Studio Magic Student Guide
advertisement
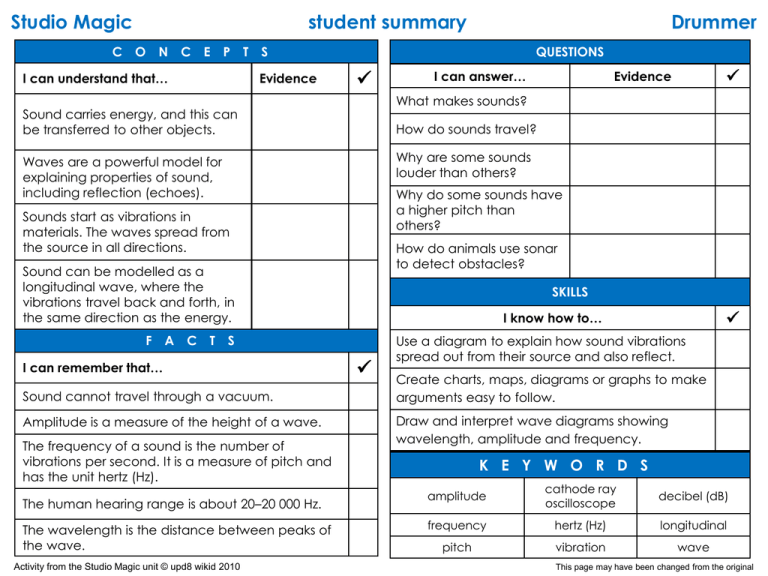
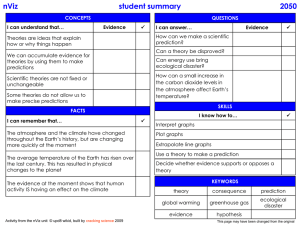
Studio Magic C student summary O N C E P I can understand that… T S Evidence QUESTIONS Why are some sounds louder than others? Why do some sounds have a higher pitch than others? Sounds start as vibrations in materials. The waves spread from the source in all directions. How do animals use sonar to detect obstacles? Sound can be modelled as a longitudinal wave, where the vibrations travel back and forth, in the same direction as the energy. C T Evidence How do sounds travel? Waves are a powerful model for explaining properties of sound, including reflection (echoes). A I can answer… What makes sounds? Sound carries energy, and this can be transferred to other objects. F Drummer SKILLS S I can remember that… Sound cannot travel through a vacuum. Amplitude is a measure of the height of a wave. The frequency of a sound is the number of vibrations per second. It is a measure of pitch and has the unit hertz (Hz). The human hearing range is about 20–20 000 Hz. The wavelength is the distance between peaks of the wave. Activity from the Studio Magic unit © upd8 wikid 2010 I know how to… Use a diagram to explain how sound vibrations spread out from their source and also reflect. Create charts, maps, diagrams or graphs to make arguments easy to follow. Draw and interpret wave diagrams showing wavelength, amplitude and frequency. K E Y W O R D S amplitude cathode ray oscilloscope decibel (dB) frequency hertz (Hz) longitudinal pitch vibration wave This page may have been changed from the original Studio Magic C student summary O N C E P T S I can understand that… Evidence Drummer Q U E S T I O I can answer… N S Evidence What is noise? (W) Sound carries energy, and this can be transferred to other objects. (W) Can the same data suggest more than one conclusion? (R) How can I communicate effectively? (R) Sound waves spread from the source in all directions. (W) S The same data can suggest more than one conclusion. (R) A C T KEY: W = wave energy understanding R = reason understanding Activity from the Studio Magic unit © upd8 wikid 2010 L S Suggest scientific reasons for results that are not consistent with the rest of the evidence. (R) Suggest an alternative conclusion to the one that I drew, which is also consistent with the data, and compare which is more likely. (R) Noise is unacceptable sound. (W) Scientists use two kinds of data – primary data is what you have collected yourself; secondary data is that which comes from another scientist. (R) L Draw a conclusion, identify the evidence that supports it and suggest a scientific explanation for the outcome. (R) S I can remember that… I I know how to… Conclusions can be questioned. (R) F K K E Y W O R D S counter argument error evidence factor inconsistent noise pattern prediction primary data secondary data This page may have been changed from the original Studio Magic C student summary O N C E P T I can understand that… S Q Evidence We need to interrogate articles and reports to spot science and media traps, to judge sources and to judge the trustworthiness of conclusions. (I) A C T E S T I O I can answer… N S Evidence How can sound be used to detect and diagnose hearing problems? (W) How does sound cause hearing problems? (W) S I can remember that… Sound energy is transferred into movement energy when it enters the middle ear. This movement is transferred through several different parts until it reaches the inner ear. (W) K E Y W O R D S audiologist bias cochlea communicate conductive (hearing loss) ear drum exaggerate inner ear middle ear opinion ossicles outer ear sensationalise sensoneural (hearing loss) persuasion U How does the ear work? (W) When communicating, we need to match the approach to the audience and purpose. (C) F Plug it KEY: W = wave energy understandings Activity from the Studio Magic unit © upd8 wikid 2010 How can we judge sources and the trustworthiness of conclusions? (I) How can we match the approach to audience and purpose? (C) S K I L L S I know how to… Use my understanding of how the ear works to explain specific hearing loss. (W) Use models of the ear to explain how sound and light transfer energy to our sensory cells. (W) Use a checklist to interrogate articles and reports. (I) Create diagrams, charts and models to explain and communicate hearing loss to a particular audience. (C) Create a clearly written summary for a non-scientific audience by matching the vocabulary and style to the audience and purpose. (C) I = interrogate understandings C = communicate understandings This page may have been changed from the original Studio Magic C student summary O N C E P T I can understand that… Q S Evidence C T E S T I O I can answer… N S Evidence What makes different coloured lights? Waves are a powerful model for explaining the properties of light, including reflection, changing direction in different materials (refraction) and spreading out around obstacles (diffraction). A U How do we see things? Light comes in different colours, which combine to make white light. F Festival How can light be made to change direction? How can we create dazzling lighting effects? How can we correct sight problems? S I can remember that… Light travels in straight lines and transfers energy. S Colours of light are primary or secondary. K I L L S I know how to… Light travels faster than sound. Deduce the effects of coloured filters and lights on the appearance of coloured objects. Light can be focused to form an image. K E Y W O R D S concave convex cyan diffraction filter image incidence laser surgery lens magenta primary colour reflection refraction unfocused Activity from the Studio Magic unit © upd8 wikid 2010 How can we make an exciting toy using light? Use ideas about waves to explain how light reflects, refracts or diffracts. Use ideas about light to work out how to correct specific sight problems. Use ideas about waves and reflection or refraction to design or adapt a device that uses light or sound, and explain how it works. This page may have been changed from the original