2nd grade math.
advertisement

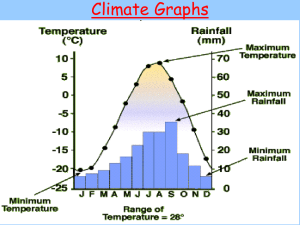
Chapter 11 Adrienne, Darrin & Katie Gathering Data • There should be a purpose to collecting data o To answer questions o Add information to our world o Compare things or groups • The data being collected should be of interest and meaning to the collectors • Data can be classified or sorted in different ways • Data is gathered from a sample of the population How to Gather Data • Pose questions that have meaning to the students o Favorites o Numbers o Measures • What are some questions you can come up with that would be good data gathering questions? • Involve the students personally, as it is a great way for the class to get to know each other better and for the students to feel a sense of individuality • Integrate the community into your data collection How to Gather Data cont'd • This is a great way to involve cross-curricular materials with science and even social studies o Do you have any ideas of how you can do this in your classroom? • Involve the students as much as possible when deciding on the data to be gathered and the questions to be asked • When there is an abundance of possible answers try and limit the amount so analyzing and graphing the data will be more valuable What is the purpose for graphs? A graph clearly shows you the data. In class teachers should have the students create their own graphs that help them see the information. Informal approach: When the students collect their own data and create the graphs the data is more meaningful for them. *Just don't let students get caught in the details of the graph too much. Most Important part of constructing a graph? • The discussion that comes from the graph is the most important part. o Factual o Inferences • Have the students interact with different graphs in case they struggle with a certain type and they can see how the information is conveyed differently Cluster graphs • Here you classify items, or sort items into different categories. • This is more of a table than a graph • Why is it good for kids to learn Cluster graphs/tables/charts? http://jmathpage.com/JIMSStatisticspage.html (simple graphs) Bar Graphs and Pictographs • Bar graph is one of the 1st ways students learn to graph data. Why do you think that is? • There needs to be countable parts like squares or objects, or tallies. http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_190_g_1_t_1.html • Different types of Bar graphs: 1) Real graph: real objects 2)Pictograph: K-3 http://www.mhschool.com/math/2003/student/ Continuous Data Graphs • Line plots: great because they show you where every piece of data is. http://www.ixl.com/math/practice/grade-2-create-line-plots • Histograms: Like a bar graph, but in equal intervals along numeric scale. Book says it is not used because it confuses kids. What scale should they use? Ex. http://www.ixl.com/math/practice/grade-5-create-histograms • Line graphs: "Used when there is a numeric value associated with equally spaced points along a continuous scale" (Lovin & Van de Walle). http://www.mathgoodies.com/lessons/graphs/line.html Which graph do you think is useful for the kids? Why? Circle Graphs • K-3 they use circle graphs which have data points, not percentages. • The circle graphs can show fractional ideas. • Let's create a Human Pie Chart! • What are you favorite Thanksgiving Dishes? • Human Circle Graph Activity. Graph changes for grades 3-5 • Bar graphs: become double bar graphs. • Pictographs now represent more than 1. This starts slightly in 2nd grade but more so in 3rd to 5th. http://www.ixl.com/math/practice/grade-3-pictographs • Continuous data Graphs: Book says histograms are still skipped unles state standards requires teachers to cover these graphs. • Circle Graphs: In grades 3-5, these graphs still show fractional ideas, but now they also show percentage. http://nces.ed.gov/nceskids/createagraph/ More Graph Changes • Also Coordinate Graph is introduced, slightly in 2nd grade but more so during the 3rd-5th grades. http://www.ixl.com/math/practice/grade-3-coordinate-graphs Which of these graphs do you think, will help the kids? • Stem and Leaf Plots: "A form of bar graph in which numeric data are plotted by using actual numerals in data to form the graph" (Lovin & Van de Walle p. 332). • 2 Stem and Leaf plot • Stem and Leaf plot activity The Classification of Data • Data Classification - The way in which data gets categorized, an activity fundamental to data analysis • Attribute Materials - Sets of objects that lend themselves to being sorted and classified in different ways o Unstructured o Structured • Classification Exercises o (three-loop activity demonstration) o ("guess my rule" class activity) • For the early grades data classification lays the foundation for later data analysis, and fosters logical reasoning Data Analysis - Statistics Statistics - numbers that describe data, and give insight to the relevance of described data • Mean, median and mode - all specific types of averages, or measures of central tendency o http://jmathpage.com/JIMSStatisticspage.html o (Leveling the Bars Activity --- The Leveling Concept of Mean) o (Balance Point Demonstration --- The Balance Point Concept of Mean) • (bowling activity data gathering/sharing) Data Analysis --- Bowling Activity • Exploring the Data gathered during this activity Mean --- Thought of as the "average" of a set of numbers Median --- The middle-value in an ordered set of numbers Mode --- The value that occurs most frequently in a set Range ---The distance between the highest and lowest data values in a set o Variance --- How dispersed the data are within the range o o o o References • • • • • • • • • • • • Johnnie's Math Page. (2010). Sort the fruit. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://jmathpage.com/JIMSStatisticspage.html IXL. (2010). 2nd grade math. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://www.ixl.com/math/practice/grade-2-create-line-plots IXL. (2010). 3rd grade math. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://www.ixl.com/math/practice/grade-3-pictographs IXL. (2010). 3rd grade math. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://www.ixl.com/math/practice/grade-3-coordinate-graphs IXL. (2010). 5th grade math. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://www.ixl.com/math/practice/grade-5-create-histograms Lovin, L. and Van De Walle, J. (2006) Teaching student-centered mathematics grades k-3. Boston: Pearson. Lovin, L. and Van De Walle, J. (2006) Teaching student-centered mathematics grades 3-5 Boston: Pearson. Macmillan-McGraw Hill. (2009). Math tool chest. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://www.mhschool.com/math/mathtoolchest/mtc_online/ Math goodies. (2010). Mrs. glosser's math goodies. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://www.mathgoodies.com/lessons/graphs/line.html NCES. (n.d.). Create a Graph. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://nces.ed.gov/nceskids/createagraph/ NLVM. (2010). Bar chart-nlvm. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_190_g_1_t_1.html. Johnnie's Math Page. (2010). Mean Runners. [Electronic graphing website]. Retrieved from http://jmathpage.com/JIMSStatisticspage.html