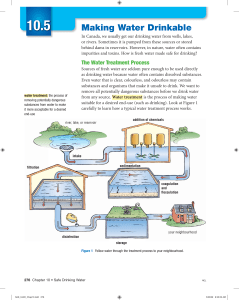
The Water Treatment Process
advertisement

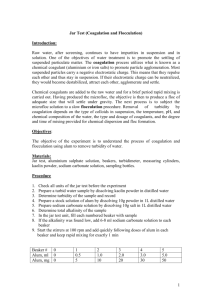
The Water Treatment Process Making Water Drinkable Review Questions 1. A rose bush was watered on Sunday. After six days the soil was dry and the leaves were wilting. Explain what happened to the water. 2. Why is the earth’s water never used up? Water Treatment Water Treatment is the process of making water suitable for desired end use (such as drinking). Water Treatment occurs as a Systematic Process through a Water Treatment Plant A Water Treatment Plant Water Treatment Process - Steps Remove large objects – a metal screen blocks objects from entering the pipe Add alum (a chemical) – attracts waste solids to form clumps – these are called floc (sticky clumps formed from the reaction of alum in water, combined with sand and other waste solids) Steps Water and Floc enter settling tank (water moves slowly) where floc settles to the bottom Partially cleaned water from top of tank moves through a sand and charcoal filter to remove remaining waste Chlorine added to kill organisms Water stored or delivered Other Treatment Options 1. Reverse Osmosis – mechanical pressure forces water through a membrane that acts like a fine filter 2. UV radiation – destroys most viruses and micro-organisms 3. In nature, water absorbs minerals calcium and magnesium from surronding rock – this makes water “Hard”. This is safe to drink but when heated leaves mineral deposits. 4. Boiling – boil for 3 minutes to kill microorganisms and bacteria and drink within a few hours Stormwater Management During spring; too much water for plant to handle so stormwater goes directly to lake Using Water Sustainably Only a small amount of world’s water is suitable for human use. A rising population, pollution and other factors are limiting this resource. Sustainability means working and behaving in a way that protects resources to ensure that they are available to future generations. Homework Questions 1. List and describe the six main steps that water goes through in the water treatment process 2. Is clear, colourless and odourless drinking water always safe to drink? Explain. 3. Why is it important to ensure that treated water remains safe to drink when it is stored after treatment? Describe one way to make stored water safe.