DUP-and-clinical-outcome-last
advertisement

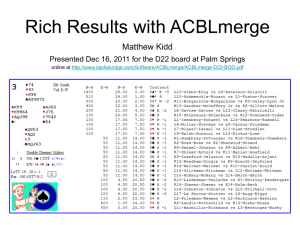
Introduction • It has been shown that the subjects improved significantly within 18 months in their level of social functioning, as measured by GAF, after an effective treatment was administered. • Now we examine how the GAF changed in relation to DUP. • GAF1 stands for GAF score at initial assessment, while GAF2 stands for GAF score at Follow-up. Positive change in GAF Scale for Short DUP Subjects (DUP of 0-5 months) changes in GAF Scale (DUP of 0-5 months) • There was a significant improvement in social functioning for subjects with short DUP. GAF Scale for Subjects with (DUP of 6+ months) change in GAF Scale (DUP of 6+ months) • There is a significant improvement in social functioning for subjects with long DUP but with seemingly some drops in the social function. • We separately examine changes in GAF scale for subjects with DUP of 6-47 months and those with DUP of 48 and above months. • We do this to observe what is happening within subjects with long DUP. Positive change in GAF Scale for Subjects with Long DUP (DUP of 6-47 months) change in GAF Scale (DUP of 6-47 months) • There is minimal improvement in social functioning for subjects with DUP from 6-47 months but with seemingly a mild frequency of drops in social function probably due to relapses. Positive change in GAF Scale for Subjects with Long DUP (DUP of 48-295 months) change in GAF Scale (DUP of 48-295 months) • For subjects with DUP from 48 and above the improvement in social functioning is minimal but significant. Conclusion • Generally DUP does not impact on clinical outcome directly • Long DUP (DUP of 6+ months) had minimal change in social functioning. That is, the longer the DUP the more likely the patient will have minimal or slow change in social functioning after effective treatment