Privatization, LWVUS Study, LWVDenver Presentation
advertisement

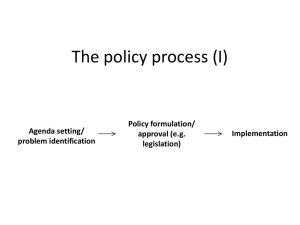
LWVUS Study LWVDenver Presentation 2012 www.lwv.org/member-resources/privatization Concepts John Maynard Keynes, Milton Friedman, Nobel Prize in Economics, 1971 “We have government of the people, by the bureaucracy, for the bureaucracy.” one of the most influential economists of the 20th century. “"His radical idea that governments should spend money they don't have may have saved capitalism.“ Times Magazine, 1999 Purpose of Study The purpose of this study is to identify policies and parameters that should be considered when any governmental entity is planning to undertake some type of privatization process. Scope of Privatization Study The purpose of this study is to identify those parameters and policy issues to be considered in connection with proposals to transfer federal, state, or local government services, assets, and/or function to the private sector. It will review the stated goals and the community impact of such transfers and identify strategies to ensure transparency, accountability, and preservation of the common good. Don’t Panic Concepts Privatization: The Public Policy Debate Privatization is a movement to deregulate private industry and/or transfer many government services, assets and functions to the private sector. Definition of Privatization Classic Total transfer of assets and authority from the government sector to the for profit or nonprofit sector Purposes: Shrink government; Reduce risk and cost Reason: Often a response to economic downturn; Ideology Definition of Privatization Modified Private sector provision of a service once/also provided by government along with private sector funding (Proprietary colleges) Private sector provision of a service with public sector funding (Direct funding for a private college; Private trash collection paid for by tax revenue) Public sector provision of a service with private sector funding (Student tuition at public colleges) Definition Deregulation …the lessening of regulatory provisions that govern individuals, entities, and systems. Definitions Decentralization Moving the authority for a function from a central agency to an agency closest to where the activity is actually performed. Privatizing Actions • • • • • • • • deregulating – reducing regulations (often used as a defining characteristic of privatization), contracting with the private sector to purchase a service (road construction), establishing incentives to encourage the private sector to provide a service, abandoning or shedding of services, reducing demand for a service, establishing quasi-public organizations (government enterprise, charters), establishing separate corporations - profit and nonprofit (authority), supplying temporary help on the part of the private sector, • • • • • • • • • • • issuing vouchers (K-12 education), issuing waivers, selling or giving away government owned assets, establishing franchises, leasing, subsidizing or making available grants to the private sector, relying on user fees rather than tax dollars to fund a service (hunting licenses), discontinuing subsidies to public entities (almost doing this with public higher education in Colorado), providing joint funding, establishing public/private partnerships, and setting up consumer self-help processes, or using volunteers Summary For the purposes of this study, privatization can be considered as occurring any time the government gives up some amount of control in any of several different ways. Examples include: Authorities (Regional Transportation District) Charters (K-12 schools) Deregulation (Higher education procurement in Colorado) Transfer of assets to a private entity (Workers Compensation/Pinnacol) Contracting with for profit or nonprofit entities (e.g., building contractors, social services) Turning over a service (provision of, funding of) to an other than government entity History Shift from central control to less central control – late 1960s/early 1970s End of “regulatory capitalism” (Yergin 1998, 8) – regulatory backlash Reducing the size of government Revitalizing entrepreneurial spirit Restoring influence of market forces Reducing taxes Recent Examples of Privatization or Suggestions to Privatize Social Security Parks Medicare Court services Student loans Free Trade Military service Eliminate food safety Highways, roads, and Eliminate environmental bridges Corrections Education Libraries safety Establish a flat tax Eliminate Workers Compensation Sale of Conrail, government owned/operated rail system Use of private entities for military support services Deregulation of airline, natural gas, electrical and telecommunications industries Attributes Attached to Public Entities Part of state Geographic boundaries Public action Public welfare Public as beneficiaries Public accountability Base on certain principles: e.g., Equality, Security, Fairness, Safety Attributes Attached to Private (nonprofit and for profit) Entities Part of the economy No boundaries except those self imposed Private action/Operated by individuals Individual freedom Privately held assets Benefits individuals What should the government do? Public Safety Defense Justice Protect public health/environment Education Ensure democracy Other? Does government have to do these things itself? What is the balance between government, business, and civil society? How can the balance best be fostered? The public agenda of privatization requires a close examination of the proper relationship between government, business and civil society. Major Issues in Privatization: Transparency and Accountability Sunshine Laws Freedom of Information Act Community Engagement Can these requirements be applied to privatization? Some thoughts on Choosing Privatization How can a community vision be developed? What are the goals and which form (government/privatization) would best achieve the goals? Which concept would best achieve quality? Which is the least costly while still maintaining other goals? How will personnel be affected? What is the political resistance? What are the legal constraints? Which provides more choice? What are the risks and hazards? Reading List - LWVUS Consensus Questions – Introduction Strategies for Best Practice State Level Privatization 2011 Privatization: The Public Policy Debate The Legal Framework of Transparency and Accountability within the Context of Privatization Reading List - LWVUS Deregulation of Railroads Privatization of a Publicly Owned Waste Water Treatment Plant Subcontracting Public Education Privatization of Prisons Reading List – Other Decentralization in U.S. Public Higher Education – Sections on Governance, Privatization and Deregulation and Choosing Privatization (Larson 2003) Government Privatization: History, Examples, and Issues (Commission on Government Forecasting and Accountability 2006) Privatization: Lessons Learned by State and Local Governments (U.S. General Accounting Office 1997) The Meaning of Privatization (Starr 1988) Comments & Questions