Joint- a place where one bone attaches to another bone. Types: 1. Immovable (suture, bones in the skull) 2. Slightly Movable (symphysis, bones of the vertebrae) 3. Freely Movable (ball-and-socket, hinge, pivot, saddle) Joints are held together by ligaments. Skeletal System Disorders: Inflammation of a Joint Arthritis Osteoporosis Ch. 36.2 Muscular System Function: movement throughout the body. Types: 1. Skeletal- moves the bones; voluntary. 2. Smooth- lines internal organs structures in the body; involuntary. Examples: lining of the stomach 3. Cardiac- found in the heart; involuntary. Allows for contraction of the heart. Muscle Contraction Muscle Fibers (cells) Myofibrils Filaments Actin & Myosin Actin and Myosin are proteins that are the basis for all muscle contraction. Muscle contraction occurs when ATP (energy) causes the actin to slide over the myosin. Muscle Contraction Clip Diagram of Actin & Myosin Filaments Neuromuscular Junction -Point where neurons make contact with a muscle cell. -Neurons release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine which stimulates the release of Ca2+ within the muscle fiber. The Muscle Bone Connection Skeletal Muscles are connected to bones by tendons. Ch. 36.3 The Integumentary System Functions: 1. barrier for protection against infection and injury. 2. regulate body temperature 3. remove waste products 4. provide protection against UV light (sun) Layers: 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Hypodermis Epidermis -outer most layer of the epidermis is made up of dead skin cells. -inner layer of the epidermis is made up of living cells. -contains the protein, keratin. Gives skin its waterproof ability. -contains the protein, melanin. Gives skin its color and protects from UV light. Dermis -inner (middle) layer of the skin. -contains collagen, blood vessels, nerves, glands, muscles, and hair follicles. -Two major glands: 1. sweat- helps cool the body 2. sebaceous (oil)- secrete sebum Hypodermis -contains adipose (fat) -functions to insulate and store nutrients Hair -made up of keratin -protects the body and internal structures -made in hair follicles -oil glands secrete oil to protect the hair Nails -made up of keratin -nails grow from the nail root -protects the tips of fingers and toes