Studying The Brain - Freeman Public Schools

Studying The Brain
Lesson 6-2
Objectives
• Identify the structure and functions of the human brain
• Discuss the different ways psychologists study the brain
Introduction
• Early Greeks thought the heart was the source of feelings and thought
• Hippocrates observed the effects of head injuries on people’s thoughts.
The Three Brains
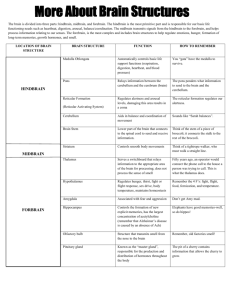
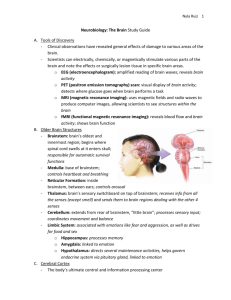
• Hindbrain
– at base of the skull
– controls most life processes (eating, sleep, appetite, thirst, mating)
– includes cerebellum, medulla and pons
Hindbrain
– cerebellum- controls posture and balance
– medulla- controls breathing
– pons- bridges messages between brain and spinal cord
Midbrain
• Integrates sensory information and relays it
Forebrain
• Includes thalamus- integrates sensory information, except smell
• hypothalamus- controls hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sexual behavior
Forebrain
• Allows for higher level thinking
• Outer layer is called cerebral cortex
• Inner layer is the cerebrum
Activity
• Color the brain according to hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain
• Label structure and function:
– thalamus
– pituitary gland
– pons
– medulla
- cerebellum
-cerebral cortex
-spinal cord
Lobes of the Brain
• Cerebrum is two sides
• Corpus Callosum is a band of fibers that connects the two sides
• Deep grooves that forms lobes
Lobes of the Brain
• Occipital Lobe- processes visual info
• Parietal Lobes- Sensory information
• Temporal Lobe- hearing, memory, emotion, speaking
• Frontal Lobe- organization, planning, creative thinking, and personality
Psychosurgery
• A prefrontal lobotomy has been preformed many times to alter psychopathic behavior
– are very controversial when preformed on prisoners
• informed consent
• role of prisons
Brain and Criminal Behavior
• Recent studies show that men convicted of violent crimes are more likely to have abnormalities of their frontal lobe and their right hemisphere.
Activity
• Color and label the lobes of the brain
Left and Right Hemispheres
• Are almost mirror images
• Left brain controls the right side of the body
– controls speech for most people
– controls mathematical ability and logic
Left and Right Hemispheres
• Right hemisphere controls left side of the body
– visual and spatial ability
• puzzles
– recognizing patterns
• music and art
– creativity and intuition
Split Brain Operations
• Corpus Callosum- lets right brain know what left brain is doing
• right brain- sees the sunset
• left brain- describes the sunset
Split-Brain Operations
• In Epileptics, split the corpus callosum to decrease number of seizures
• seizure is massive uncontrolled electrical activity that begins in either hemisphere and spreads to the other
Split-Brain Operations
• Roger Sperry did experiments on people with split brain operations
– Nobel Peace prize in 1981
• Holds ball in right hand can say it is a ball, but put in left hand, can’t say it is a ball.
• Showed each half had specialized functions
Activity
• Right brain or left brain??
How Psychologists Study the
Brain
• Physiological Psychologists or
Psychobiologists study the role of the brain in behavior
Recording
• Electrodes- can be inserted into the brain to record electrical activity
• electroencephalograph- EEG records electrical activity from whole areas of the brain
• See p. 167
Stimulation
• Electrodes can be used to set off the firing of neurons
• Stimulate brains of patients during surgery to find out what function they perform
• have been used to relieve pain of terminally ill cancer patients
• experimented with use to control violent emotional behavior
Lesions
• Cut or destroy a small portion of an animals brain
• They then monitor the animal for changes in behavior
• Assume those changes are controlled by that part of the brain
• Rhesus monkey study
– no longer fearful and aggressive
Accidents
• 1848- Phineas Gage
– RR foreman
– showed good judgement, restraint, worked well with others
• tamping iron enters Gage’s head right below left eye (13 pounds, 3 feet long)
• survived, but personality changed greatly
Accidents
• Dr. Paul Broca discovered the connection between left brain and speech
– area now called Broca’s area
Images
• Computer Axial Tomography (CAT)
– xrays pass around and through a person’s head
– radiation absorbed based on density of brain tissue
– transforms into a 3 dimensional picture
Images
• Positron Emission Topography (PET)
– captures a picture as different parts are being used
– Uses a radioactive solution into the blood and then measures the amount absorbed by blood cells.
Images
• Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
– study both structures and activity
– pass radio frequencies through the brain
– used to identify tumors or brain damage
Closure
• Web activity from prentice hall site
• Read articles on brain injury on prentice hall site and report to class. Each student reads a different one.
• Web activity- Probe the brain
• Research a brain disorder