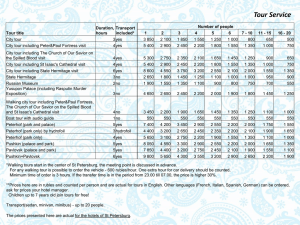
File
advertisement

P3 review the different types of interrelationships and provide examples What do those big words mean? • Interrelate- connect (two or more things) or (of two or more things) to become connected to each other. • Channels of distribution-Comprises all of the businesses and people involved in the physical movement and transfer of ownership of goods and services from producer to consumer. Big words continued • Integration – this is the bringing together of organisations. • Interdependencies- This is when companies depend on one another. Interrelationships in the T&T industry • No single component of the travel and tourism industry can operate alone without relying on other parts of the industry. • For example who does a hotel rely on? • Transport links • Visitor attractions to bring tourists into the local area. Chain of distribution • This is the way of getting a product to a customer. • Can you think of the chain of distribution for milk? • A traditional chain of distribution in the travel and tourism industry might look like this: Accommodation Transport Tour operator Travel Agent Customer However chains of distribution are now a lot more complicated! • Example – many airlines with the exception of British Airways, EasyJet and Ryanair, rely on tour operators and travel agents to sell seats on their aircraft. • The tour operator often owns the airline such as Tui and Thomas Cook . These companies have their own aircraft s to fly their customers as part of their package holiday. • Even if the tour operator may not own the airline, they rely on the tour operator to use their services in their holiday packages. • Tour operator packages, as we saw before are sold through various travel agents Fully integrated chains of distributions • This is where the chain is owned by the same company E.G: Thomas Cook Airlines Thomas cook tour operators (Thomas Cook, club 18-30 ETC). Thomas Cook Retail Thomas Cook Ancillary Services (Currency exchange, travel insurance ETC) TUI chain of distribution MyTravel airlines Going Places retail MyTravel ancillary Services (Insurance, Exchange, Parking ETC.) • There are simpler chains. For example, accommodation holidays, such as villas in France, are sold through businesses that promote France as a destination for a holiday. The properties appear in the business’ brochure and bookings are made via the business, which then handles the payment. Integration • Until recently booking a holiday could mean having to deal with different businesses, which provided different parts of the package. • Now, as we saw before chains of distribution are changing and businesses are starting to expand their area of operation. This process is known as integration. • The advantage of one business offering all elements of a holiday is that the business is able to control its cost and ensure that their customers receive a guaranteed high standard of service. There are 2 types of integration: • Horizontal integration- where businesses at the same level in the chain of distribution merge together or are purchased by another. • Vertical integration – where a business at one point on the chain of distribution purchases or acquires a business at a higher or lower level of the chain of distribution. • Accommodation provider Accommodation provider Vertical Integration • Tour operator • Travel agency Tour operator Horizontal Integration Travel agency Example • In 2000, the tour operator, Manos, which specialises in holidays to Greece and Turkey, was brought by another tour operator, MyTravel. A press release issued at the time described Manos as “a well-known and successful specialist tour operator, which will add to the Group’s existing product portfolio and provide opportunities for cost savings and distribution benefits. Example • The tour operator Thomson, brought Lunn Poly, a chain of travel agents in 1972. The Lunn Poly brand name was kept until 1994, when the company was rebranded Thompson Holidays. Interdependencies • Organisations can not work in isolation, each are dependent on the other for its effective operation. • For example Visitor attraction reply on transport industry to bring customers to the attraction. • Tourist boards (local and regional) • Businesses enter into arrangements like this with one another so that they can all benefit from a single booking. If a customer has purchased a flight, they may also need accommodation or a car. • By providing booking services for these two components of the trip, Easyjet can earn more from the initial booking of a flight. The customer benefits from these arrangements because of the convenience.