Digital Cameras
advertisement
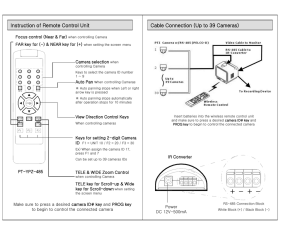
Digital Cameras BISD Instructional Technology Mavica FD 200 Shutter Release Zoom control Flash Lens/ Cover Mavica FD 200 Right View Floppy Disk Drive Memory Stick Slot Mavica FD 200 Back View Power Switch Floppy Disk Release Floppy Disk/ Memory Stick Switch Backlight control Flash control Focus button Program control Display control USB attachment Menu Joystick Movie/Still/Playback setting Mavica FD 200 Left View Power Adapter Video Out Sony Cybershot P93 4 3 1 2 Looking at the front of the camera there is the lens (1). The lens ring (2) will list the characteristics of the lens. Optical zoom is important because it shows the true ability of the camera to capture distant objects. A digital zoom is handy but the quality of the image degrades quickly. The flash (3) on this camera is located next to the optical view finder (4). Flashes on cameras generally have several modes including normal, redeye, auto and manual. The 5.1 mega pixel refers to the number of dots that make up an image. The more pixels the better. However for web or computer images 1 mega pixel is plenty. Top View Digital Cameras have a number of settings that can be overwhelming. However, only a few buttons are needed to take your first picture. The rest will become more apparent as they are needed. 2 1 Most cameras will have a power button1 and a mode selector. This particular Sony P93 camera uses a dial2 to select modes. Generally the camera icon3 represents the mode for normal picture shooting. Playback is shown as the “Play”4 button you see on a DVD or CD player 3 4 Side View Digital Cameras must have a power supply. This camera uses standard AA size batteries (1) . It can also use rechargeable AA batteries that will extend shooting time dramatically. Some cameras use rechargeable batteries that are non-standard or proprietary. Make sure these batteries are available and that it comes with the camera. They can be expensive. To the left of the battery compartment is the memory stick slot (2). Cameras use a variety of memory devices. Sony uses a Memory Stick®. Other types include Compact Flash®, Compact Flash II®, and SD®. Older memory devices can be difficult to purchase. 1 2 Back View 5 1 The back of the camera contains the majority of the controls. Most cameras have a zoom control labeled “T” and “W” for tight and wide(1). Other buttons may include a flash control, menu button, macro control, and buttons for scrolling left and right (2). Input and output connections are located on the back of this Sony. They include the Power connection, the USB and the A/V (3). 2 4 3 The LCD panel (4) allows you to view the image exactly as it will appear when the image saves. These panels have gotten larger with newer cameras. It does consume power so the optical viewfinder (5) can be used in place of the panel Accessories The Sony CyberShot uses standard AA batteries and must be removed to be recharged. Memory devices are included with a camera generally, but are fairly small in capacity. This particular Memory stick was only 32 MB. In high resolution the CyberShot will use around 2 MB per picture. A Geometry Scavenger Hunt Focus: TLW make a list of some shapes that are visible from their seat. Objective: TLW will find a set of geometric shapes in the environment and take digital pictures of the shapes to create a PowerPoint presentation labeling the shapes. Modeling: The teacher will show students images of various environmental shapes in a PowerPoint presentation. (or pictures) Model camera operation. Have students take pictures in groups of 3-4. Give students a week or two to develop a slide show. (Keep shows to no more than five slides) TA TEKS:K-8th grade 2a Use of input devices, CD-ROM, joystick (foundations) 6-8th grade 126.12c8d(problem solving) Importing Digital images in PowerPoint Importing Digital images in Photo Editor Adding Picture Shortcuts to Office Picture Manager Importing Digital images in Word Ideas for Using Digital Cameras 1. Create a photo journal of field trips which can be displayed in a PowerPoint Presentation. 2. Class newsletter illustrations. 3. Photos for greeting cards. 5. Photos of vocabulary terms for any subject. 6. Bulletin board photo journal of classroom activities. 7. Create a video scrapbook of student’s year: art, handwriting, portrait photos, etc. 8. Create a personal or classroom alphabet with pictures. 9. Use pictures for concept illustration (art, math, science). 10. Make an art catalogue of student work for Open House or parent review. Camera ideas extracted from: http://k-12.pisd.edu/techs/dhitt/digital/camideas.htm