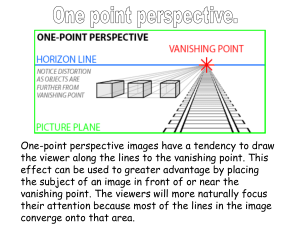
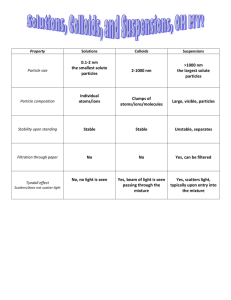
Why is the Sky blue?
advertisement

Why is the Sky blue? Carley D. Welcome !! Have you ever looked up and wondering why is the sky blue? Well for this project I went into detail to really find out why the sky is blue. My website goes into great detail explaining why the sky is blue. You can easily navigate through my website to find the answer and diagrams explaining this question. Enjoy!! Table of Contents Table of Contents Rayleigh Scattering Why Not Violet? The Tyndall Effect Vocabulary Welcome !! Concluding… Graph Related Links =) Rayleigh Scattering Table of Contents The blue color of the sky is mainly do to a certain effect called Rayleigh Scattering. Rayleigh Scattering is when light moves through the atmosphere, most of the longer wavelengths pass straight through. Little of the red, orange and yellow light is affected by the air. It’s a physical phenomenon that causes the light to scatter when it passes through particles that have a diameter one-tenth of that of the wavelength of the light. Sunlight is made up of all different colors of light, but because of the elements in the atmosphere the color blue is scattered much more efficiently than the other colors. The Tyndall Effect Table of Contents The Tyndall Effect is similar to Rayleigh Scattering. The first steps towards correctly explaining the colour of the sky were taken by John Tyndall in 1859. He discovered that when light passes through a clear fluid holding tiny particles in the air, the shorter blue wavelengths are shown more strongly than the red. Why not violet? Table of Contents Why not violet?? If smaller wavelengths are shown more strongly, then there is a debatable question as to why the sky appears blue and not violet, the color with the smallest visible wavelength. The visible spectrum of light projection from the sun is not the same at all wavelengths, and additionally is absorbed by the high atmosphere, so there is less violet in the light. Our eyes are also less sensitive to violet. -Yet a rainbow shows that there remains a significant amount of visible light shown as indigo and violet beyond the blue. The rest of the answer is in the way our vision works. We have three types of color receptors in our retina. They are red, blue and green because they respond the strongest to light at those wavelengths. As they are stimulated in different proportions, our visual system constructs the colors we see. Concluding… Table of Contents Concluding that the sky is blue for two main reasons those being, Rayleigh Scattering and The Tyndall Effect. These are basically saying that light reflects and when it does the color blue shows up the strongest out of ROYGBIV. Table of Contents Vocabulary Table of Contents Rayleigh Scattering-the scattering of light by particles that are very small in relation to the wavelength of the light, and in which the intensity of the scattered light varies inversely with the fourth power of the wavelength. Tyndall Effect-the phenomenon in which light is scattered by very small particles in its path; it makes a beam of light visible; the scattered light is mainly blue Suspension-the state in which the particles of a substance are mixed with a fluid but are un-dissolved. John Tyndall-Irish-born British physicist known for his work on the transparency of gases and the absorption by gases of radiant heat. Related Links =) Table of Contents Why is the sky blue? By Science Made Simple – This webpage has lots of information about the sky and certain aspects of why it’s blue. It also has information about sunsets and the color patterns involved in them as well as rainbows. Why is the Sky blue? – This webpage has a lot of information on why the sky is blue. Including the Rayleigh Scattering and the Tyndall Effect. It also has some great images and some more information also about sunsets and color effects and the sky. How Stuff Works-Why is the Sky blue? – This webpage had lots of information about why the sky is blue and also had many links to many other un-answered science related questions.