The Rise of Islam
advertisement

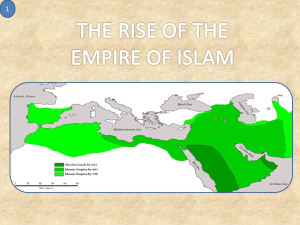
Muslim Civilizations Chapter 10 The Rise of Islam Section 1 The Rise of Islam Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. Bedouins-A desert dwelling Arab nomad. Muhammad-Prophet of Islam, born in Mecca in 570 A.D. Mecca-City in western Saudi Arabia; birthplace of the prophet Muhammad and the most holy city in Islam. Yathrib-The final destination of Muhammad’s hijra and the 1st home of Muslims. Later named Medina. The Rise of Islam Vocabulary 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Hijra-Muhammad’s journey from Mecca to Medina in 622 A.D. Medina-City where Muhammad preached. Kaaba- The most sacred temple in all of Islam in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. Mosque-Muslim house of worship. Quran-The holy book of Islam. The Rise of Islam Vocabulary 10. 11. 12. Hajj-Pilgrimage to Mecca that all Muslims are expected to make in their lifetime. Jihad-In Islam, an effort in God’s service. Sharia-Body of Islamic law that includes interpretation of the Quran and applies Islamic principles to everyday life. The Rise of Islam The Story of Muhammad- I. A. B. C. D. E. Born in Mecca in 570 A.D. Started working as a shepherd, but became a successful merchant in Mecca. Often meditated in the hills of Mecca. When he was 40, the angel Gabriel came to him while meditating and called for him to be the messenger of God. He didn’t understand how he could be the messenger of God when he was illiterate. The Rise of Islam F. G. H. He devoted his life to spreading Islam and getting Arabs to stop worshipping pagan gods. Merchants feared Islam would drive pilgrims away from Mecca (pagan worshipers visited the Kaaba). Took his hijra from Mecca to Yathrib, later name Medina in 622. The Rise of Islam I. J. Thousands of Arabs began adopting Islam. Muhammad returned to Mecca in 630 and destroyed pagan idols in the Kaaba and claimed it for Islam and Allah. Teachings of Islam II. A. B. Quran- The sacred text of Islam and contains the sacred words of God revealed to Muhammad. It is an ethical guide to life in all aspects. The Rise of Islam C. D. The Quran is a DIRECT and UNCHANGABLE word of god. Contains the 5 Pillars of Islam. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. E. Shahadah - Declaration of Faith Salat - 5 daily prayers Zakat - Charity Sawm - Fasting during Ramadan Hajj - Pilgrimage to Mecca and the Kaaba. Islam worships the same God as Jews and Christians The Rise of Islam Sharia – Islamic code of conduct III. A. Regulates all aspects of life and applies religious principals to all situations. Women in Islam IV. A. B. C. Expanded the rights of woman by promoting spiritual equality. Quran gave rights to women they did not have in Arab society. Women’s roles and styles differed depending on cultures conquered by Islam. Questions Du Jour 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What was Muhammad’s occupation? Describe the situation of Muhammad becoming the prophet of Islam. Why was Muhammad driven out of Mecca? What city is cited as the 1st home of Islam? What is the name of the Islamic code of conduct? Describe it. Explain how Islam has affected the rights of women in the Middle East. Answers Du Jour 1. 2. 3. Muhammad was a merchant. Muhammad was meditating on a hill in Mecca when he claimed the angel Gabriel came to him and told him he was to be the messenger of God. Meccan merchants were afraid Islam would drive away pagan pilgrims coming to the Kaaba. Answers Du Jour 4. Medina 5. Sharia. It is a the body of Islamic law that 6. includes interpretation of the Quran and applies Islamic principles to everyday life. It promoted spiritual equality and gave them rights they had not previously had in Arab society. Section 2 Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. Abu Bakr- Muhammad’s father in law and 1st caliph of Islam. Caliph-Successor to Muhammad as political and religious leader of the Muslims. Sunni-Believe inspiration came from the example of Muhammad as recorded by his early followers. Shiite-Believe the descendents of Muhammad’s daughter and son-in-law, Ali, are the true Muslim leaders. Section 2 Vocab 5. 6. 7. Sufis- Muslim mystics who seek communion with God through meditation, fasting, and other rituals. Umayyad-member of the Sunni dynasty of caliphs that ruled a Muslim empire from 661750. Abbasids-Dynasty that ruled in Baghdad from 750-1258. Section 2 Vocab 8. 9. 10. Baghdad-Capital city of present day Iraq; Capital of the Muslim empire during Islam’s golden age. Minaret-Slender tower of a mosque, from which Muslims are called to pray. Sultan-Muslim ruler. Chapter 10 Section 2 Building a Muslim Empire I. Early Challenges to Islam A. B. Death of Muhammad left no successor. Abu Bakr- Muhammad’s father-in-law. He became the 1st caliph. 