Chapter 8 v4.0 Jeopardy
advertisement

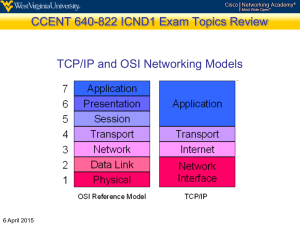
IT Essentials 1 JEOPADY Chapter 8 OSI and Router Networking WANNetworking WAN Router Network Ethernet Router Topologies TCP/IP Types Devices Standards Commands Modes Concepts Encapsulation Services Basics Models ►►► Final Jeopardy ◄◄◄ 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Network Types 100 The three methods of connecting network devices. Question A: What are Copper Cabling, Fiber Optic, and Wireless? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Network Types 200 A group of interconnected devices that is under the same administrative control. Question A: What is a LAN? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Network Types 300 The most common example of a WAN Question A: What is the Internet? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Network Types 400 Device that connects wireless devices to form a wireless network Question A: What is an Access Point? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Network Types 500 Devices are connected directly to each other without any additional networking devices between them. Question A: What is a Peer to Peer network? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Concepts 100 The amount of data that can be transmitted within a fixed time period Question A: What is Bandwidth? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Concepts 200 Data flows in one direction at a time. Question A: What is half-duplex? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Concepts 300 A number that is used to identify a device on the network.. Question A: What is an IP address? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Concepts 400 Class of IP addresses used by small networks. Question A: What is Class C? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Concepts 500 Subnet mask for a Class B network Question A: What is 255.255.0.0? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Components 100 Device that extends the range of a network by receiving data on one port, and then regenerating the data and sending it out to all other ports. Question A: What is a hub? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Components 200 A device used to filter network traffic between LAN segments Question A: What is a bridge? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Components 300 A device that connects entire networks to each other. Question A: What is a router? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Components 400 Network devices that perform more than one function. Question A: What is a multipurpose device? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Networking Components 500 The noise generated by adjacent pairs of wires in the cable Question A: What is Crosstalk? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Topologies 100 Each computer connects to a common cable. Question A: What is Bus Topology? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Topologies 200 This topology has a central connection point, which is normally a device such as a hub, switch, or router. Question A: What is a Star topology? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Topologies 300 This topology connects all devices to each other. Question A: What is a Mesh topology? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Topologies 400 This logical topology is first come, first served for transmitting data on the network. Question A: What is a broadcast topology? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Topologies 500 Controls network access by passing an electronic object sequentially to each host. Question A: What is a Token Passing logical topology? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Ethernet Standards 100 EIA/TIA Category 3,4,5 Question A: What is 10-Base-T? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Ethernet Standards 200 100-BaseTX maximum length. Question A: What is 100 metres? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Ethernet Standards 300 10-Base-T is susceptible to this problem. Question A: What is electro-magnetic interference (EMI)? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Ethernet Standards 400 One of the fiber-optic Ethernet standards Question A: What is 10BASE-FL, 100BASE-FX, 1000BASE-SX and 1000BASE-LX ? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Ethernet Standards 500 This wireless Ethernet standard can transmit up to 300 ft (91m) Question A: What is 802.11g? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 OSI and TCP/IP Models 100 Has 7 layers. Question A: What is the OSI model? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 OSI and TCP/IP Models 200 Bottom level of the TCP/IP model Question A: What is Network Access? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 OSI and TCP/IP Models 300 Where IP addressing and routing take place in the TCP/IP model Question A: What is the Internet layer? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 OSI and TCP/IP Models 400 Provides physical addressing and media access procedures (OSI model). Question A: What is the Data Link layer? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 OSI and TCP/IP Models 500 The Network Interface layer in the TCP/IP model is the same as ________ in the OSI model. Question A: What are the Physical AND Data Link layers of the OSI model? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Final Jeopardy The AT Command to reset the modem Question A: What is ATZ? 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500