Information & Organization
advertisement

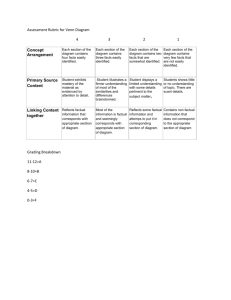
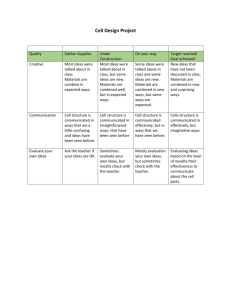
Where are we? Assignments Library map E-mail assignment Biography Defining the Research Question (Tutorial 1) Organization Paragraph Netiquette Quiz Read E-mail website(s) Any Questions? Organization paragraph Similarities How is information organized? What it is and Making sense of it What is information Your thoughts? Information Written knowledge Books, magazines, newspapers & internet What else? Anything else? Information Stone tablet Comic book Oral folktale passed through generations Idea communicated electronically via television or computer Information Definition according to American Library Association (information experts) “All ideas, facts, imaginative works of the mind which have been communicated, recorded, published and or distributed formally or informally in any format” Organization Arrangement of items into a system Establishes rules or reasons for arranging items in a consistent way Who sets the rules and what are they? The need to organize Value of information is enhanced if it can be used more than once, heard by more than one person viewed by more than one viewer, or communicated to more than one reciever If info can’t be “re-used” or has no access, may as well be no information at all Misinformation vs. wrong information (Is there a difference?) Organization Arrange and organize into a system so that arrangement makes the parts interdependent. Methods of organization? Descending (even this is a method) As collection grows you need more sophisticated level of organization Organization by content vs. format (What is content? What is format?) Using music as an example. Methods of organization Content What its about Format medium used: audio, visual, audio-visual, digital Audio (Format) Sub formats Cds, lp’s, cassettes….. Microfilm, paper, color, black and white, slides, videos, dvd’s, film, vhs, floppy or Content & organization of Information Content Subject of the information in an item Characteristic of information in an item Factual or analytical Subjective or objective Primary or secondary Libraries Organize by subject Different systems Dewey Decimal System Library of Congress Classification System (LC) NOTE: classification system allows the assignment of only one subject number to each item in the system. Web organization There is no one system that organizes the information on the web Billions of web pages housed on servers There are many organization systems in place on many web sites Web as a whole is not organized Info characteristics & Determining your info need Determining your information need Narrrowing your topic Broadening your topic Synonyms Related terms Short presentation or in-depth Determining your need One source or many? Overview or in-depth Current or historical (time) Type of Source Scholarly vs. popular Primary, Secondary or Tertiary Characteristics Primary information Not published anywhere else, or put into context or interpreted or translated by anyone else Professor’s lecture notes Account of crossing into the United States by your parent First report of a scientific study by your chemistry group Handwritten manuscript – poem by Jim Morrison Blog published on WWW (you) Characteristics Secondary Information Removed in some way from original source and repackaged. A restatement, examination,or interpretation of information from one or more primary sources Borrowed notes from a friend from class missed Television documentary on lobotomies Article critiques a Frida Kahlo painting Article critiques Tupac’s lyrics to “Dear Mama” Characteristics Tertiary Information A source that leads you to secondary information Bibliography on computer games Bibliography on fishing Indices or indexes Determing your need Format Slides, audio sources, power point other visuals Factual or analytical Viewpoint? Determing your need Factual information provides no explanation of its statements Analytical information requires searching periodical articles and books Usually takes more than one source Characteristics continued Objective information Helps you choose a single aspect of a topic Subjective information Helps when you need to evaluate Formats Books Print Electronic Formats Periodicals Print Bound Unbound Electronic Microform Microfilm microfiche