The Muslim World Chapter 10 – Sections 2 & 3

The Muslim World
Chapter 10 – Sections 2 & 3
Use this information and your notes to help you understand important concepts/ideas/information
“Rightly Guided Caliphs”
Abu-Bakr, Umar, Uthman and Ali – all had known
Muhammad
Used Qur’an and Muhammad’s teachings as guides to leadership
Rule was called a “caliphate” – they were elected to lead the people in the ways of Islam.
After Muhammad’s death, some people abandoned
Islam and/or refused to pay taxes.
“Rightly-Guided” Caliphs
As a result of this dissent, Abu-Bakr invoked
“jihad” which means “striving.” (Remember the firefighter’s words in the video about this concept? – inner struggle against evil) The word is also used in the Qur’an to mean an armed struggle against unbelievers. Abu-
Bakr applied this meaning to encourage and justify the expansion of Islam
“Rightly-Guided” Caliphs
All the caliphs used military might to expand the ideas of Islam.
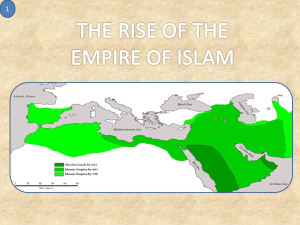
By 750 A.D. (this started about 632 A.D.) the
Muslim state controlled 6,000 square miles of territory. (Remember your geography/mapping activity?)
Conquer – but co-exist
Muslims allowed conquered peoples to follow their own religion with Christians and Jews receiving special consideration because they were “people of the book.” All paid taxes, but
Christians and Jews could pay to exempt themselves from military duty.
Internal Conflict and the Umayyads
Although Muslims made great gains on the battlefield, they were conflicted amongst themselves. A civil war broke out, and the concept of having an “elected” caliph was ended. The Umayyads then came to power.
Umayyads moved the Muslim capital to
Damascus and surrounded themselves with wealth – very unlike previous caliphs.
The SunniShi’a split
Many Muslims accepted Umayyad rule, but some continued to resist.
Muslims split into separate groups because they disagreed about who should have succeeded
Muhammad.
Sunni – believe first four caliphs were “rightly guided”
Shi’a – believe that Muhammad’s son-in-law Ali should have succeeded him
Sufi – reject luxury – pursue life of poverty and devotion to a spiritual path.
Umayyads lose power to Abassids in 750.
Out with the Umayyads – In with the
Abassids!
The Umayyads are ruthlessly slaughtered, but one prince escapes, Abd Al-Rahman and flees to Spain – remember the video?! What does he do there?
Abassids move capital from Damascus to
Baghdad which is on a key trade route offering them better access to trade goods, gold and information. (see page 261)
Innovations of the Muslims
Treasury keeps track of the flow of money
Special department manages the army
Diplomats are sent to courts in Europe, Africa and Asia to conduct imperial business (not courts of law – but what kind of court?)
Taxed land, imports, exports and muslim wealth (see taxes have been around
FOREVER!)
Economic Innovations
What do we mean by “economic”?
Muslim banks offered letters of credit called
“sakks.” In Europe, the word was pronounced as “checks.”
Had a single currency – the Abassid “dinar”.
Get this currency and speak Arabic and you could trade anywhere in the empire!
Muslim Culture
Al-jabr is Algebra – lucky for you the Muslims thought of Algebra, huh?! It is the “art of bringing together unknowns to match a known quantity.”
House of Wisdom – located in Baghdad it is a combination of a library, academy and translation center. Its purpose was to translate all of the important scholarly works to Arabic. Scholars of different cultures and beliefs worked side-by-side to achieve this.
Muslim Art
Does not contain images of living beings.
Is colorful and intricate
Includes calligraphy, arabesque decoration and mosaics.
Pattern in Islamic Art
Islamic Architecture
The usual ending….
Need a copy of this PowerPoint?
Send an e-mail to: lisa.childers@fraserk12.org
I will also put this PowerPoint on the “M” drive under Childers/Medieval World History