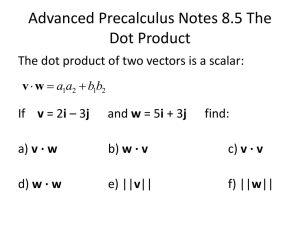
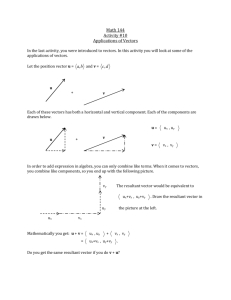
Vectors PPT
advertisement
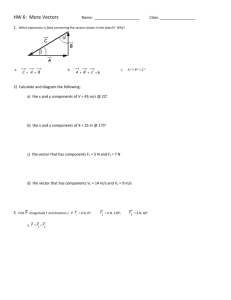
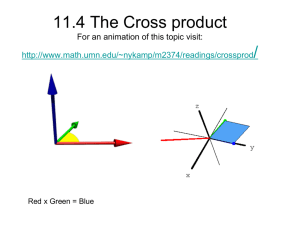
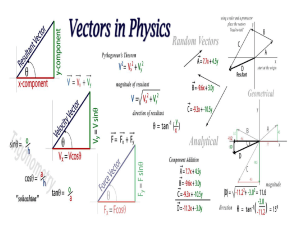
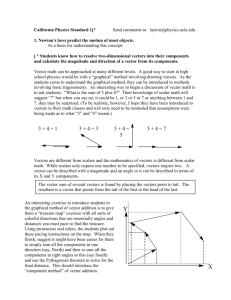
Vectors Vectors • Scalar Quantity = A measured quantity needing only magnitude. • Examples: Distance and Speed • Vector Quantity = A measured quantity having both magnitude (size) and direction. • Examples: Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Vectors • A vector quantity can be represented by an arrow tipped line segment. • The length of the line, drawn to scale, represents the magnitude of the quantity. • The direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the quantity. • This arrow tipped line segment represents a vector. Addition of Vectors • Can add vectors by using the tail to head method. • Place the tail of the second vector to the head of the first. • The sum or resultant is the length of the line drawn from the tail of the first to the head of the last. Addition of Multiple Vectors The order of addition does not effect the sum. Addition of Vectors in Two Dimensions • Using Pythagorean theorem the resultant vector can be determined when vectors are at right angles Problem: Find the magnitude of the addition of the following two vectors 11 meters North + 11 meters East Trigonometry with Vectors East of North Vectors Practical Application of the Addition of Vectors