p) Vectors - Student - school
advertisement

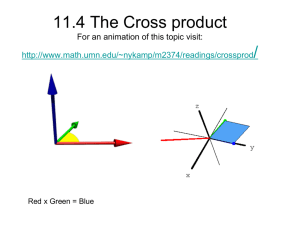
Vectors Learning Outcomes Understand the difference between a vector and a scalar use vector notation Add and subtract vectors and use vector diagrams Know that if one vector is a multiple of the other, they are parallel Prove three points lie on the same line by proving they have a common point and that the vectors which compose them are parallel Understand and use position vectors Vectors Vectors A vector has a magnitude and direction. a (i) a + b b (ii) a - b (iii) 2a Vectors (iv) 2a + 3b Vectors (iv) 2a - 2b Vectors and Geometry Vectors A a O B b a C B b D A 2a Vectors Vectors and Geometry B C is the midpoint of line BD A BD AB a AD b C a b D Write down in terms of a and b: BD AC Exam Question Vectors In the diagram below, and OF OG represent the vectors 5a and 10b. H is a point on FG such that FH : HG = 1 : 4 F H O G Express in terms of a or b or both (a) FG (b) (c) FH OH From a point T, below the line OG, a line TG is drawn equal length and parallel to OH. (d) Express in terms of a or b or both FT OT Additional Notes Vectors Learning Outcomes: At the end of the topic I will be able to Understand the difference between a vector and a scalar use vector notation Add and subtract vectors and use vector diagrams Know that if one vector is a multiple of the other, they are parallel Prove three points lie on the same line by proving they have a common point and that the vectors which compose them are parallel Understand and use position vectors Can Do Revise Further