Meredith PPT - Daren C. Brabham, Ph.D.
advertisement

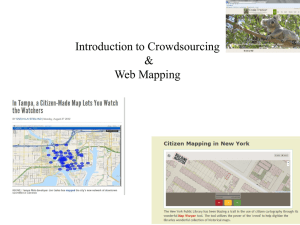
Managing Crowdsourcing Ventures Daren C. Brabham, Ph.D. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill October 27, 2011 MBA 812: Strategic Communication & Social Media Prof. Michael Meredith Agenda • How and why I study crowdsourcing • What crowdsourcing is – Four types for four kinds of problems • Effective management principles for crowdsourcing ventures • Q&A How & Why I Study Crowdsourcing How & Why I Study Crowdsourcing • Crowdsourcing as a model for problem solving • A critical, humanist approach • More concerned with relationships & human experience – I’m optimistic, multi-method, holistic in research • Less concerned with performance & efficiency – Those are the computer scientists and business innovation scholars A Struggle Over the Term • Challenges “in the form of an open call” • “An online, distributed problem solving and production model” • Like anything in Wired, “crowdsourcing” was an instant buzzword • Old wine in new bottles? • A bloated concept makes for unclear research Generally, Crowdsourcing is… • A process whereby: – an organization poses a specific challenge to an online community (a crowd) – the crowd answers that challenge – the organization benefits from the crowd’s labor • Driven by collective intelligence & wisdom of crowds • Openness + top-down management A Crowdsourcing Typology • • • • Knowledge Discovery and Management Broadcast Search Peer-Vetted Creative Production Distributed Human Intelligence Tasking Knowledge Discovery & Mgmt • Online communities challenged to uncover existing knowledge in the network • Amplify discovery capabilities of an organization with limited resources • Ideal for info. gathering, organizing, and reporting problems (e.g., creating collective resources) Knowledge Discovery & Mgmt Broadcast Search • Online communities challenged to find empirical solutions to difficult problems • Casting a wide net finds the “needle in the haystack” – the genius able to solve the problem • Ideal for ideation problems with empirical solutions (e.g., scientific problems) Broadcast Search Peer-Vetted Creative Production • Online communities challenged to develop and choose solutions to ideation problems • Inviting lot of diverse input brings in many (different) ideas. People “find the best stuff” • Ideal for ideation problems where solutions are matters of taste or market support (e.g., design/aesthetic and policy problems) Peer-Vetted Creative Production Peer-Vetted Creative Production Distributed Human Intelligence Tasking • Online communities tasked to perform simple tasks that computers cannot do well • Decomposing a problem/task requiring human intelligence into smaller pieces and distributing it is faster, better • Ideal for large-scale data analysis requiring human intelligence Distributed Human Intelligence Tasking Typology Summary • KD&M – Knowledge exists “out there.” Let’s find it and organize it. (collective resources) • BS – There’s an empirically right answer. We just don’t know it. Let’s find it. (scientific problems) • PVCP – The “right” answer is a matter of taste. Let’s have the market submit and select what it wants. (design & aesthetic problems) • DHIT – We have lots of data to analyze. Computers won’t do. Let’s break the problem down and get people to do the work. (data analysis problems) 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 1. Clearly define your problem, solution parameters, and selection mechanism. 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 2. Determine your level of commitment to the outcomes. The impact of the crowd’s ideas on your organizational decisions Policy Advisory 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 3. Know the crowd and their motivations. or or or 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 4. Invest in usable, interesting, well designed tools. 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 5. Invest in legal help. Consider legal needs of you and the crowd. 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 6. Have a promotional plan & a plan to grow and sustain the community. 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 7. Be honest, transparent, and responsive. 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 8. Be involved, but let go of control. 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 9. Acknowledge users and follow through on obligations. 10 Crowdsourcing Mgmt Principles • 10. Assess the project from many angles. – Site traffic analytics, user registration data – Interviews with participants – Analysis of submissions – Public relations impact (even in failure) Thank You! • Questions? www.linkedin.com/in/darenbrabham @dbrabham darenbrabham