(3) Mangione CTSI_K_Award 201402_13
advertisement

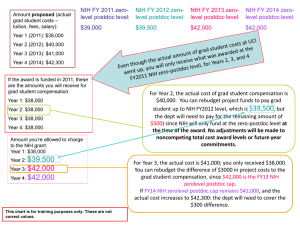
Navigating the K Award Process CTSI K Award Workshop February 13, 2014 Carol M. Mangione, MD, MSPH Professor of Medicine and Public Health Career Development Awards (K Awards) for Individuals with a Health-Professional Doctorate Types of CDAs • K01: To qualify, you need to be a clinician or Ph.D. in the fields of epidemiology and outcomes research and must have accomplished independent research experience after earning your degree. • K08: You are seeking salary and research support for full time supervised career development in health related research that does not involve patients. • K12/KL2: Provides support to an institution for the development of independent scientists. Most, but not all K12 s focus on the careers of physician scientists (required element in CTSA). Types of CDAs • K23: You have completed specialty training and are seeking salary and research support for full time supervised career development in patient oriented research • K99/R00: Purpose is to provide an opportunity for scientists to receive both a 1 to 2 year “mentored” K (phase 1) and a 3 year independent “R” (phase 2) in the same award. To qualify, you must have a clinical or research doctorate and no more than five years of postdoctoral research training at the time of application. • See the K award wizard to help you select the correct mechanism: • http://grants.nih.gov/trainingcareerdevelopmentawards. htm • Diversity Supplements: After administrative review these are added onto a funded grant, with extra resources for the trainee to develop and conduct mentored research Timing: When to Apply to NIH Timing: When to Apply Time Commitment and Salary Caps • Time Commitment: • 75% full time effort (50% for surgeons in some specialties) • Salary Cap increased to: • 95K for K08 and K23 and 105K for K02 (May 18, 2012, NOT-NS-12-018) • There is variability and exceptions at the Institute level, check the website for your institute Support from Other Awards: NOT-NS-09-015 • “Within the first 3 years of a mentored K award, those who obtain an R01 or federal equivalent, may obtain up to 80% of their institutional base salary, as long as the R01 represents an expansion of the K award project” • “A minimum of 75% effort must still be devoted to the K award during the first 3 years of support.” • “During the final two years of the K, additional salary may be obtained from the awarded R01, or from another R01, for effort exceeding the 80% level. If appropriate or desired, the level of effort on the mentored K award may be reduced to a minimum of 50% during the last two years of the award.” • If you have R01 support during the final 2 years of the K…In accordance with present NIH policy, additional salary support may also be obtained from the R01 or federal equivalent Additional Salary Support while on a CDA • During the last two years of a mentored career development award (K01, K08, K22, K23, K25), NIH will permit you to receive concurrent salary support from any peer-reviewed grant from any federal agency, if you meet the following criteria: – You are a PI on a competing research project grant, or director of a sub-project on a multi-component grant, from NIH or another Federal agency. – Your K award is active. – Under those circumstances, you may reduce your K award's time and effort to 50% person months. NIH Policy Concerning: Leave, Temporary Adjustments to % Effort, and Part-Time Appointments • See NOT-OD-09-036 • Developed to accommodate personal or family situations such as parental leave, child care, elder care, medical conditions, or a disability. • Will not be approved to accommodate job opportunities, clinical practice, clinical training, or joint appointments More on Part Time Status… • Must submit a written request to the NIH awarding institute requesting a reduction in effort to less than 75% for up to 12 continuous months • Will be considered on a case-by-case basis • In no case will it be permissible to work at less than 50% effort (equivalent to 6 person-months) • At the time of application and initial award, must meet the full-time appointment requirement as well as the minimum 75% effort requirement • Must commit at least 75% effort (of the part-time appointment) to research and career development activities. Governmental Alphabet Soup • NIH - National Institutes of Health • AHRQ - Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality • PCORI – Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute • RFA - Request for application • RFP - Request for proposals • PA - Program announcement Approach of the NIH U.S. Government Congressional Appropriation NIH funds allocated to each institute Investigator Initiated RO-1 K awards NRSA Institute Initiated RFP - contracts RFA - grants Organization of the NIH • Establish relationships with the program officers at the institutes in your research area • Each Institute handles career development funds in slightly different ways – Review their websites • 2 parts: – Program- Includes the Institutes that set the research priorities – Review - CSR or Center for Scientific Review • Evaluates the scientific merits of the proposals • http://www.csr.nih.gov NIH Review Process • • • • Takes about 9-10 months at best Initial Administrative review Importance of the title and “steering the proposal” Peer Review - Study sections made up of scientists from universities and other