Hand, Wrist & Fingers
advertisement
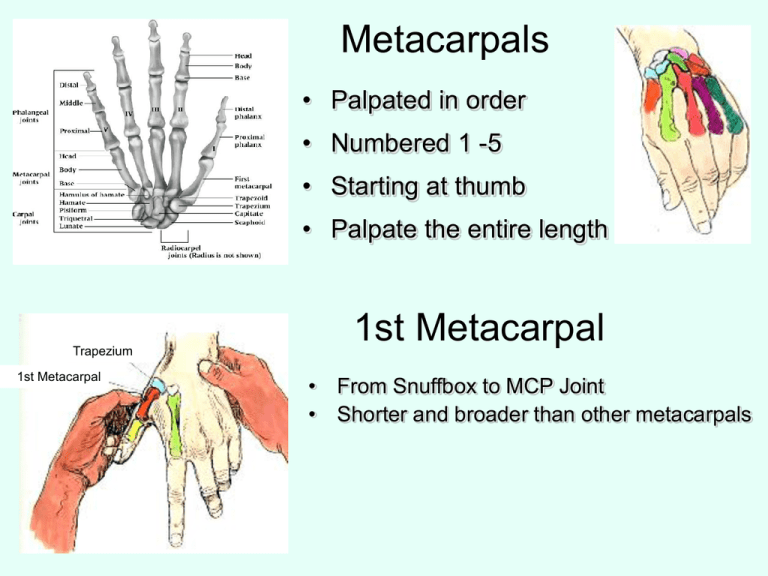
Metacarpals • Palpated in order • Numbered 1 -5 • Starting at thumb • Palpate the entire length Trapezium 1st Metacarpal 1st Metacarpal • From Snuffbox to MCP Joint • Shorter and broader than other metacarpals Metacarpal Fracture – Etiology • Direct axial force or • Compressive force • 5th metatarsal – Boxing or martial arts – (boxer’s fracture) – Signs and Symptoms • • • • Pain Swelling Crepitus Possible deformity – angular – rotational – Fracture tests • • • • Palpation Compression Axial compression Percussion – Management • • • • • RICE Analgesics X-ray examination Deformity is reduced Splinting – 30 degrees of flexion – 4 weeks Phalangeal Fractures Proximal Fracture • Etiology – Direct trauma – Twist • Signs and Symptoms Middle Fracture • Management – RICE – Proximal Fracture • Splint • Buddy taping – Middle Fracture – Pain • No deformity – Swelling • Deformity – Deformity – Crepitus – Buddy tape w/ thermoplastic splint for activity – Immobilization for 3-4 weeks – Protective splint for an additional 9-10 weeks during activity Distal Phalangeal Fracture • Etiology – Crushing force • Signs and Symptoms – – – – Pain Swelling Crepitus Subungual hematoma • Management – RICE – Protective splint • 0º flexion Joints • Metacarpophalangeal Joint • Proximal Interphalangeal Joint – (PIP Jt.) • Distal Interphalangeal Joint – (DIP Jt.) • Interphalangeal Joint – Thumb (IP) IP Joint Anatomy Middle Phalange Collateral Ligament Accessory Ligament Volar Plate Checkrein Ligament Collateral Ligament Accessory Ligament Distal Middle Phalange Proximal Phalange Proximal Volar Plate IP Joint Sprains • Etiology • Special Tests – Fingers are prone to sprains – Fracture tests – Direct blows or twisting – Radial and Ulnar deviation – Occurs w/ axial loading or – Valgus/varus stresses – Similar to fractures and dislocations – Injury can damage • Collateral ligaments • Volar plate • Assess collateral ligaments – Anterior and posterior glide tests • Assess joint capsule Interphalangeal Joint Sprains • Management – RICE – X-ray examination – PIP sprain • 30 - 40º flexion • 10 days – DIP Sprain • Splint for a few days • Full extension • Taping Collateral Ligament Volar Plate Metacarpophalangeal Joints (MC-P Joints) Head of 2nd Metarsal • Palpation • Assessment – Place joint in flexion – Place joint in full flexion – Joint exposed better – Radial deviation – Groove for extensor tendon – Ulnar deviation – Rotation PIP and DIP Dislocations – Etiology • Hyperextension Dorsal PIP • Axial load on a partially flexed DIP joint – Management • RICE • Reduction by MD • Post reduction splinting – Signs and Symptoms • • • • Obvious deformity Swelling Possible avulsion volar plate Possible fracture • Buddy taping • Begin motion at 3 weeks • Large bone fragments splint 30-60º flexion • Small bone fragments buddy taping Mallet Finger (baseball or basketball finger) – Etiology • Caused by a blow that contacts tip of finger Jersey Finger – Etiology • DIP joint injury • Rupture of flexor muscle • Common injury to football lineman Subungual Hematoma •Bruising bleeding under fingernail •Extremely painful due to build-up of pressure under nail –Pressure must be released once hemorrhaging has ceased –Release as distally as possible –Bandage with antibiotic ointment –Hot paper clip –Finger nail drill –Scalpel