File
advertisement
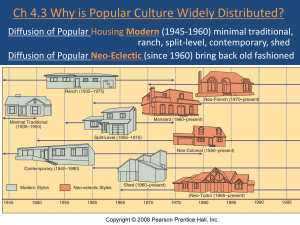
Folk & Popular Culture Why is Popular Culture Widely Distributed? Popular culture varies more in time than in place What does this mean??? Material Posessions Unlike folk culture, pop culture does NOT reflect the local environment; looks the same everywhere Some regional differences in MDCs, but much less than in past; Food Clothing Shelter Popular Housing Styles Influences of shapes, materials, detailing etc. Modern house styles (1945-60) “Family room” added in 1950s Neo-eclectic house styles (since 1960) Clothing Styles Clothing habits as reflection of type of work rather than environment (suit vs. jeans) Higher income = up-to-date wardrobe (especially women) Communication speed, manufacturing Diffusion; Travel, TV, Internet Can you think of a clothing style that was adopted from folk costume? Jeans Became mainstream in US in 1960s Price of jeans?? Used to be associated with low status, manual laborers $10-???? Value of Levi’s around the world What do jeans have to do with communism?? Popular Food Customs Consumption patterns of alcohol & snack-foods Fast-food/Restaurants Variations within US much less significant than differences between US & LDCs Alcohol Preferences in the U.S. Fig. 4-12: Per capita consumption of rum (top) and Canadian whiskey (bottom) show different distributions and histories of diffusion. Diffusing Popular Culture Through TV Significant pop. custom for 2 reasons TV’s in US in 1930s but diffusion blocked Most popular leisure activity in MDCs Most important mechanism for diffusing culture 1945 = 10,000; 4 years later…1949 = 1,000,000 1951 = 10,000,000 1959 = 50,000,000 Internet follows similar pattern More rapid pace Diffusion of TV, 1954–1999 Fig. 4-14: Television has diffused widely since the 1950s, but some areas still have low numbers of TVs per population. Gov’t Control of TV Private corporations vs. Government owned How do they make $$ CTV, CityTV, VS. CBC, TVO Ads, licenses Satellites banned (China, Saudi Arabia) Gov’t censorship