institutions • Most applications are not funded on the first round • For detailed information on success rates: http://report.nih.gov/success_rates/index.aspx • You can resubmit one time within 37 months of the original submission NIH Review Process • Final decision by Council -- where the previous contact with administrators can matter! • If successful, final administrative procedures to set up the budget Mentored K Awards: Review Candidate Mentor Career Development Plan Research Plan Institutional Environment Mentored K Awards: Review Candidate Prior Research Experiences • Potential for conducting research. • Evidence of originality Publications (first-author); productivity Likelihood of research independence Justification of need for additional research mentoring Letters of Reference Mentored K Awards: Review Mentor Track record in mentoring Appropriate scientific expertise Research funding and publications Commitment to mentoring candidate (letter of support) Mentored K Awards: Review Institutional Environment Necessary resources for proposed research and career development Interactions with other investigators Detail opportunities for research and career development Institutional commitment to candidate assurances that the institution intends the candidate to be an integral part of its research program commitment to protect at least 75% of the candidate’s effort for proposed career development activities Mentored K Awards: Review Career Development Plan Activities other than research alone that will facilitate transition to independence Additional coursework to fill-in gaps? Grant-writing workshops? Seminars, journal clubs Participation in CTSI Translational Science Training Program (TSTP)? Mentored K Awards: Review Research Plan Should include new research training Hypothesis- vs. discovery-driven Provide a logical path to research independence (away from mentor) Detailed experimental plan with potential pitfalls, expected outcomes, alternative approaches (K99/R00:distinct research phases) Key to a Strong Career Development Training Plan • Understand the intent of the mentored K award is to help new investigators achieve independence (i.e., R01-level funding). – Preparing for the R01 grant application that the candidate will submit at the end of the K award should be the organizing principle of the K grant application, which includes both a training plan and a research plan. Career Development Training Plans • Make a compelling argument why the mentee needs a K award. – Identify critical gaps or deficiencies in the mentee’s knowledge or skills. – Explain how additional training or mentored research experience in these areas will enable the mentee to compete successfully for R01 funding. – Be specific; provide examples. Career Development Training Plans • Develop a career development training plan that is uniquely suited to the mentee. – Given their previous training and research experience, mentees should propose a mix of didactic training and hands-on research experience that address the gaps or deficiencies in their knowledge or skills. – Fully exploit the training opportunities available. – The training plan should be as carefully thought out and presented as the research plan. Helping Candidates Develop a K Award Research Plan • The research plan is a training vehicle. Should be well integrated with the candidate’s training plan and provide an opportunity to acquire new skills • The research plan is a means to achieve independence. Should be viewed as a precursor for the next state of research – ideally, an R01. • Mentored K awards provide limited funding. The scope needs to be appropriate and feasible ($25K-$50K/year). General NIH Reviewer Guidelines Significance • Does this study address an important problem? Do you make a compelling case? • If the aims of the application are achieved, how will scientific knowledge be advanced?? • What will be the effect of these studies on the concepts or methods that drive this field? How might this change the field? Be convincing!!! Approach • Are the conceptual framework, design, methods, and analyses adequately developed, wellintegrated, and appropriate to the aims? • Does the applicant acknowledge potential problem areas and consider alternative tactics? • Is there an appropriate work plan included? • Does the project include plans to measure progress toward achieving the stated objectives? How will you know when you are half way there? Innovation • Does the project employ novel concepts, approaches or methods? • Are the aims original and innovative? • Does the project challenge or advance existing paradigms or develop new methodologies or technologies? Investigator • Is the investigator appropriately trained and well suited to carry out this work? • Is the work proposed appropriate to the experience level of the principal investigator and other significant investigator participants? • Is there a prior history of conducting (fill in area) research? Does not fund empty aspirations! Environment • Does the scientific environment contribute to the probability of success? • Do the proposed experiments take advantage of unique features of the scientific environment or employ useful collaborative arrangements? • Is there evidence of institutional support? • Is there an appropriate degree of commitment and cooperation of other interested parties as evidence by letters detailing the nature and extent of the involvement? Budget • Are all requests