1. 2. C. Muslims refuse to follow him and withdraw their loyalty to Islam. He regained their loyalty and united them under one ruler. Muslim Empire overtook both the Byzantine and Persian Empires II. Divisions Emerge Within Islam A. Shiites Felt Muhammad designated his son-in-law, Ali, to lead Islam 1. 2. B. They felt the successors to Muhammad were Ali and Fatima (Muhammad’s daughter). Shiites could divinely interpret the Quran. Eventually another group felt anyone could lead because there could be no other prophet.(Sunnis) II. Divisions Emerge Within Islam 1. 2. C. Sunnis believed the successor should be a pious man from Muhammad’s tribe. They believe inspiration comes from the example of Muhammad recorded by his early followers. Both Sunnis and Shiites are still divided today. 1. 90% of Muslims are Sunni. II. Divisions Emerge Within Islam D. Sufis Muslim mystics who fast, meditate and do other traditions to find oneness with God. 1. They spread Islam by traveling, preaching, and being a good example. III. Umayyad Caliphs Build an Empire. A. Umayyad Caliphate Sunni group who set up an empire after Ali’s death. 1. B. Spread Islam from Spain to India. Umayyads were VERY successful. 1. 2. 3. 4. Weakness of the Byzantines and Persians. “Arab Liberators”. Bold efficient fighting methods. Desire to glorify Islam. III. Umayyad Caliphates Build an Empire C. Muslims allowed Christians, Jews, & Zoroastrians to practice their religions. 1. 2. 3. 4. Forced them to pay taxes. Christians & Jews played key roles in Arab societies (doctors, government officials). Muslims prohibited looting and destruction of cities. Arab remained separate from regular population. III. Umayyad Caliph Builds an Empire D. Many people eventually start converting to Islam. 1. 2. 3. E. For political or economic reasons. Islam had a very simple message. There is no hierarchy. Umayyads begin to decline (fall in 750) 1. 2. Arabs had to adapt from living in the deserts to ruling huge territories. Ruled like tribal leaders instead of kings. III. Umayyad Caliph Builds an Empire 3. 4. They often relied on non-Arab officials to help rule their land. Economic tensions rose between the wealthy and the poor when wealthy conquests began to slow down. (Caliphs continued to lived luxuriously) Umayyad Review When did the Umayyad Caliphate begin? Why were the Persians and Byzantines weakened? What are 3 reasons why Umayyads were so successful? Why did so many people convert to Islam? How did geography and economics play into the decline of the Umayyad Empire? Umayyad Review When did the Umayyad Caliphate begin? Why were the Persians and Byzantines weakened? After Ali’s death (661) They had fought each other to the point of exhaustion What are 3 reasons why Umayyads were so successful? Weakness of Byz. and Per., “Arab Liberators”, bold fighting styles, glory of Islam Umayyad Review Why did so many people convert to Islam? For power or wealth, its simple message, equality (no hierarchy) How did geography and economics play into the decline of the Umayyad Empire? Arabs had to adapt from living in the desert to ruling large territories and they ruled those lands like tribes, not kingdoms (Geography). Their was an economic between classes when conquests began to slow down (Economics) Rise of the Abbasids/Muslim Empire Declines 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Which groups helped Abu al-Abbas gain power? What was the Abbasid capital? Why did they move it there? Who was Harun al-Rashid? Where did the surviving member of the Umayyad family flee to? How did Islam become a more universal faith? What 2 places in Europe were ruled by Muslims? How were non-Muslims treated? What did the Seljuk Turks and Mongols have in common? What happened to the Muslim Empire? Rise of the Abbasids/Muslim Empire Declines Which groups helped Abu al-Abbas gain power? 1. Shiites and non-Arab Muslims What was the Abbasid capital? Why did they move it there? 2. Baghdad. Centrally located on a river, center of learning and culture. Who was Harun al-Rashid? 3. Abbasid ruler who promoted culture and learning. Rise of the Abbasids/Muslim Empire Declines Where did the surviving member of the Umayyad family flee to? 4. 5. 6. They fled to Spain and set up an independent Muslim state. How did Islam become a more universal faith? It was more tolerant than other religions, it ended discrimination against non-Arabs, encouraged learning. What 2 places in Europe were ruled by Muslims? Spain and Sicily Rise of the Abbasids/Muslim Empire Declines How were non-Muslims treated? 7. They were tolerated. What did the Seljuk Turks and Mongols have in common? 8. Came from C. Asia, conquered Baghdad, adopted Islam. What happened to the Muslim Empire? 9. It fragmented and broke apart into several smaller states.