04 critical race theory
advertisement

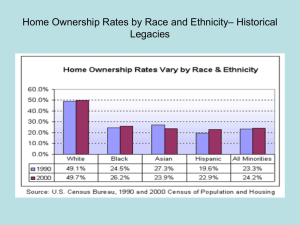
GRDG626 LITERACY, LANGUAGE, & DIVERSITY IN AMERICAN EDUCATION Week 4 – Critical Race Theory and Community Cultural Capital Dr. Gloria E. Jacobs St. John Fisher College AGENDA Sharing Minilecture Small Group Discussion Break Focused Discussion Next week Community & School Analysis SHARING CRT & COMMUNITY CULTURAL CAPITAL Challenges the deficit idea that minority students and families are at fault for poor academic performance because of lack of normative cultural knowledge and skills or that parents don’t value education. OVERVIEW OF CRITICAL RACE THEORY CRT theorizes and challenges the ways race and racism impact society Intercentricity of race/racism Challenges dominant ideology, white privilege, race neutrality Commitment to social justice Centrality of lived experience Interdisciplinary Racism disguised in normative values Schools simultaneously oppress/marginalize, but hold power to emancipate OVERVIEW OF COMMUNITY CULTURAL CAPITAL Capital: What people have Economic (money) Social (who you know) Cultural (what you know) Assumes that if you don’t have it, you are deficient and need to be fixed. Think about McDermott & Varenne’s message Community Cultural Capital Community Cultural Capital Aspirational – holding dreams in face of barriers Navigational – ability to move through institutions Social – networks of people Lingusitic – the intellectual and social skills achieved through facility in more than one language Familial – Sense of community history, memory, cultural intuition Resistance – Knowledges and skills fostered through opposition behaviors that challenge inequality SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION Group 1 Abbie Alyssa Kit Melissa Group 2 Jessie S. Meghan Lauren Jeff Group 3 Kalina Kathryn Emily Kimberly Group 4 Julie Jessica M. Laura J. Jennifer J. Group 5 Laura C. Amanda Rachel Justine Group 6 Ashley M. Chelsea Cassie Ashley F. FOCUSED DISCUSSION See Handout (top portion) Community & School Analysis Select a partner Someone who lives or works in the same district as you Pre-service teachers should team up with an inservice teacher or some one who is regularly in a school and knows that school Collaboration - Use technology to help you For instance, use Google Docs to co-author your paper You do not have to meet in person to do this project Last 30 minutes of class next week will be workshop time. Contents of Paper See Syllabus Use the class texts to help you think about what is happening in the district/community/school Morrison taught us the assumptions WE make Bronfenbrenner provided a tool for thinking about how the individual is related to the family, school, community, and culture The podcasts and website demonstrated how race is socially constructed, but has very real societal impact. McDermott & Varenne explain how difference and disabilities are constructed are an artifact of culture rather than existing outside of culture. Yosso discussed the wealth of knowledge families have so that we can resist the deficit model. Sleeter helps us understand how privilege gets in the way of understanding issues NEXT WEEK Correction to Course Schedule Reading Compton-Lilly Chapter 5 Anzaldua (on wiki) Christensen (in Au) Tateishi (in Au) Writing Reflective Question BREAK Reconvene in the Curriculum Library (ground floor of Lavery Library)