Unit Organizer
advertisement
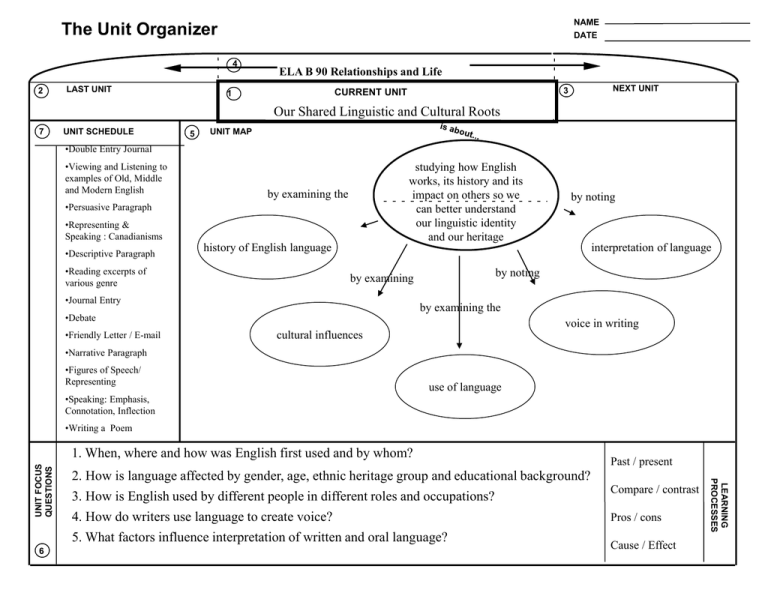
NAME DATE The Unit Organizer 4 2 LAST UNIT ELA B 90 Relationships and Life 3/ CURRENT CURRENT UNIT UNIT 1 NEXT UNIT Our Shared Linguistic and Cultural Roots 7 UNIT SCHEDULE 5 UNIT MAP •Double Entry Journal •Viewing and Listening to examples of Old, Middle and Modern English studying how English works, its history and its impact on others so we can better understand our linguistic identity and our heritage by examining the •Persuasive Paragraph •Representing & Speaking : Canadianisms •Descriptive Paragraph •Reading excerpts of various genre history of English language by examining •Journal Entry interpretation of language by noting by examining the •Debate •Friendly Letter / E-mail by noting voice in writing cultural influences •Narrative Paragraph •Figures of Speech/ Representing use of language •Speaking: Emphasis, Connotation, Inflection •Writing a Poem 6 2. How is language affected by gender, age, ethnic heritage group and educational background? 3. How is English used by different people in different roles and occupations? 4. How do writers use language to create voice? 5. What factors influence interpretation of written and oral language? Past / present Compare / contrast Pros / cons Cause / Effect LEARNING PROCESSES UNIT FOCUS QUESTIONS 1. When, where and how was English first used and by whom? The Unit Organizer Our Shared Linguistic and Cultural Roots NAME DATE Expanded Unit Map 9 studying how English works, its history and its impact on others so we can better understand our linguistic identity and our heritage by examining the history of English language by examining by noting interpretation of language by noting by examining the voice in writing cultural influences use of language NEW UNIT SELF-TEST QUESTIONS 10 The Unit Organizer Our Shared Linguistic and Cultural Roots NAME DATE Expanded Unit Map 9 studying how English works, its history and its impact on others so we can better understand our linguistic identity and our heritage by examining the history of English language by examining the voice in writing cultural influences use of language -gender, age, ethnic heritage group, educational background -words that originate from other cultures and our own (e.g. Canadianisms) NEW UNIT SELF-TEST QUESTIONS 10 interpretation of language by noting by examining -of oral and written language -the printed book (IPad, Kindle, old, middle and new English) -Chaucer, Shakespeare, etc. by noting --e-mail. msn, texting, facebook (differences in formality) -audience -in different literary examples -tone and style -figures of speech -written: connotation, denotation -oral: emphasis, inflection, pausing