KS3 Probability 1 - Growth Mindset Maths
advertisement

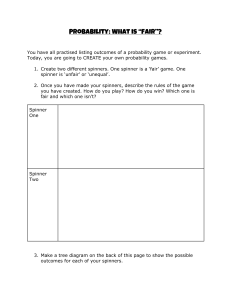
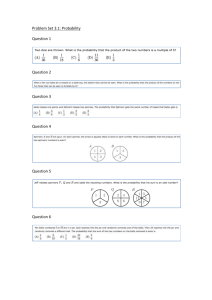
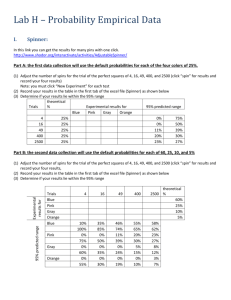
Lesson Plan - APP Probability Objectives Pupils to self assess their understanding of probability. Teacher to carry out an APP assessment using probing questions. Keywords :Outcome, Event, Sample Space Diagram Mental and Oral Starter Pupils to revisit the never heard the word grid to check their understanding of the key words. Main Explain that the purpose of this lesson is to assess their understanding so although they can ask a friend for help they must be honest when they come to self assess at the end of the lesson. Explain that if they find their chosen challenge either too hard or too easy they should swap for a different challenge. Ensure that pupils are aware that they only have this lesson to complete their chosen challenge so they must stay on task and work to the best of their ability to be able to accurately assess themselves. Plenary Hand out the pink APP sheets. Ask pupils to look at their assessment sheet and colour in all the levels they feel that can achieve independently. Tell pupils that they must complete the ‘Tips / Hints’ box by explaining in their own words the maths they did today. Ask them to also describe any help that they had. Explain to pupils that you will be marking their work and completing the ‘my teacher’s’ boxes. Remind students that next lesson for the starter activity they must come in and look for the question you have set and respond either by answering it or by explaining why the question is too hard for them to answer. Probing Questions Level 5 Find and justify probabilities based on equally likely outcomes in simple contexts. For example: The letters of the word REINDEER are written on 8 cards, and a card is chosen at random. What is the probability that the chosen letter is an E? On a fair die what is the probability of rolling a prime number? Can you give me an example of what is meant by ‘equally likely outcomes’? Level 6 How do you go about identifying all the mutually exclusive outcomes for an experiment? Use a sample space diagram to show all outcomes when two dice are thrown together, and the scores added. What strategies do you use to make sure you have found all possible mutually exclusive outcomes for two successive events, One red and one white dice are both numbered for example rolling two dice? 1 to 6. Both dice are thrown and the scores added. Use a sample space to show all possible How do you know you have recorded all the possible outcomes? outcomes. Level 7 What might be different about using theoretical probability to Recognise that repeated trials result in find the probability of obtaining a 6 when you roll a dice, and experimental probability tending to a limit, and using experimental probability for the same purpose? that this limit may be the only way to estimate probability. Describe situations where the use True or false of experimental data to estimate a probability Experimental probability is more reliable than theoretical would be necessary. probability; Experimental probability gets closer to the true probability as more trials are carried out; Relative frequency finds the true probability. LO To assess your Understanding Reflect, Assess, Explain, Communicate RAG 13-Apr-15 Starter Activity Look back at the Heard the Word Grid that you completed at the start of the unit. Are there any words that you understand now and can describe which you couldn’t before? LO To assess your Understanding Reflect, Assess, Explain, Communicate RAG 13-Apr-15 In today’s lesson you will be reflecting upon what you have learnt in the last few maths lessons. You will be completing a challenge. You are allowed to look back in your book but you should be working independently.. Key Words Event Outcome Random Biased / Unbiased Theoretical Probability Experimental Probability Mutually exclusive Never heard before? Heard of but not sure what it means? Know what it means and can explain it in context Jot down your ideas here... Key Words Event Outcome Random Biased / Unbiased Theoretical Probability Experimental Probability Mutually exclusive Never heard before? Heard of but not sure what it means? Know what it means and can explain it in context Jot down your ideas here... Additional Task You could add a new task for level 3 where pupils can match pre coloured spinners to statements. Which is certain Which is impossible, Which is an even chance….etc You have been given 4 colours; Red, Blue, Green and yellow Spinner 1 Yellows must be most likely to win Spinner 22 colours are equally likely to win Spinner 3Blues are least likely to win Spinner 4 Reds can never win You have been given 4 colours; Red, Blue, Green and yellow Spinner 1 Yellows must be most likely to win Spinner 22 colours are equally likely to win Spinner 3Blues are least likely to win Spinner 4 Reds can never win Level 4 Challenge Using at least 3 colours, colour the spinners so that the statements in the table are true. Then move to level 5. If you are not ready to move to level 5 then 1.) Ask your teacher for some more blank spinners and colour them differently so that the statements are still true? 2.) Make up some statements of your own and colour the spinners to make the statements true. Level 5 Challenge After you have coloured in the spinners describe the probability of getting each colour as a fraction. For example - Spinner 1 (P) Red = (P) Blue = (P) Green = (P) Yellow = Level 6 Challenge Draw a sample space diagram to show all the possible outcomes when spinners 1 and 2 are spun together. What is the probability of :a) getting two colours the same b) getting at least one blue c) getting a blue and a yellow d) not getting a red Level 7 Challenge Answer the following questions:What might be different about using theoretical probability to find the probability of obtaining a 6 when you roll a dice, and using experimental probability for the same purpose? True or false Experimental probability is more reliable than theoretical probability? Experimental probability gets closer to the true probability as more trials are carried out? Blank Spinners To be a better learner I could................ Less Helpful More Helpful Work Faster / do more Be neater Try the harder ones Stay on task. Clearly show my working out. Put my hand up to ask a question when I don’t understand. Talk less Make sure that when I am talking to the people on my table, I am talking about the Maths. Listen more when the teacher is talking. Contribute answers and questions during the explanation part of the lesson. level 7 Probability Skills I understand the difference between experimental and theoretical probability. I can use relative frequency as an estimate and to compare the outcomes of experiments. 6 I can complete a sample space diagram and use it to calculate probabilities. 5 I can describe the probability of an event happening using a fraction, decimal or percentage. 4 I can use I the language of probability to describe the probability of an event occurring. 3 I can use the probability words impossible, certain and even chance to describe the probability of an event occurring. Top Tips / Hints ...... My teachers comment ...... My teachers question is ...... My answer is ...... Plenary Complete the Pink Assessment Sheet. Fold it in half and glue it into your book. Answer the question that you have been set.