justified scientifically • Do special items have quotes • Is the project feasible with the given budget – Low budget often viewed worse than high budget, • Low budget - applicant does not understand what is need to do the work - may worsen the score – -High budget -: will get cut but usually not worsen score, unless really high Other Key areas • Protection of human subjects (closely reviewed) – HIPAA plan – data and safety monitoring plan – inclusion of women, minorities & children – recruitment plan – evidence (not plan) of proposed partnerships • Animal welfare • Biohazards • Evaluation NIH grant application scoring system • 9-point rating for the impact/priority score with 1 = Exceptional and 9 = Poor. • Ratings in whole numbers only (no decimal). Approach of the NIH RO-1, NRSA, or K applications CSR assigns the application to 1) Study Section 2) An Institute Study Section assigns a Priority Score (1-9) Institute uses the Priority Score to rank the application among those received from various study sections Advisory Council reviews the priorities Applications are funded in order of priority until the money runs out! Funding Climate NUMBER OF RESEARCH CAREER AWARDS* 4,500 4,000 Number of Awards 3,500 3,000 2,500 2,000 1,500 1,000 500 0 1998 1999 2000 2001 * Includes both individual and institutional awards. The actual number of individual participants is higher. 2002 Fiscal Year 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 TOTAL AND AVERAGE AWARD AMOUNT OF INDIVIDUAL RESEARCH CAREER AWARDS Total Award Amount (in millions) Average Award Amount $160 $700 $140 $600 $120 $500 $100 $400 $80 $300 $60 $200 $40 $100 $20 $0 $0 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Fiscal Year 2004 2005 2006 2007 Average Award Amount (in thousands) Total Award Amount $800 NUMBER OF INDIVIDUAL RESEARCH CAREER AWARDS BY INSTITUTES AND CENTERS 600 500 NIH Institutes and Centers G NI 400 S M N RI HG M NL Number of Awards I LB H I H N NIM NC K DD ID S NI NIA ND A NI NID NIA D S CH NI IAM A A N CD R A NI NID DC I NE NI RR S NC IEH NR N NI B BI NI NC 200 100 0 M CA N HD M C 6 20005 20 4 200 3 200 2 200 1 200 0 200 9 199 8 199 C FI 300 Fiscal Year NIH CAREER DEVELOPMENT (K) GRANTS Competing Applications, Awards, Success Rates and Total Funding by NIH Institutes/Centers and Activity Code Made with Direct Budget Authority Funds Fiscal Year 2010 Number of Applications Reviewed Number of Success Rate Applications Awarded Total Funding K01 465 185 39.8% $24,377,709 K08 480 211 44.0% $30,787,581 K23 558 211 37.8% $31,635,065 See Table #204 at “report.nih.gov/FileLink.aspx?rid=551” for more details. NIH CAREER DEVELOPMENT (K) GRANTS Competing Applications, Awards, Success Rates and Total Funding by NIH Institutes/Centers and Activity Code Made with Direct Budget Authority Funds Fiscal Year 2011 Number of Number of Applications Applications Reviewed Awarded Success Rate Total Funding K01 441 151 34.2% $19,779,309 K08 425 177 41.6% $26,461,116 K23 599 203 33.9% $31,036,760 See Table #204 at “report.nih.gov/FileLink.aspx?rid=551” for more details. NIH CAREER DEVELOPMENT (K) GRANTS Competing Applications, Awards, Success Rates and Total Funding by NIH Institutes/Centers and Activity Code Made with Direct Budget Authority Funds Fiscal Year 2012 Number of Number of Applications Applications Reviewed Awarded Success Rate Total Funding K01 522 168 32.2% $22,586,026 K08 371 157 42.3% $23,254,142 K23 555 203 36.6% $31,820,630 See Table #204 at “report.nih.gov/FileLink.aspx?rid=551” for more details. NIH CAREER DEVELOPMENT (K) GRANTS Competing Applications, Awards, Success Rates and Total Funding by NIH Institutes/Centers and Activity Code Made with Direct Budget Authority Funds Fiscal Year 2013 Number of Number of Applications Applications Reviewed Awarded Success Rate Total Funding K01 483 160 33.1% $21,515,902 K08 346 124 35.8% $19,659,367 K23 555 178 32.1% $28,555,388 See Table #204 at “report.nih.gov/FileLink.aspx?rid=551” for more details. Success Rates and Pay Lines Institute Success Rate 2010 Success Rate 2011 Success Rate 2012 Pay line 2012 Pay line 2013 NCI 17.1 13.8 13.6 7 9 NHLBI 19.9 17.4 14.7 10 11 NIDDK 25.9 20.7 19.8 13 11 NIA 14.5 16.1 15.5 11 11 NIMH 22.1 17.0 21.6 10 10-20 ?? Research Supplements to Promote Diversity in Health-Related Research (Admin Supp) – PA 12-149 NIH Research Supplements to Promote Diversity Fiscal Year 2007 NIH Office of Extramural Research: Prepared July 2008 Diversity Supplements FY07 47 NIH-WIDE TRENDS SUPPLEMENTS TO INDIVIDUALS FROM UNDERREPRESENTED GROUPS OR DISADVANTAGED BACKGROUND FISCAL YEARS 1990-2008 Number of Awards Expenditures (millions) $90 1600 $80 1400 $70 1200 $60 1000 $50 800 $40 600 $30 400 $20 200 $10 0 $0 2008 2006 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 2008 2006 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 Fiscal Year Fiscal Year 48 NIH-WIDE TRENDS EXPENDITURES AS A PERCENTAGE OF EXPENDITURES FOR ELIGIBLE RESEARCH GRANT AWARDS* SUPPLEMENTS TO INDIVIDUALS FROM UNDERREPRESENTED GROUPS OR DISADVANTAGED BACKGROUND FISCAL YEARS 1990-2007 Percentage of Expenditures 0.70% 0.60% 0.50% 0.40% 0.30% 0.20% 0.10% 0.00% 2008 2006 2004 2002 2000 1998 1996 1994 1992 1990 Fiscal Year *Eligible grant mechanisms: R01, R10, R18, R22, R24, R35, R37, R41, R42, R43, R44, P01, P20, P30, P40, P41, P50, P51, P60, U01, U10, U19, U41, U42, U54, S06. Diversity Supplements FY07 51 Questions? • More coming up from Dr. Salusky on proposal preparation