Ecosystems, Food Chains & Webs: Biology Presentation
advertisement
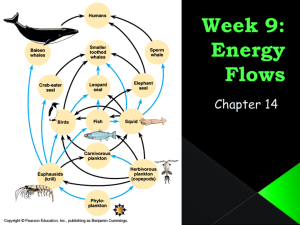
Ecosystems Learning Intention • To be able to describe what is meant by a habitat, population, community and ecosystem. Habitat • An organisms habitat is the place where it lives. Population • A population is all the members of one species in an ecosystem. Population of sea turtles Population of dolphins Water habitat Community = all the plants and animals in a habitat Example of an ecosystem: Ecosystem = Community + Habitat Learning Intention • To be able to: – Give an example of a food chain. – Identify the producers, primary and secondary consumers in a food chain. What is a food chain? Photosynthesis......... What happens to the food plants make in photosynthesis? Food Chains • Food chains show which organisms eat other organisms Grass Rabbit Fox • The arrows show the transfer of energy from one organism to the next. • It also helps to think of the arrows as meaning ‘is eaten by’. • Producers - organisms which can make their own energy from carbon dioxide and water using sunlight for energy (plants) Primary consumer organisms which eat producers. Secondary consumers - organisms which eat primary consumers. Secondary consumers are predators Arrange these into food chains 1. 2. 3. 4. Lion, grass, Zebra Weasel, fieldmouse, owl, wheat Greenfly, oak leaf, thrush, ladybird Herring, animal plankton, human, plant plankton 5. Frog, hawk, grass, snake, grasshopper Learning Intention • To be able to describe the path of energy flow in a food chain. Energy loss • Some energy is lost at each stage in a food chain. • Each organism in a food chain uses some of the energy to build up its body and grow. • Most of the energy that organisms gain in a food chain is used up when the organism moves about, and in warm-blooded animals, to keep warm. • This means that, as humans, it is more efficient for us, and we receive more energy from, eating plants. Questions 1. What is the source of energy entering a food chain? 2. What does every food chain begin with? 3. Name two ways in which energy can be lost in a food chain. 3 things • Write down 3 things you know now that you didn’t know at the start of the lesson. • Once you have both finished, share them with the person beside you. Learning Intention • To be able to give an example of a food web. What is a food web? • A food web is made up of 2 or more food chains joined together. • For example – Grass – Grass – Grass Rabbit Fox Caterpillar Bird Beetle Mouse Fox Would make this food web More complex food webs Food Webs Small bird Ladybird Spider Owl Vole Earthworm Greenfly Herb The Food Web shown is from a typical woodland community. Soil fungi Moth caterpillar Live oak leaf Dead oak leaf Carnivores Herbivores Decomposers Producers Constructing a food web Consumer Rabbit Food Oak, Primrose Vole Snail Frog Weasel Owl Hedgehog Fox Primrose primrose snail Vole, rabbit Vole Snail, vole Frog, hedgehog, rabbit, weasel Learning Intention • Explain relationships between different organisms in a food web and effects of removing a species. Questions 1. What will happen to the number of clown fish if the sharks become vegetarian? 2. What effect will this have on the number of zooplankton? 3. What will happen to the Blue Regal fish if a disease wipes out the small invertebrates. Food Web Great Whi te Shark Blue Regal Clown Fish Zooplankton Small Invertebrates Algae Sea Turtle Learning Intention • To be able to arrange organisms from a food chain into pyramids of number and biomass. FOOD CHAIN GRASS 1000 GRASS PLANTS! CRICKET FROG 100 CRICKETS! 10 FROGS! HAWK 1! Discussion • What do you notice about the size of the actual organisms as you move along a food chain? • What do you notice about the number of organisms at each stage as you move along a food chain? • Why do you think the number of organisms at each stage is changing? (Do big organisms eat the same amount as small organisms?) Pyramids of Number • The relationship takes the form of a pyramid because – The energy loss at each link in the food chain limits the quantity of living matter that can be supported at the next level. PYRAMID OF NUMBERS • Shows population size at each stage in a food chain 1 HAWK 10 FROGS 100 CRICKETS 1000 GRASS PLANTS PROBLEM!!!!! Can you explain the shape of this pyramid of numbers??? Choose one of the pyramids of numbers above to represent each of the three food chains below. DANDELIONS PEAR TREE RABBITS APHIDS GREEN PLANTS FOX LADYBIRDS SLUGS FROG FLEAS PARTRIDGE FOX Pyramids of biomass • The biomass of a population is the total mass of living things. • In a food chain the biomass of the producer is greater than the biomass of the primary consumer, which in turn is greater than that of the secondary consumer. • Since biomass decreases at each level, it can also be represented as a pyramid shape. Pyramid of Biomass The pyramid of biomass shows the biomass of a population in an ecosystem. E.g. Oak tree Insects Birds Birds Insects Oak tree A pyramid of biomass is always a true pyramid shape.