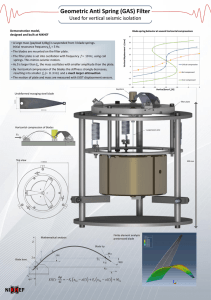
To the teacher
advertisement

Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B To the teacher: • This CPO Science PowerPoint presentation is designed to guide you through the process of presenting the lesson to your students. The presentation uses a 5-E teaching model: Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate. • The PowerPoint Slide notes indicate where you may want to bring in various lesson elements such as quizzes, readings, investigations, animations, and practice materials. Additional science background information is provided in the slide notes where appropriate. You can view these notes by selecting “View,” then “Normal.” You will see the notes pane at the bottom of the PowerPoint workspace. Additionally, the slide notes are available as a separate document, accessible from the lesson home page. • The slides that follow are intended for classroom use. Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B Why did this mountain explode? • On the morning of May 18, 1980, Washington’s Mount St. Helens erupted violently for nine hours. A magnitude 5.1 earthquake kicked off the huge explosion. In just minutes, the 9,677 foot-high mountain collapsed, reduced 1,200 feet by the explosion and a mammoth landslide. So much ash was released that the sky got dark. • Mount St. Helens is located along the boundary of two massive tectonic plates. The plates move and shift, creating both volcanoes and earthquakes. Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B Time to investigate! • Complete the lesson investigation: – Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B Divergent plate boundaries • Mid-ocean ridges occur where two plates are moving apart. This type of boundary is found over the rising part of a mantle convection cell. As the plates move, molten rock fills the empty space between them. The rock cools and becomes new ocean floor. • Rift valleys occur where two continental plates move apart. The East African Rift Valley is a famous example. Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B Convergent plate boundary 1 • A deep-ocean trench is a valley on the ocean floor created when an older, denser oceanic plate subducts under a younger, less dense oceanic plate. Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B Convergent plate boundary 2 • What happens when an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate? • The denser oceanic plate subducts under the continental plate. • The Andes Mountains, pictured here, formed as the subducting oceanic plate deformed and pushed up the land at the edge of the continental plate. Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B Convergent plate boundary 3 • When two continents collide, mountains form! • The Himalaya Mountains are the result of the collision between India on the Indo-Australian Plate and China on the Eurasian Plate. Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B Transform fault boundary • A transform fault boundary occurs where two plates slide by each other. • Offsetting occurs when a feature like a creek or road crosses a transform fault. The movement of the fault will break, or offset the feature, causing a zig-zag appearance. • Earthquakes sometimes occur at transform fault boundaries. Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B Time for Practice! • Complete the lesson practice activity: – Continental United States Geology • As you read this activity sheet, make a list of major land features of the United States and identify which types of plate movements were involved in their formation. Plate Tectonics: Features: TEKS 8.9B Show what you know! • Try the lesson’s interactive quiz, or complete a quiz that your teacher can print out for you. • Hint: – You might want to review your lesson reading piece one more time before trying the quiz.