OracleArchitecture - Wainganga College Of Engineering
advertisement

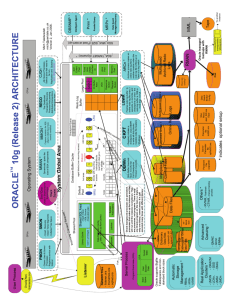
Oracle Architecture Client Computer Lan Or Internet Application Server Lan Or Internet Oracle Database Client Server Environment Application By Java or .Net Framework Oracle Versions • • • • E.F.T. Codd implement rules for RDBMS. Oracle 7 ( Implements 7 Rules) Oracle 8 (First stable version of Oracle) 9i (integrated with java and supports all utilities which are used By Java.) • 10G (Data Grid) • 11i called Oracle Financials Strong competitor for SAP and ERP. • JD Adward, People Soft, SBAAN are new competitor to SAP and ERP. Oracle Platforms • Solaries is the 1st oracle platform provided by Sun Micro system ( Now JAVA is oracle prod). • Oracle for Linux. • PWR Builder introduce by oracle used for data ware housing competitor for ETL sys. By Informetica. • Cognos powerful tool as Infor. Used for data ware housing. • ERWIN strong competitor to Oracle designer. • IDE as VB & .net called SQL developer & J Dev. • Mysql, Teradata, sybase, DB1,DB2, MS. Sql server. • 3rd Party tools as TODD by Quest Technology. What is Data? 64 ## Data is Defined as • A value for an attribute of an entity. • Entity is Real World Thing which exist and can be described in terms of one or more attributes. • Database is Organized value of all SAME type of entity. Memory of ORACLE( Data Dict.) • Arrangement of system table stores data about data called as METADATA. • RDBMS discovered for non procedural access. Storage LOGICAL Table Space PHYSICAL Schema Parameter File, Control File, Redo Log File, Data File Parameter File • This is the first file oracle read at start of the database. Parameters are system variables sets environment of system, file also called as init.ora. • From Oracle 9i SPFILE is introduce and this file is binary formatted and it is the binary version of init.ora. Control File • Its important file of Oracle Database and if control file is lost it means no recovery is possible also it is binary formatted. • Oracle multiplex the file and stored in 3 files same locations name as control1.ctl, control2.ctl, control3.ctl. 3 Important Numbers • SCN : System Change Number. It is assigned by oracle to every committed transaction always increasing.. • LSN: Log Sequence Number. The sequential number assign to redo log as they get filled and recycled. • CPC : Check Point Counter. Its is also ever increasing number and to every check point is assigned. Logical Database Structure • Oracle uses logical database structure to store data on physical operating system file. • DATA BLOCK : Is the foundation of oracle storage. It consist of number of bytes of disk space in OS. • EXTENT : An extents is two or more contagious oracle data blocks and a unit of space allocation. • SAGMENT : A segment is a set of extents allocated to logical structure like table or oracle objects. • TABLESPACE : A table space is a set of one or more data files consist of related Segments. Schema • Schema is set of objects own by User Account. • Each schema has user account but each user don’t need schema. • A user account is account with database having privileges to perform predefined activities on data. • Schema may not exist with user account but user account is exist without schema. • Purpose : Maintenance of object like backup & recovery, implementation of security and access level. Redo Log File • Oracle used redo base recovery and allow to recover only committed transaction till the point of failure. • The redo base recovery in oracle is implemented through the redo log file. • When system fails then oracle read history from these redo log file and guaranties the recovery till the point of failure. • These files are created at the creation of oracle db. • The files are reusable and used as round robin passion. • Maximum size is 50Mb. Redo Log Copies stored to 10 different geographic locations Redo log N.. Redo log 7 Redo log 6 Redo log 1 Redo log 5 Redo log 4 Redo log 3 Redo log 2 Log Switch Redo log 2 Redo log 1 System Global Area SGA Large Pool Fixed Pool Data Buffer Pool Redo Log Buffer Shared pool area / Data S Diction. Shared SQL Area 3 Types of Buffer • Free Buffer : A buffer which is ready to take new data. • Pinned Buffer : A buffer which have data under use (not committed or not rollback.) • Dirty Buffer : A buffer which have data which is committed called permanent. LRU Algorithm • List Recently Used : This algorithm is used to write data from data buffer pool (dirty buffers) in to data files. Data Buffer Pool: Divided into 3 sections. Keep Buffer Pool : It holds the frequently requested data.(Based on MRU). Recycle Buffer Pool : The data which is not requested immediately after used is loaded in recycle buffer pool and eliminated after used. Default Buffer Pool :The data which is not required in above pools is loaded in this pool. Redo Log Buffer • The redo log buffer is the place where data or entries are stored before writing to redo log file. • All entries are written in serially to redo log file due to SCN. • When user commits the data the data written to redo log file. • If not commit or rollback then 75% full written to redo log file. Shared Pool Area • This is the most busy area of SGA. • 3 stages of SQL. • Parsing : It resolve the reference made to the different object in SQL statement resolution of privileges. • Planning : After parsing the statement hand over to Optimizer for drawing execution plan to performing activities in SQL statement. Optimizer breaking down the SQL statement to get result. • Execution : To get result and display as per request. Parsing Types • Hard Parse • Soft Parse • • • • Important Processes Reco Lck Smon Presentation End • Sangeet Kolhe Oracle DBA, System Admin (Linux) Wainganga College Of Engineering & Management