https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/multimedia/display.cfm?IM_ID=7783
Models of the Solar System
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
Florida Benchmark
SC.8.E.5.8 Compare various historical models of
the Solar System, including geocentric and
heliocentric.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
Models of The Solar System
What is a planetary system?
• A planetary system is a star and all of the
celestial bodies that revolve around it.
• An example of a planetary system is the solar
system which includes the sun and the planets
and other celestial bodies orbiting the sun.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
What is the Center of the Solar System?
• The early scientists, in their attempt to answer this
fundamental question created various models of
the solar system.
• Models, which placed Earth at the center, are
called Earth-centered, or geocentric, models.
http://childrenlearningonline.net/children-science-Lessuniver1.html
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
The Geocentric Model
• The early philosopher and astronomer believed
that everything in the universe is “perfect”; and
that the planets are perfect spheres circling in
perfect circular orbits.
• They believed the Earth was the most important
object in space and therefore assumed it to be the
center of the universe.
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ptolemaic_system_2_(PSF).png
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
The Geocentric Model
• Aristotle, a Greek philosopher reasoned that if
Earth circled around the sun, then the relative
positions of the stars would change as Earth
moves.
• This apparent change in the position of an object
when viewed from different angles or locations on
Earth is known as parallax.
• What Aristotle did not take into account is the fact
that stars are very far away. At such great
distance parallax cannot be observed without a
telescope.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
The Geocentric Model
• The geocentric model of the solar system became
a very important part of ancient Greek Astronomy
beginning in the sixth century B.C.E.
• The Greek philosopher Aristotle (384–322 B.C.E.)
was among the first scholars to put forward an
Earth-centered model of the Solar System.
• His model positioned the moon, sun, planets, and
stars on a series of circles that moved around
Earth.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
The Geocentric Model
• Aristarchus, a Greek astronomer and
mathematician, is believed to have proposed a
sun-centered model of the solar system.
• Ptolemy an astronomer, geographer, and
mathematician, exploited Aristotle’s Earthcentered view and developed a complex
geocentric model that was used by astronomers
over the next thousand years.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Historical Models of the Solar System
The Geocentric Model
• According to Ptolemy’s model, the planets moved
on small circles that in turn moved on larger
circles.
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Geocentric_system.png
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Historical Models of the Solar System
The Geocentric Model
• Ptolemy’s “wheels-on-wheels” model seemed to
make sense since it very well illustrated
observations made at the time going back
hundreds of years.
• Scientist for many centuries used Ptolemy’s model
to make predictions of the motions of planets
years into the future.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
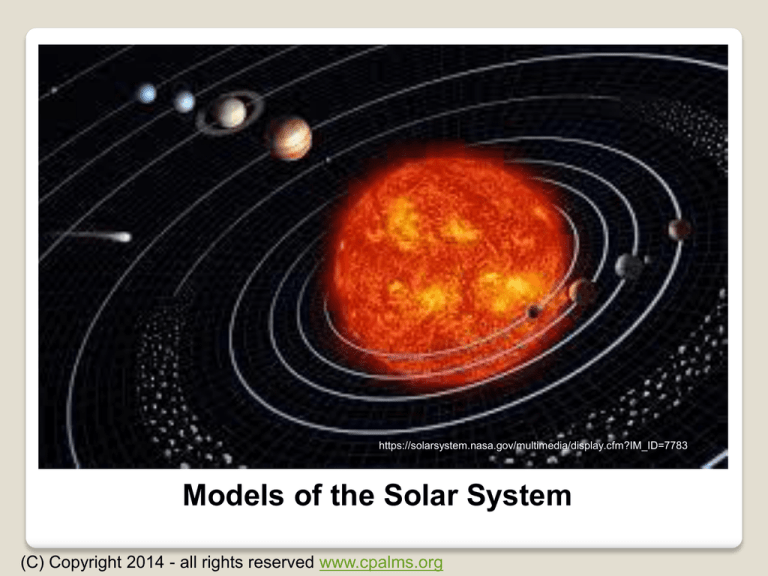
Historical Models of the Solar System
The Heliocentric Model
(Sun-Centered)
https://www.flickr.com/photos/nasablueshift/7368861386/
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
The Heliocentric Model
• The model which placed the sun at the center is called
the heliocentric or sun-centered model.
• The Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus
watered-down Ptolemy’s model of the solar
system since he thought the model was way too
complicated.
• Although Copernicus adopted Ptolemy’s idea that
planets’ orbits are perfect circles, he however
developed Aristarchus’s primitive sun-centered
model into a well thought out heliocentric model.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
The Heliocentric Model
• The heliocentric model was fiercely rejected until it was
refined and published by Copernicus and J. Kepler, a
German mathematician, in the late 16th to early 17th
centuries.
• Copernicus’s model eventually became more
widely accepted as it fit observations significantly
better than Ptolemy’s geocentric model.
• Copernicus’s model is known as the most
influential of modern astronomy.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
The Heliocentric Model
• Galileo Galilei was a scientist who conducted his
experiments in the manner of moderns scientists.
He actually used a very systematic approach very
similar to the scientific methods.
• Galileo’s observations showed that they are other
celestial objects beside Earth with orbiting
satellites.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Models of the Solar System
The Heliocentric Model
• His discovery best fit the heliocentric model.
• Galileo also observed that Venus went through
phases similar to the phases of Earth’s moon.
• The observation of these phases was more in line
with the idea that planets revolve around the sun
rather than the Earth.
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org








