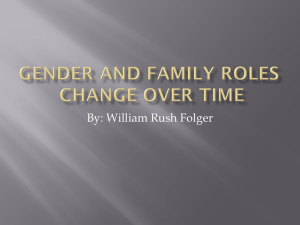01_VolB_Intro_Circling_the_Mediterranean
advertisement

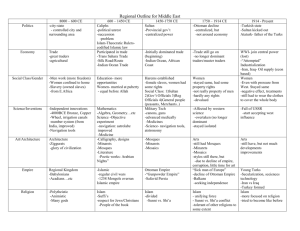
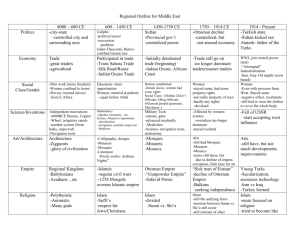
Circling the Mediterranean: Europe and the Islamic World (Volume B) History and Nation Roman Rule of Judea “Christianity” Constantinople Islam • • • • • “obedience” Prophet Muhammad Ca. 632 C.E. monotheism Shi’a, Sunni Islam Spread of Islam Islam: Articles of Faith Sunni Muslims • God’s oneness • angels • four books • messengers (prophets) • days of judgment and resurrection • destiny Shi’a Muslims • God’s oneness • justice • prophethood • day of judgment • caliphate (leadership) Abbasid Empire Mongol Invasion • • • • • • Baghdad, 1258 Ottomans, 1453 Arabic language al-Andalus Persian influence Shahnameh, Ferdowsi Ottoman Empire, 1300 C.E. • cultural elite = new converts from Christianity • linguistically and religiously diverse • languages: Turkish, Arabic, Persian • nomadic origins resigned to character tales • slave-based political and military elite • feudal army • religious tolerance did not mean equality Mi’raj The Thousand and One Nights Mappamundi Crusades • First Crusade, 1095 • Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem • economic opportunities • anti-Semitism • Song of Roland Literary Developments • • • • • • • epic romance Beowulf Ferdowsi, Shahnameh Chrétien de Troyes Marie de France French and Italian as literary languages Petrarch Frame Narrative Travel Literature • accuracy, truth value • descriptive elements • writer’s impressions, personal values • versus travel guides “They would have wild elephants and lots of unicorns that are no smaller than elephants: they have hair like buffalo and feet like elephants, with a very thick, black horn in the middle of the forehead. And I tell you it doesn’t do harm with its horn but with its tongue” (p. 815). Marco Polo • merchant guide • prison writing • French-Italian vernacular • Silk Road • Kublai Khan John Mandeville • • • • synthesist work Classical influence Sumatra nudity, marriage, property Europe, North Africa, Arabia, Asia Minor & Western Central Asia Europe Test Your Knowledge In 382 Saint Jerome was commissioned to produce: a. a common prayer book b. a Latin Bible c. a translation of Plato’s work d. a synthesis of Greek philosophy and Christian doctrine Test Your Knowledge Which of the following were recognized as capital cities in the Roman Empire under Constantine? a. Rome and Constantinople b. Cairo and Damascus c. Persia and Europe d. Athens and Constantinople Test Your Knowledge What text is central to the Islamic faith? a. the Qur’an b. Muhammad c. Allah d. the Latin Vulgate Test Your Knowledge Which of the following is NOT a frame narrative? a. The Thousand and One Nights b. Decameron c. Mi’raj-nameh d. Canterbury Tales Test Your Knowledge Which of the following was pivotal in helping to solidify the idea of “the West”—i.e., of Christian Europe—during the Middle Ages? a. the fall of the Ottoman Empire b. the discovery of America c. the Crusades d. the sack of Rome This concludes the Lecture PowerPoint presentation for The Norton Anthology Of World Literature Visit the StudySpace at: http://wwnorton.com/studyspace For more learning resources, please visit the StudySpace site for The Norton Anthology Of World Literature.