Unit 1 Vocabulary terms
advertisement
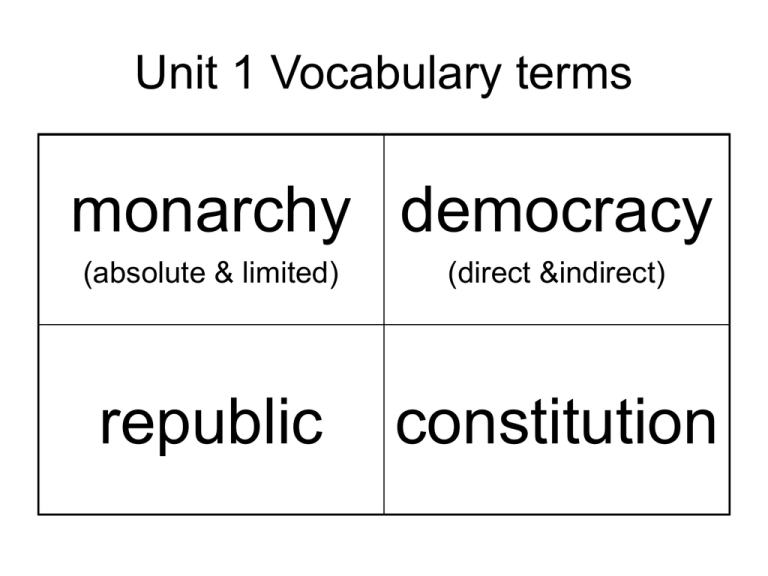
Unit 1 Vocabulary terms monarchy democracy (absolute & limited) (direct &indirect) republic constitution Unit 1 Vocabulary terms Due Process amendment (of law) Divine Right of Kings natural rights Unit 1 Vocabulary terms Social Contract separation of powers Parliament ratify Unit 1 Vocabulary terms revolution philosophe liberalism radicalism Unit 1 Vocabulary terms conservatism moderate citizen federal system Unit 1 Vocabulary terms coup d’etat salon nobles tyranny Unit 1 Vocabulary terms Judeo-Christian values theocracy aristocracy anarchy bourgeoisie clergy Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Monarchy- A system of government led by a king or queen. Succession is hereditary. Absolute = with total, complete power; Limited = monarch is restrained by certain guidelines or laws. (ex. Constitutional Monarchy) Republic- Democracy- a system of government where decisions and laws are made by its citizens. direct= originated in ancient Greece, each citizen participates in governing at an equal level; indirect= developed in the Roman Republic, citizens elect representatives to make decisions for them. Constitution- a government that a written set of laws and practices representative, or guidelines that determine indirect democracy. how a nation is to be ex) I pledge allegiance to the flag of the governed. USofA, and to the republic, for which it stands… Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Amendment Due process (of law) a change; used to A formal process to which a describe a change made to person is entitled if accused of a a constitution or law. crime. Its purpose is to ensure fair treatment guided by established rules. Divine Right of Kings Natural rights The belief that monarchs receive Rights endowed to every person their power directly from God; simply by act of being born, monarchs used it to justify their regardless of any class distinction; power and to answer to no one but Also known as human rights, or God. inalienable rights. Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Social contract Separation of powers agreement between a government a system of government in which and the people where society executive, legislative & judicial agrees to be governed by the branches can limit and control general will; in return the each other through a system of government is responsive to this will checks and balances. and should be abolished if it is not. Parliament Ratify a representative body of advisers to a government leader; England’s decisionmaking body. to legally approve, or accept Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Revolution politically, a change in government; usually radical, immediate and violent. Philosophe French for philosopher; used to describe the Enlightenment thinkers of 18th-century Europe who rejected traditional beliefs in favor of rational or scientific thinking. Liberalism political philosophy which emphasizes the protection of basic rights of all individuals; seeks to limit government power over people. Radicalism a political philosophy which supports extreme change in existing views or institutions; may support drastic action to make change occur. Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Conservatism political philosophy which supports traditional views & social stability; promotes obedience to authority & church. Moderate politically “in-between” philosophy; seeks change through non-extreme methods; supports social stability and individual rights. Neither conservative nor radical. Citizen Federal system a form of government where power is shared between a central (national) government and state governments. an individual who has political rights and privileges in a society Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Coup d’etat overthrow of a government by a small group; a coup. Nobles people of a wealthy, landed or titled class; collectively known as the “Nobility”; also known as aristocrats; a title of a feudal political system. Salon formal meeting rooms in large homes where people gathered to discuss the Enlightenment ideas of philosophes; hosted mostly by women; contributed to the spread of Enlightenment ideas. Tyranny oppressive government where absolute power lies with one individual, known as a tyrant. Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Judeo-Christian values Theocracy belief system that is rooted in the teachings of Judaism and Christianity. a system of government led by the church, or its officials. Aristocracy Anarchy a system of government where the wealthy rule. a society with a complete absence of government. Bourgeoisie Clergy the middle class; also includes wealthy people without noble rank. As a group, made significant contributions to the French Revolution. Church officials, or clerics.