01a Vedic Upanishadic

Review:
INDUS VALLEY CULTURE:
Review Terms:
Yoga
Prana
Linga
Yogin
Indus Valley Belief System:
Yoga / Meditation
Unification with Divine
Non-duality
Shiva linga? 3000BC, Harappa
Shiva linga, 20thc, Banaras
Pre-Vedic/Hindu Concepts
Unity: male ( linga ) and
Female ( yoni )
Non-duality
: divine and individual
Metaphor: man vs. cosmos
Swastika: “well being to all”
Seal with Swastika,
3000 BCE. Indus Valley
Swastika as symbol of auspiciousness
Rajasthan, NW India
Appropriation of Sacred Symbols
Decline of the Indus Civilization
• In decline in 1800 BCE
WHY?
• “Indo-Aryan Invasion” ?
• Climactic Factors
• Gradual decline more likely
Vedic Civilization
Indo-Aryan Migration: 1500 BCE
•Migration from the northwestern areas of Central Asia
•Aryans: same groups that also went to Europe
• Distinctive language and ethnic group
•Language: Indo-European family: SANSKRIT
- later the sacred language of Hinduism
Vedic Civilization
1000-500 BCE
• Self-Designation: ARYA “noble/honorable/first”
• Aryans distinctive from the indigenous people, in terms of language, religion, and ritual
Settled in central India: dominance over the Dravidians
DRAVIDIAN vs ARYANS
1. Aryan Migration vs Cultural Transformation
- The sacred Aryan text, Vedas, speak of subduing the cities of the their enemies, — the dark-skinned
Dasas
Vedic Civilization:
New Ideas and Culture
SOURCES:
• VEDAS “ vid ” = knowledge
Sanskrit language
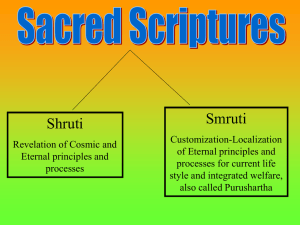
Revealed scriptures SRUTI “that which is heard” [by the sages]”
Source of all Hindu tradition
oral tradition: divine in origin; revealed to sages who were in charge of transmitting this gift to others
the priests, Brahmans, preserve the text through oral recitation with care and accuracy
VEDAS :
4 Vedas:
Rig
Yajur
Sama
Atharva
4 Categories: (chronological)
Samhita:
Brahmanas
Aranyakas
Upanishads:
Rig Yajur Sama Atharva
Rig Veda
• Oldest and most important, composed 1500 BCE
• Hymns to Vedic gods
• Vedic cosmology and ritual
Vedic Cosmology and Ritual
Cosmology : Golden Embryo (Hiranyagarbha)
C reation of universe: sacred primordial world that was not created but simply self-existed. Within this realm was the germ of life "golden embryo/ germ”
In the beginning, was darkness swathed in darkness;
All this was but unmanifested water
Whatever was, that One, coming into being
Hidden by the Void, was generated by the power of heat
(tapas )
In the beginning this [One] evolved
Became desire, first seed of Mind
Wise seers, searching within their hearts
Found the bond of Being in Non-being
Hiranyagarbha “Golden Embyro”
“In the beginning the Golden Embryo [stirred and] evolved
Once born, he was the one Lord of every being
This heaven and earth did he sustain
What god shall we revere with the oblation?
Vedic Ritual
1. Yajna (Sacrifice)
Vedic sacrifice and sharing of meal with each other and the gods ( devas )
Fire Sacrifice : gods propitiated for material benefits
: Cosmic Order ( rta )
Fire god: AGNI :
• purification
• mediator between gods and humans
• priest required for sacrifice
•Transports death to the realm of YAMA, the god of death
, and takes all offering to realm of gods
Plant god: SOMA
• soma drink: (ephedra?)
Vedic Pantheon and Mythology
Devas : “gods” vs. Asuras “demons”
Gods:
• Gods of the Three Realms:
1. Heaven: sky god, of the night, Varuna
2. Atmosphere: warrior god Indra, wrathful god Rudra
3. Earth: Soma, fire god Agni
33 Gods of the Vedic pantheon
Primordial Man
VARNA: as COSMIC ORDER ( Rta ):
VARNA: “COLOR” (Caste System)
1. Priests (Brahmins): from mouth of cosmic man
2. Warriors (Kshatriyas): from arms
3. Common people (Vaisyas): from thighs
4. Untouchables (Sudras): from feet)
UPANISHADS
Also called VEDANTA “end of the Vedas: 600 BCE
Highly philosophical: metaphysical questions
NEW IDEAS:
1. SAMSARA: notion of rebirth and death as painful
2. KARMA
UPANISHADS: New Ideas
BRAHMAN = atman
UNIVERSAL = individual
Spiritual Methods:
• Contemplation, not ritual
• Meditation
• Ascetism and yoga
• Renunciation of the world
• Detachment of wordly action