EIGRP
深圳职业技术学院计算机系网络专业
© 2006, Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
1
教学目标( Objectives )
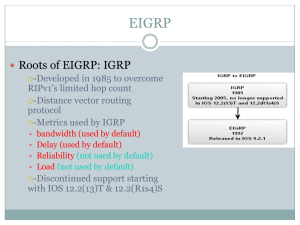
1. EIGRP关键特征
(Key Characteristics of EIGRP )
2. EIGRP三张表
(EIGRP Maintains Three Tables)
3.后继和可行后继
( Successor and Feasible Successor )
4.可行距离和通告距离( FD and RD )
5. EIGRP 数据结构(EIGRP Data Structure)
6.配置EIGRP(Configuring EIGRP)
7.验证EIGRP(Verifying EIGRP)
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
2
EIGRP关键特征(Key Characteristics of EIGRP )
(1)是高级距离向量路由协议,CISCO私有协议
It is an enhanced distance vector routing protocol.
(2)用带宽、延迟、负载、可靠性作为度量值
Metric: bandwidth,delay,load,reliability
(3)支持非等价负载均衡
Uses unequal-cost load balancing.
(4)最大跳数为225
Maximum hop is 225
(5)采用DUAL算法计算到目的地的最短路径
Uses Diffused Update Algorithm (DUAL) to calculate the shortest path.
(6)合并了距离向量路由协议和链路状态路由协议优点
Uses a combination of distance vector and link-state features
(7)EIGRP用“EX”识别外部路由
EIGRP will tag routes by EX learned from any outside source as external .
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
3
EIGRP三张表
(EIGRP Maintains Three Tables)
1.邻居表(Neighbor table )
在EIGRP中,邻居表最为重要
The neighbor table is the most important table in EIGRP.
2.拓扑表(Topology table )
在自治系统中,路由表由拓扑表计算
The topology table is made up of all the EIGRP routing tables in
the autonomous system.
3.路由表(Routing table )
路由表是到达目标网络的最佳路径,路由器为每种被路由的协议维护
一张拓扑表和路由表。
The EIGRP routing table holds the best routes to a destination.
Each EIGRP router maintains a topology table and routing table for
each network protocol.
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
4
后继( Successor )
后继路由器是到达指定目的最优的下一跳邻居路由器
A succesor is a neighbor router that is the next hop in a
least-cost path to any given destination.
后继路由是主要路由。
A successor is a route selected as the primary route to
use to reach a destination.
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
5
可行后继( Feasible Successor )
通过指定可行后继路由器,EIGRP路由器在后继路由器失效时,能够马上将
该路由安装到路由表
By identifying feasible successors,EIGRP router can immediately
install alternate route if a successor fail.
可行后继是备份路由。
A feasible successor (FS) is a backup route.
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
6
可行距离和通告距离( FD and RD )
1.可行距离是到达目标网络最小的度量值
Feasible distance (FD ) is the lowest
calculated metric to each destination.
2.通告距离是邻居路由器通告它到达目标网络的
距离
Reported distance (RD) is the distance
reported by an adjacent neighbor to a
specific destination.
3.可行性条件(feasible condition):RD<FD
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
7
EIGRP 算法(EIGRP Algorithm )
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
8
EIGRP 数据结构(EIGRP Data Structure)
•
•
•
•
•
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
Hello
确认( Acknowledgment )
更新( Update)
查询 ( Query )
应答 ( Reply )
9
Hello
1. EIGRP依靠hello包来发现、验证和再发现邻居路由器。
EIGRP relies on hello packets to discover, verify, and rediscover
neighbor routers.
2. EIGRP发送hello包的周期,称为hello interval。
EIGRP routers send hellos at a fixed but configurable interval,
called the hello interval .
3.在IP网络中,EIGRP路由器使用组播地址224.0.0.10来发送hello包。
On IP networks, EIGRP routers send hellos to the multicast IP
address 224.0.0.10.
4.OSPF需要邻居有相同的hello和dead间隔,而EIGRP没有此限制。
OSPF requires neighbor routers to have the same hello and dead
intervals to communicate. EIGRP has no such restriction.
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
10
EIGRP默认hello间隔和hold时间
(Default Hello Intervals and Hold Times for EIGRP)
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
11
确认(Acknowledgment)
1.确认包是单播。
Acknowledgment packets are unicast.
2.确认能被捎带完成,如应答包。
Acknowledgments can be made by
attaching them to other kinds of EIGRP
packets, such as reply packets
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
12
更新(Update)
1.当路由器发现新的邻居时用到更新包。
Update packets are used when a router
discovers a new neighbor.
2. EIGRP 路由器向新的邻居发送单播更新。
An EIGRP router sends unicast update
packets to that new neighbor .
3. EIGRP路由器向所有邻居发送组播更新来通过
网络变化。所有的更新包要可靠传输。
EIGRP router sends a multicast update packet
to all neighbors, which alerts them to the
change. All update packets are sent reliably.
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
13
查询和应答(Query and Reply)
1.如果EIGRP路由器失去后继,并且没有可行后继,DUAL算法将路由
置为活跃状态,然后以组播向所有的邻居发送查询包,试图定位后继
。邻居路由器必须发送应答包来响应。
If an EIGRP router loses its successor and cannot find a feasible
successor for a route, DUAL places the route in the Active
state. A query is then multicasted to all neighbors in an attempt
to locate a successor to the destination network. Neighbors
must send replies that either provide information on
successors or indicate that no information is available.
2. 查询包可以是组播或单播,应答包一直是单播。
Queries can be multicast or unicast, while replies are always
unicast.
3. 查询和应答都要可靠传输。
Both packet types are sent reliably.
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
14
配置EIGRP(Configuring EIGRP)
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
15
EIGRP 自动汇总
(EIGRP Automatically Summarizes)
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
16
配置EIGRP手工汇总
(Manual Summarization with EIGRP)
EIGRP基于接口来用“summary address”命令手工
配置汇总
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
17
配置汇总(Configure Summary)
RTC(config)#router eigrp 2446
RTC(config-router)#no auto-summary
RTC(config-router)#exit
RTC(config)#interface serial 0/0
RTC(config-if)#ip summary-address eigrp
2446 2.1.0.0 255.255.0.0
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
18
验证EIGRP(Verifying EIGRP)
show ip eigrp neighbors
show ip eigrp topology
Show ip route
Show ip protocols
show ip eigrp interface
debug eigrp neighbors
debug eigrp packets
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
19
Case Study
配置EIGRP协议,使整个网络通,并且在R2、R3看到172的手工汇总路由
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
20
思考题(Questions)
1.EIGRP的特征包括哪些?
2.什么是后继和可行后继?
3.什么是RD和FD?
4.如何理解可行性条件?
5.Hello的作用是什么?
6.EIGRP包括哪些数据包?
7.EIGRP支持手工汇总吗?
8.EIGRP支持非等价负载均衡吗?
© 2006 Shenzhen Polytechnic. All rights reserved.
21