skills day-sand dunes-lesson 1
advertisement

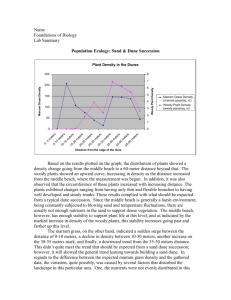
Welcome to the A’ Level Geographical Fieldwork and Skills Day Preparing you for the Unit 2 & Unit 4A examinations fieldwork investigation questions What do you need to know…? The Unit 2 paper will have a fieldwork question worth 25 marks where you have to draw upon fieldwork you have experienced as part of your Geography course. You could be asked about one or more of the following: • • • • • Purpose – Aims / Hypotheses / Location / Theoretical background. Data collection & Sampling Techniques. Data presentation & Statistical Techniques. Analysis and conclusion. Risk assessment. The same foci are used for the Unit 4a st What do you need to know…? Unit 4A is a more challenging examination than the AS equivalent Unit 2. The questions have to demonstrate elements of both synopticity and stretch and challenge. Essentially, the differences between the two examinations can be summarised as: - Unit 2 — assesses what I did on my fieldwork - Unit 4A — assesses why I did what I did on my fieldwork • Hence, all questions in Unit 4A will be evaluative (though can expect one or two for Unit 2). It is suggested that there is a limited range of questions that could be asked. The table below summarises a range of possible questions. What do you need to know…? POA, Today! • Lesson 1: Purpose of the fieldwork investigation • Lesson 2: Methods of data collection, sampling techniques & risk assessment • Lesson 3: Data presentations & statistical tests • Lesson 4: Data analysis & evaluation • Lesson 5: Geographical skills – Basic statistical & graphical skills Aim: How and why does vegetation change across a psammosere at Llobregat delta, Barcelona? Purpose of the investigation: Aims, Hypotheses, Location & Theory Aim – what it it? / Click to reveal Where is the Llobregat Delta? S.W. of Barcelona / Discuss justification for location – provide excellent example of zonation and succession + influence of winds (blow outs) +poss human intereference in formation of Psammosere (recreation & trampling) + plagio climax (pine trees)– students note 1st page What is the ‘textbook’ theory of psammosere succession? Theoretical background • • • • • • • • • Expectations: High wind and high pH values to develop the embryo dune. Grasses such as lyme grass and sea couch grass then appear. A humus layer builds up which traps both water and nutrients. Marram grass is the most common species. Vegetation reaches 100%. Sand sedge and sea spurge start to dominate and small shrubs appear for the first time. Shelter from winds and a true soil begins to develop. Dune slacks. Climatic climax vegetation is reached at the mature dune. Develops a soil which can support shrubs and trees. Debrief from their sheets and show / see end of teacher pack A transect across a sand dune system The transect above has hidden ‘hotspots’. Move your mouse over the diagram and these will be revealed. Progress across the transect using these hot spots. You can return to this diagram at any time by using the return button You can advance quickly from one slide to the next by using this button You can go from this slide to the revision materials by using this button Embryo and Fore Dunes: the environment Click on photo to reveal annotations on-shore winds high water mark poor water retention sand builds up against pioneer plants seaweed deposits humus transient dunes pH 7 %OM 0.1 sand alkaline Embryo and Fore Dunes: the plants The plants which grow here have adaptations which allow them to grow in a difficult environment : • waxy leaves to retain moisture and withstand winds • prostrate (low) habit to avoid strong winds • deep tap roots to obtain available moisture Sandwort Frosted orache • high salt tolerance Saltwort Sea rocket Sea couch Yellow Dunes: the environment Click on photo to reveal annotations above the level of high tides reduced wind speeds pH 6.5 %OM 0.23 ‘Soil’ slightly less alkaline and more water retentive Some humus forming Surface continually blown away and replenished with fresh sand Yellow Dunes: the plants The dominant plant species is Marram grass: • Salt tolerant • Thrives on being buried by sand • Inrolled leaves to reduce moisture loss • Long tap roots • Underground rhizomes stabilise the sand Other plants such as Ragwort, Red fescue and Sand sedge begin to appear Grey Dunes: the environment Click on photo to reveal annotations sheltered by higher, seaward dunes lower pH little mobile sand pH 5 - 6 %OM 1.0 sand no longer accumulating higher humus content a more closed vegetation community in which marram grass is no longer able to compete Grey Dunes: the plants • higher species diversity • mainly perennials • marram becomes more sparse • surface lichens give ‘grey’ appearance Older grey dunes may have extensive covering of lichens and heather Dune Slacks: the environment Click on photo to reveal annotations occur in low lying hollows between dune ridges soil acidic pH 4 - 5 %OM 8.5 water table high – especially in winter relief intersects the water table Dune Slacks: the plants The community which develops here comprises moisture-loving plants commonly found in many fresh water wetland areas e.g. Flag iris rushes Phragmites reeds Bog cotton Dune Heath/Woodland: the environment Click on photo to reveal annotations well sheltered from winds maritime influence is minimal acidic soil nutrient rich pH 4 % OM 12.1 soil has high organic matter content Dune Heath / Woodland: the plants Human interference means that true mixed woodland climax vegetation is rarely seen on dune systems in the UK Most dune systems develop into a community of heathland, woody perennials (often spinous) and scattered trees. Heather Revision materials Heather Sea buckthorn Psammosere: summary of stages Theoretical background Theoretical thump-up! Question 1 Question 5 Question 9 Question 2 Question 6 Question 10 Question 3 Question 7 Question 11 Question 4 Question 8 Question 12 Starter lesson 4 For any Geography fieldwork study you have undertaken: Describe the purpose of the investigation You have only……….. For any Geography fieldwork study you have undertaken: Describe the purpose of the investigation For any Geography fieldwork study you have undertaken: Describe the purpose of the investigation For any Geography fieldwork study you have undertaken: Describe the purpose of the investigation What are other likely opening questions at AS Level? What are other likely opening questions at A2 Level?